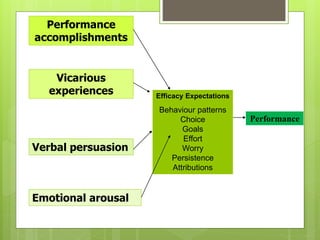
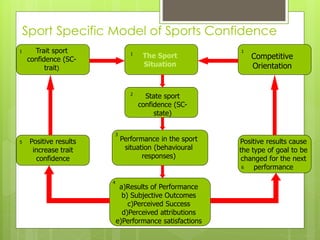
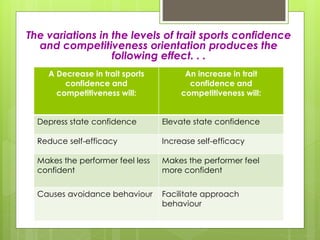
The document discusses self-confidence and self-efficacy in sports. It defines self-confidence as a general belief in one's abilities, while self-efficacy refers to confidence in a specific situation or task. The document outlines Bandura's theory of self-efficacy, including the four main factors that influence self-efficacy: performance accomplishments, vicarious experiences, verbal persuasion, and emotional arousal. It also discusses Vealey's sport-specific model of sport confidence, which distinguishes between trait and state confidence and how the sport situation and competitive orientation impact state confidence. The document provides strategies for improving self-efficacy and sport confidence based on these theories.