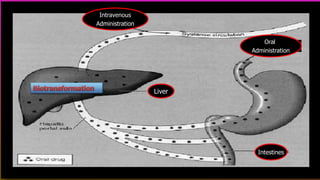
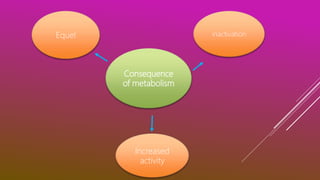
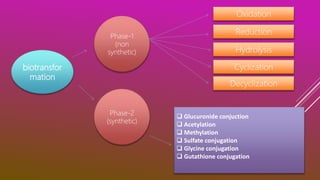
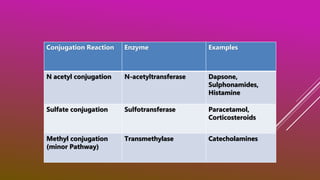
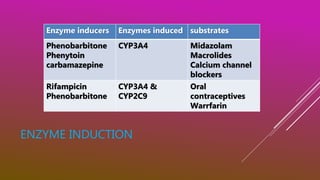
This document discusses drug metabolism. It defines metabolism as the network of chemical processes that maintain life. Drug metabolism occurs through various phases including oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, and conjugation reactions. These reactions are catalyzed by enzymes like cytochrome P450 and occur mainly in the liver and intestines. The consequences of metabolism can include inactivation of drugs, production of active metabolites, or increased activity as in the case of prodrugs. Factors like genetic polymorphisms and drug interactions can impact the metabolism of drugs.