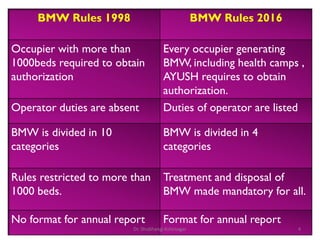
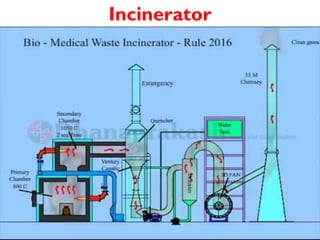
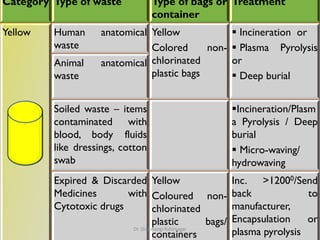
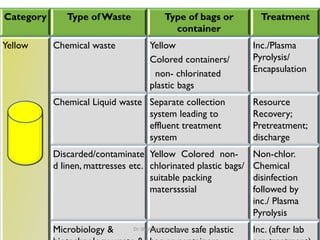
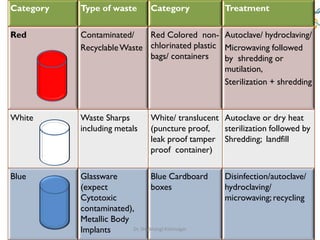
The document outlines the Bio-Medical Waste Management Rules, 2016 in India, focusing on the systematic collection, segregation, transport, treatment, and disposal of biomedical waste. It categorizes biomedical waste into multiple types, detailing treatment methods and the responsibilities of operators and occupiers in managing this waste safely and effectively. Furthermore, it highlights the health hazards associated with exposure to hazardous waste and emphasizes the importance of adherence to the specified guidelines to mitigate risks.