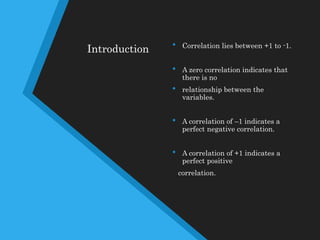
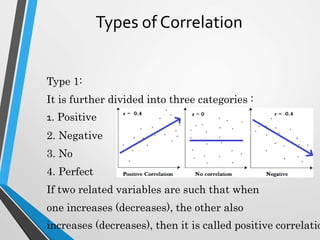
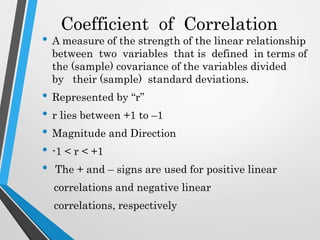
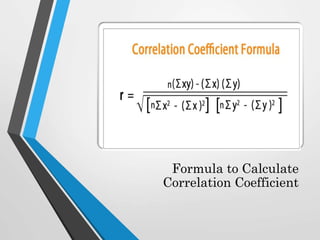
This document discusses correlation analysis and different correlation techniques. It defines correlation as the relationship between two variables and how a change in one causes a change in the other. Correlation can be positive, negative, or no correlation. Methods for studying correlation include scatter diagrams, Pearson's coefficient, and Spearman's rank correlation. Pearson's coefficient represents the strength and direction of correlation between -1 and 1. Spearman's rank correlation determines correlation when data is in rank form rather than numerical values. Various types of correlation and formulas for calculating correlation coefficients are also outlined.