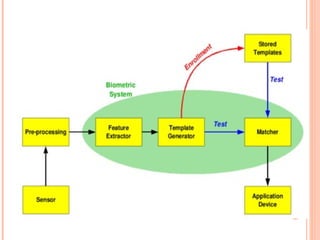
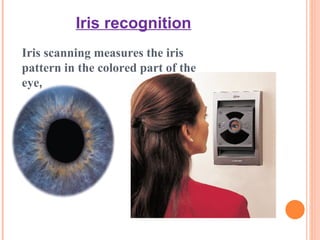
Biometrics refers to automatic identification of individuals based on physiological or behavioral characteristics. This document discusses different biometric recognition techniques such as fingerprint recognition, hand geometry recognition, iris scanning, facial recognition, signature verification, voice recognition, and keystroke dynamics. It also outlines applications of biometrics such as security for ATMs, computers, buildings, and more. Biometrics could replace the need for passwords, pins, keys and other traditional identification methods.