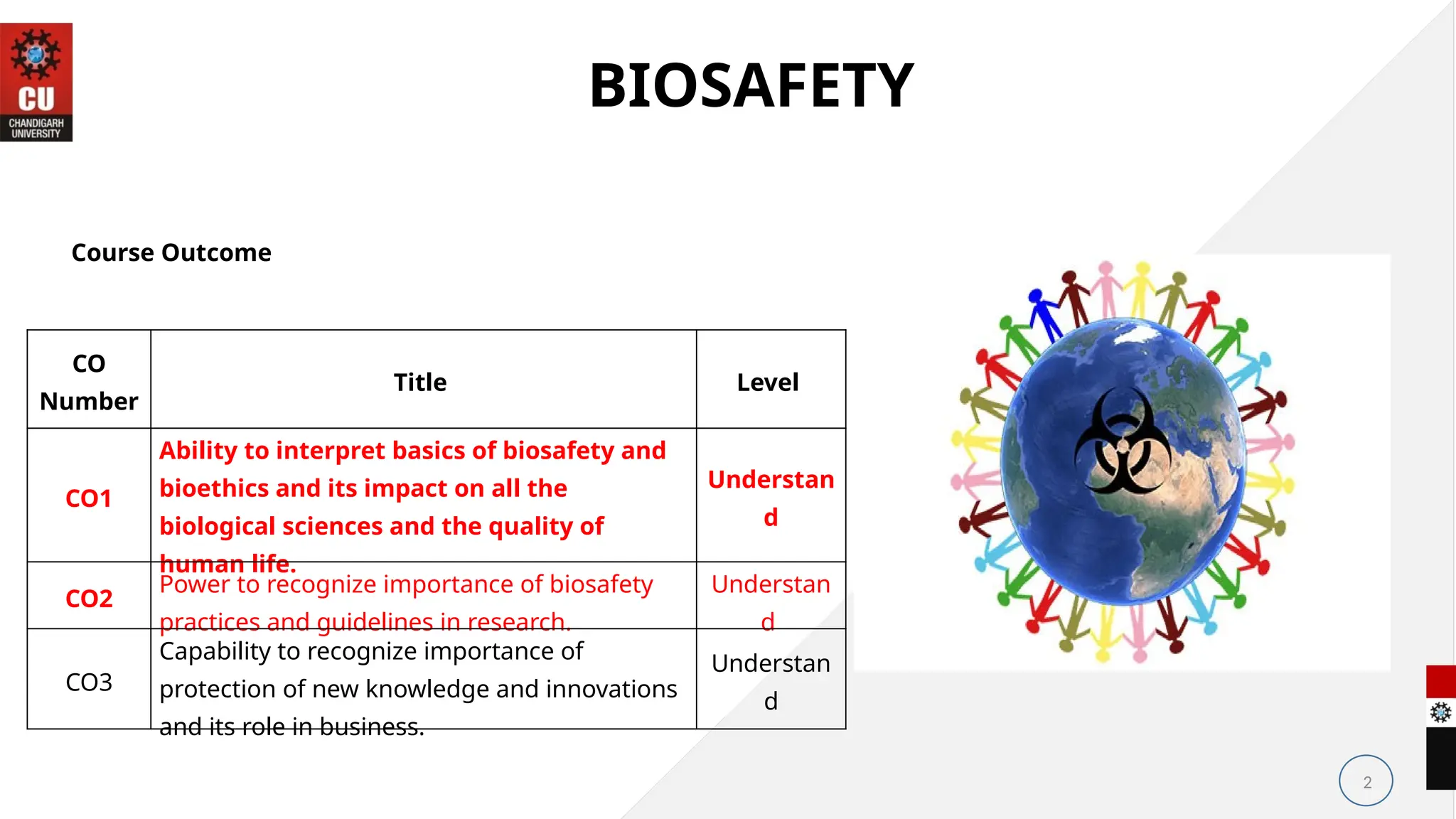
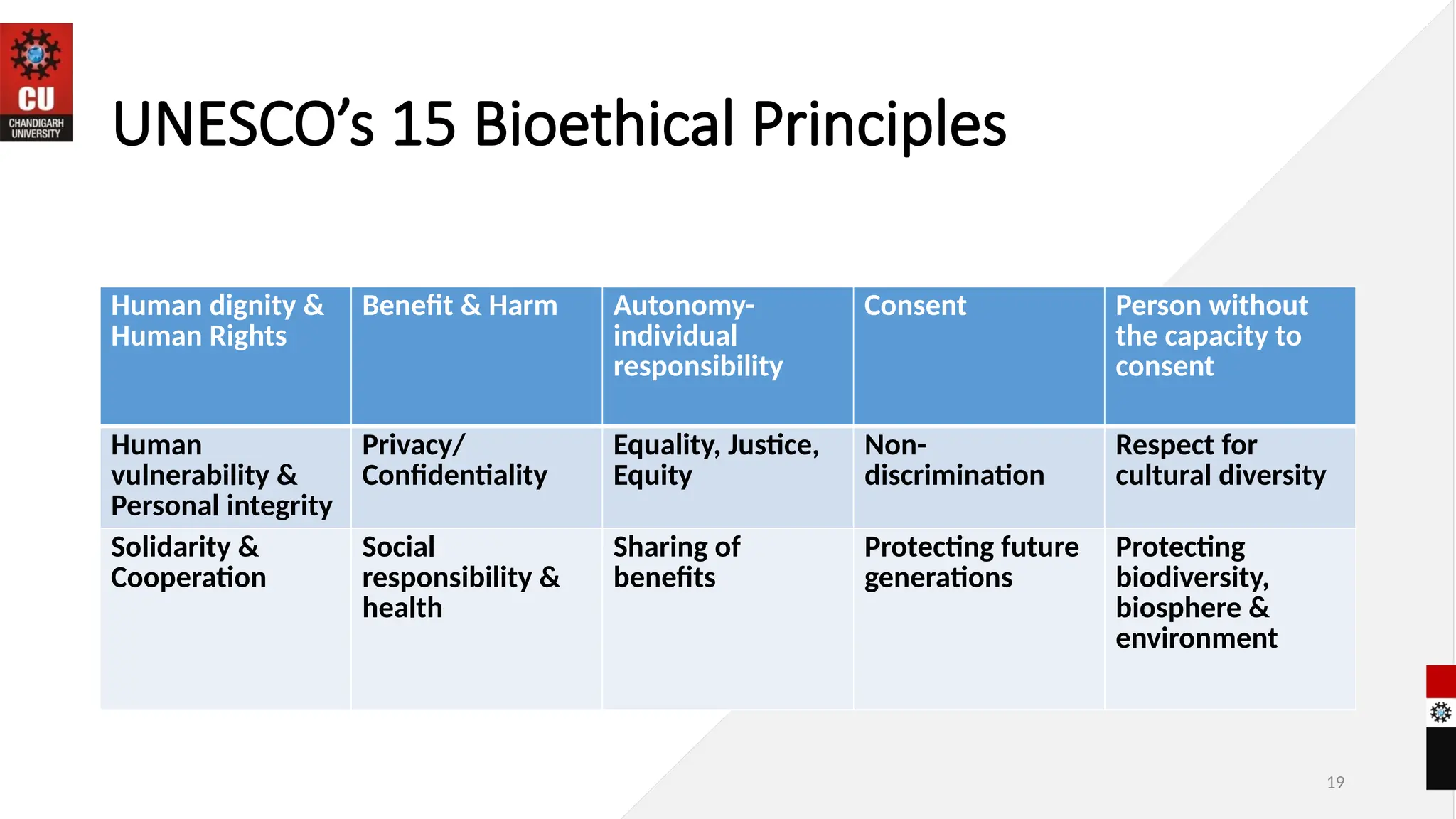
The document outlines a course on bioethics within a biotechnology program, focusing on the intersection of biological sciences and ethical considerations. Key topics include the principles of bioethics, medical ethics, and the importance of biosafety practices in research, emphasizing the need for ethical decision-making in healthcare. Additionally, it highlights the role of professional attributes, teamwork in healthcare, and UNESCO's bioethical principles.