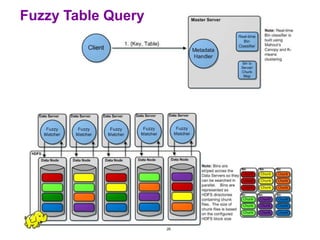
The document discusses the application of Hadoop in managing large-scale, low-latency distributed fuzzy matching databases for biometric data, highlighting its role in solving challenges associated with big data and unordered fuzzy matching. It covers various aspects of biometrics, including data operations for enrollment, verification, and identification, while emphasizing the importance of fuzzy matching due to the inherent noise in biometric data. The presentation also highlights the growth of biometric databases and proposes 'fuzzy table' as a solution for efficient and scalable low-latency searches.