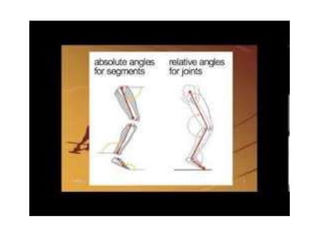
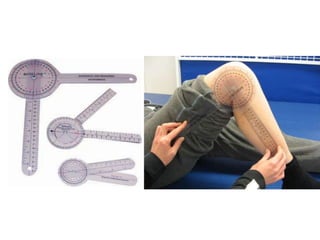
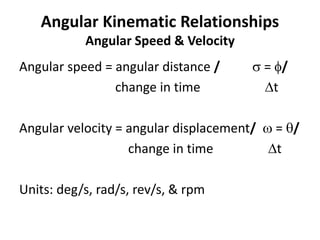
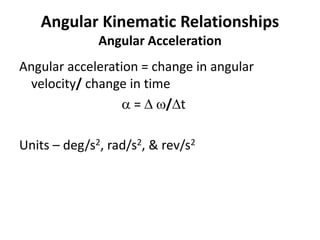
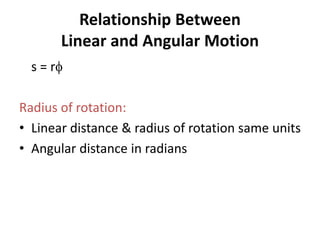
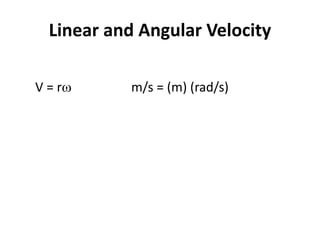
This document discusses angular kinematics of human movement. It defines relative and absolute angles and describes tools used to measure body angles like goniometers, electrogoniometers, and inclinometers. It also discusses instant centers of rotation and angular kinematic relationships like angular distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. Additionally, it covers the relationships between linear and angular motion and velocity.