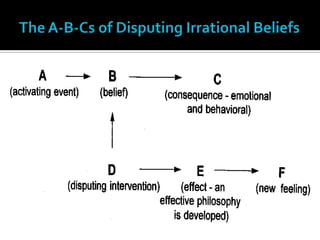
This document provides biographical information about Albert Ellis, the founder of Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT). It discusses Ellis' childhood, education, early career focusing on writing, and eventual development of REBT. The summary is:
Ellis was born in 1913 in Pittsburgh and raised in New York. He had a difficult childhood but developed a passion for reading and problem-solving. After trying various careers including writing, he turned to psychotherapy and developed REBT which focuses on disputing irrational beliefs that cause emotional disturbances. REBT became his life's work and he published extensively on the topic until his death in 2007.