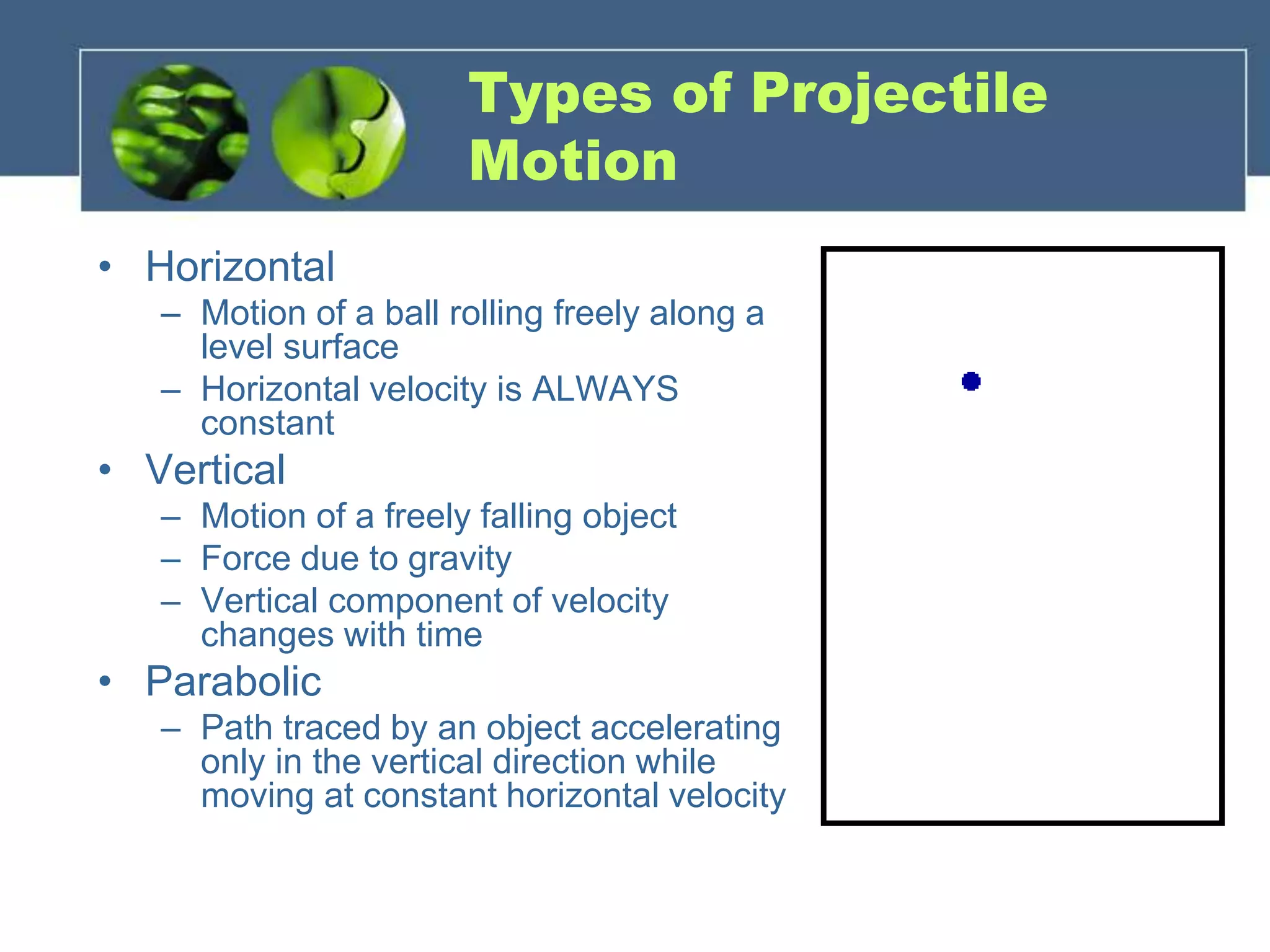
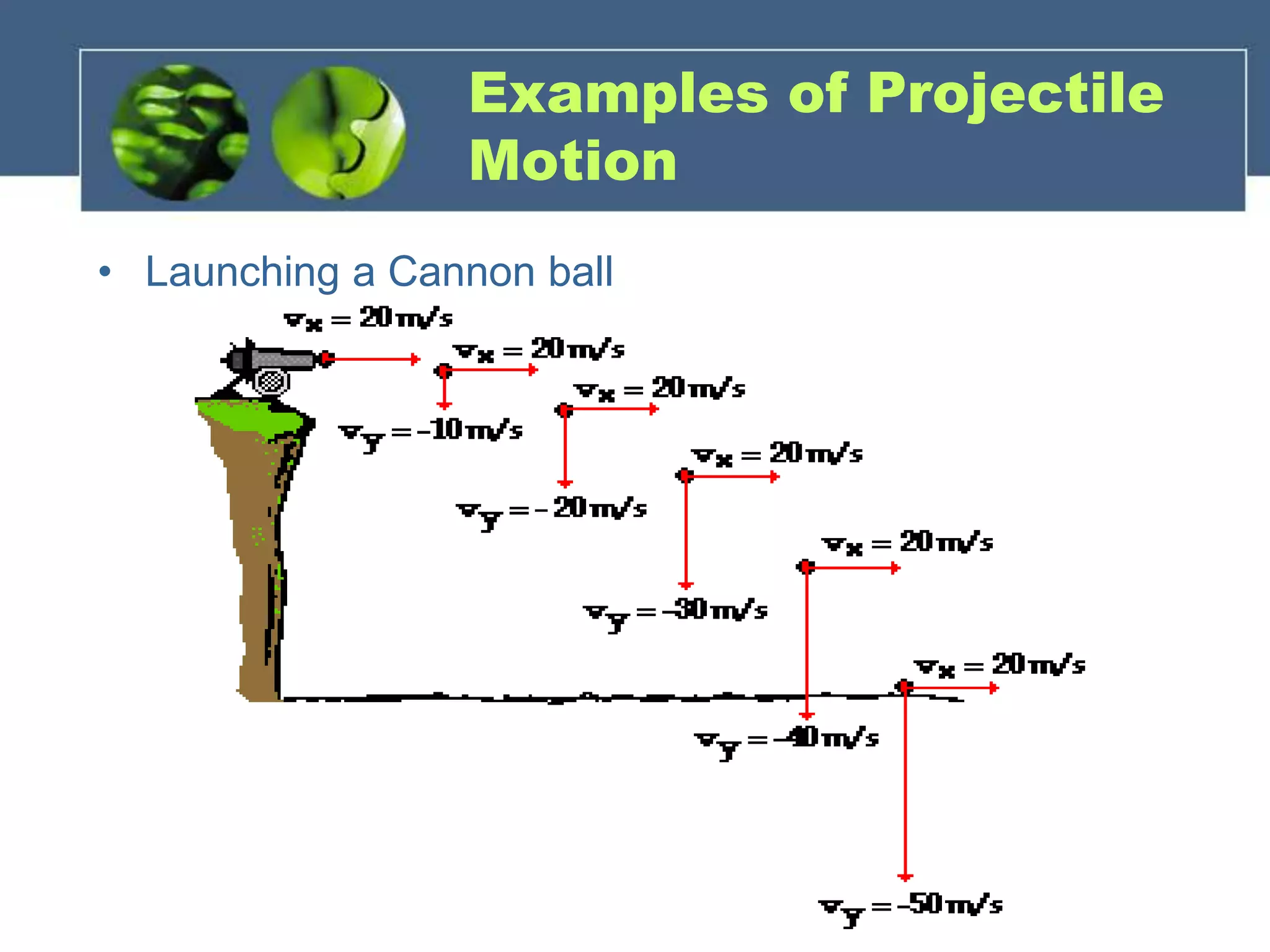
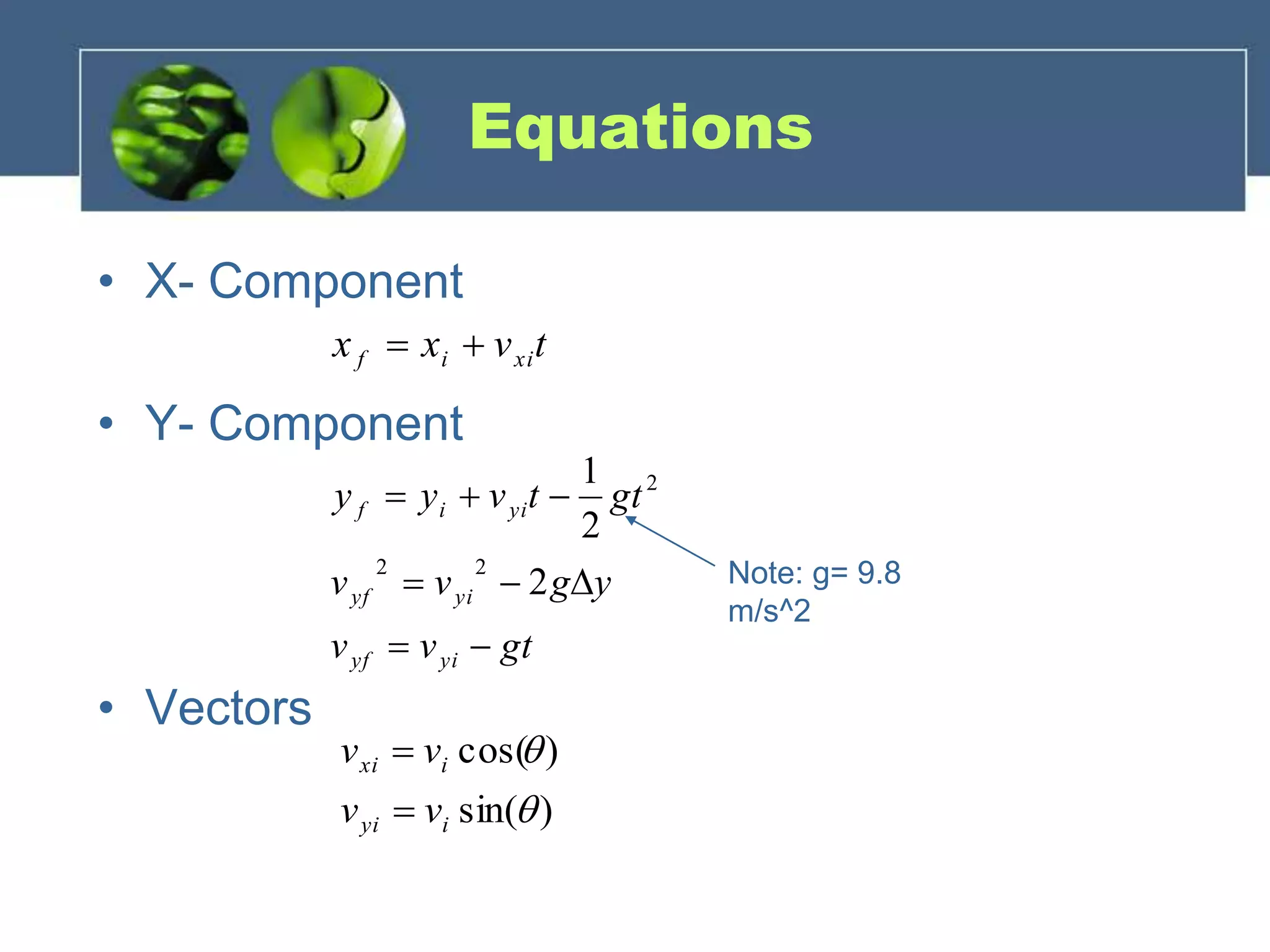
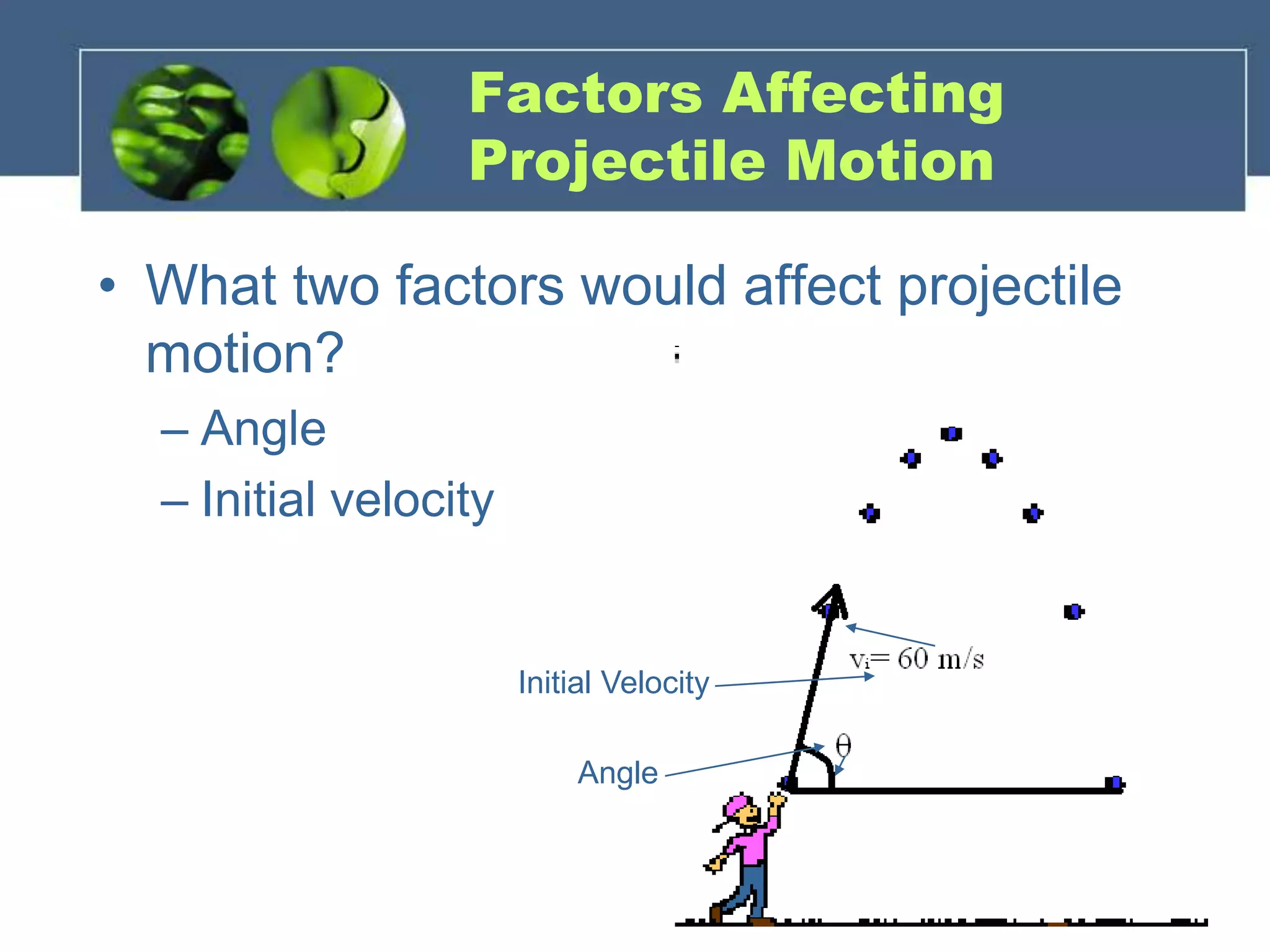
Projectile motion refers to the two-dimensional motion of objects through both horizontal and vertical components. There are three types of projectile motion: horizontal, vertical, and parabolic. Horizontal motion involves constant horizontal velocity, vertical motion involves acceleration due to gravity with changing vertical velocity, and parabolic motion follows a curved path with constant horizontal velocity and changing vertical velocity due to gravity. Factors like initial velocity and launch angle affect the motion. An example problem calculates the horizontal distance traveled and height of an object launched at an angle after 2 seconds.