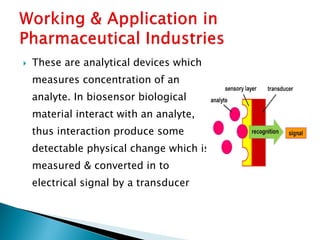
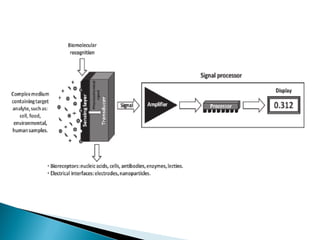
Biosensors are devices that detect specific substances or analytes, such as glucose and lactate, by producing electrical signals proportional to their concentrations. They consist of a biological component that interacts with the analyte and a transducer that converts this interaction into measurable electrical impulses. Various types of biosensors include calorimetric, potentiometric, amperometric, and optical, each utilizing different physical principles to measure biochemical reactions.