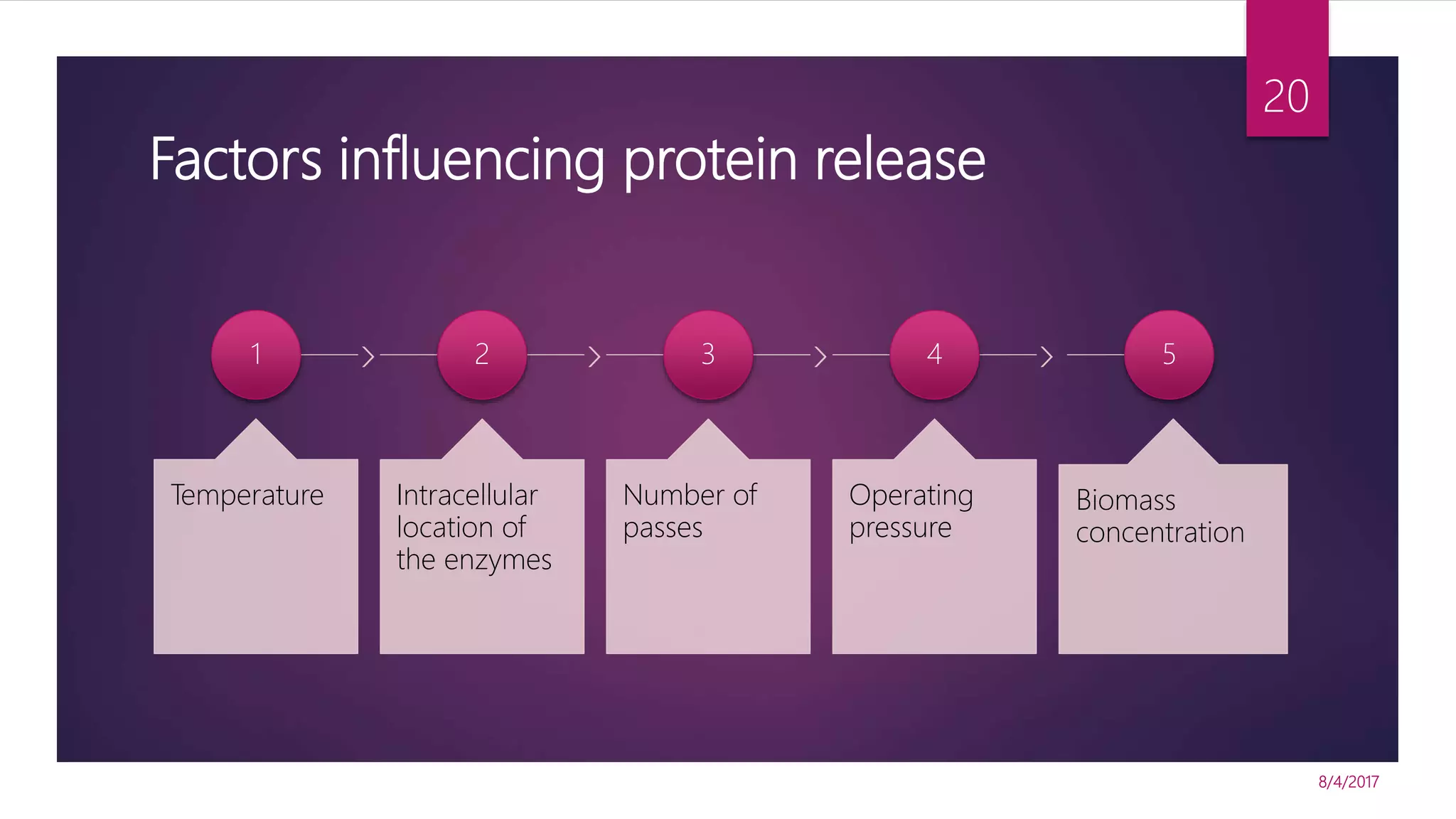
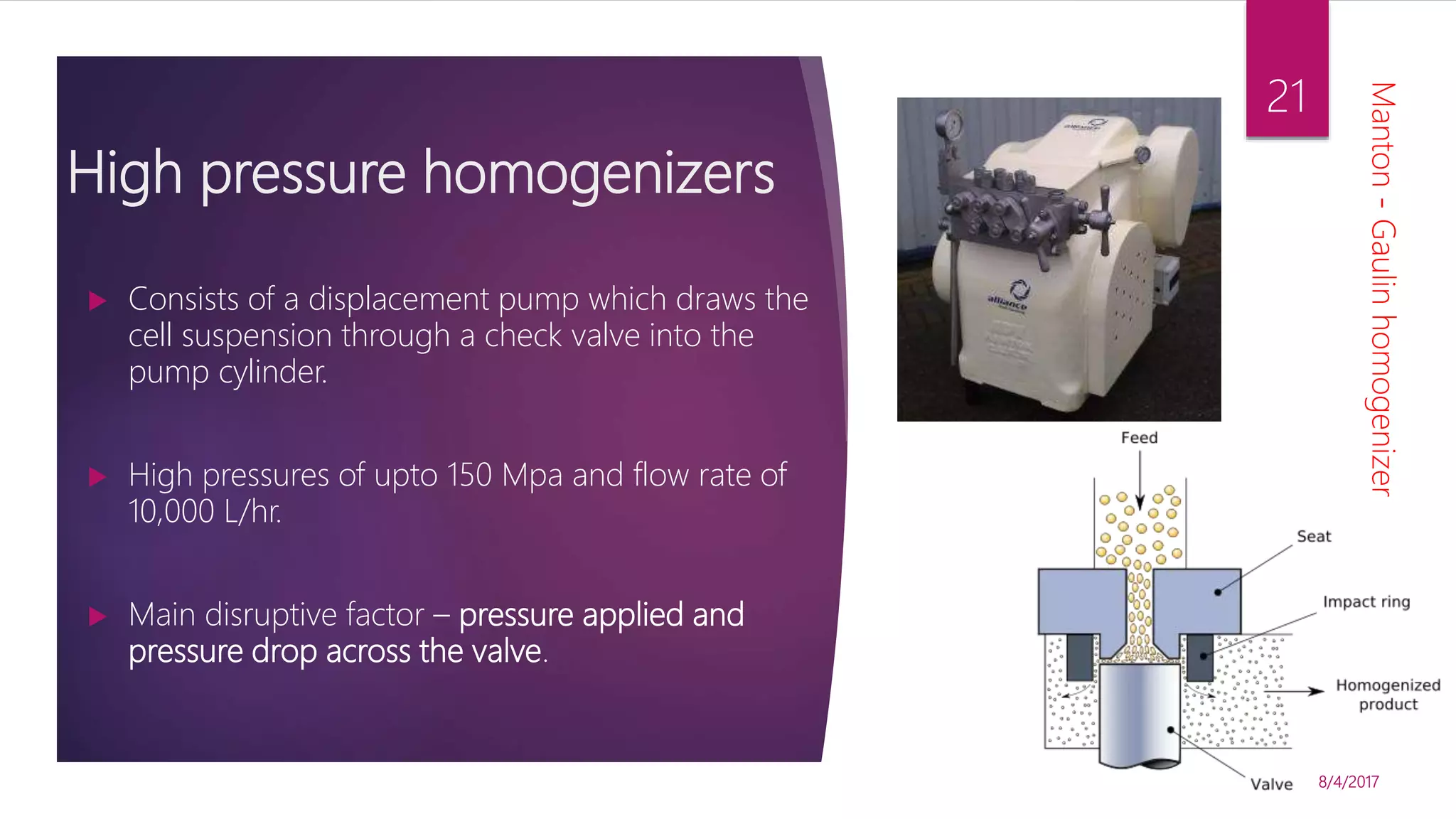
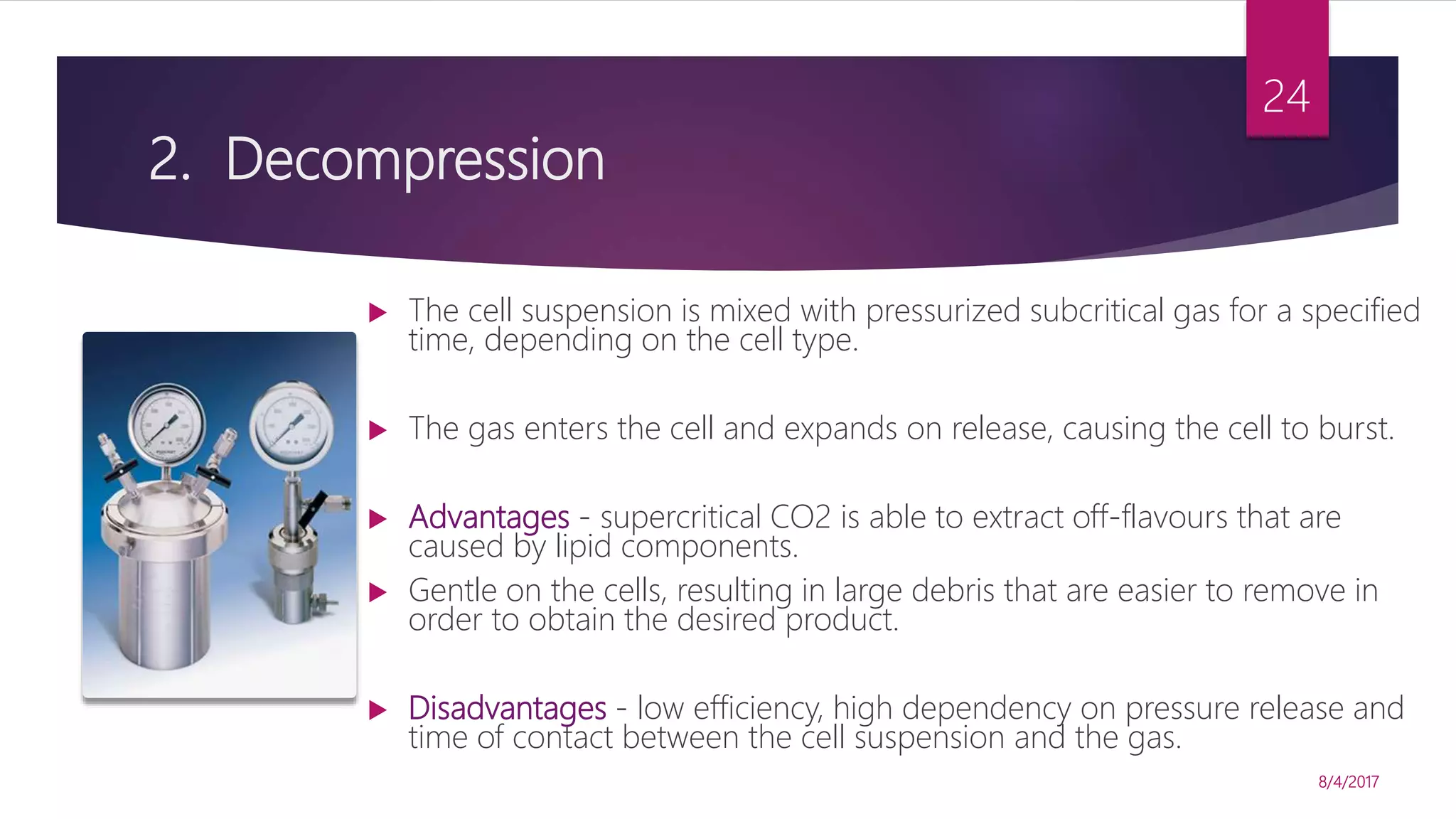
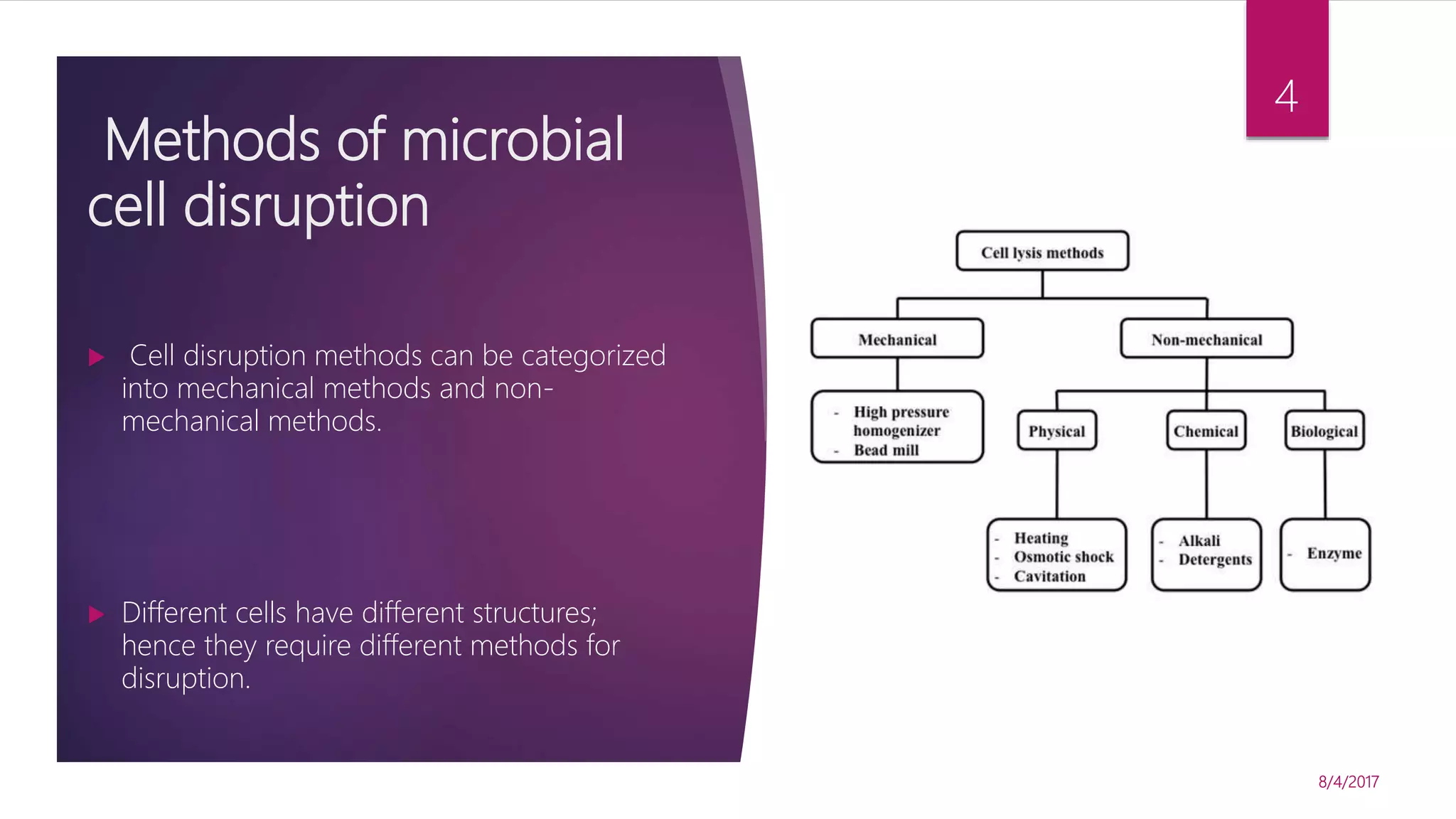
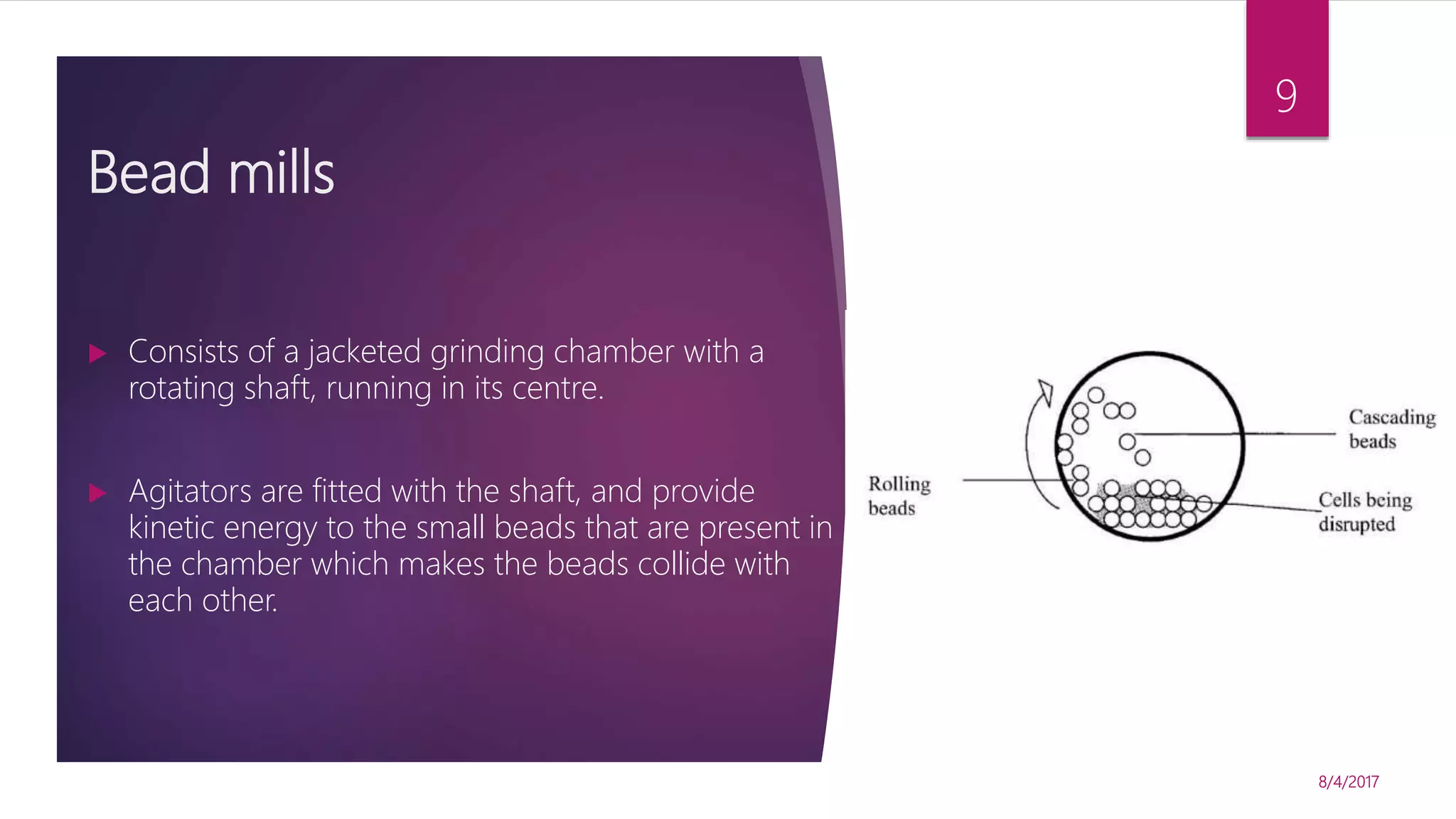
The document discusses various methods for microbial cell disruption, which is necessary to extract biological products located inside or outside of cells. It categorizes methods as mechanical (e.g. bead mills, ultrasound, French press) or non-mechanical (e.g. thermolysis, osmotic shock, detergents). Mechanical methods use physical forces for disruption but have issues with scale-up and contamination risk. Non-mechanical methods like chemical treatments can denature proteins. An ideal method achieves high product release without damage, is easily scaled, and has low particulate/contaminant release. Each cell type and product may require a different optimized disruption method.







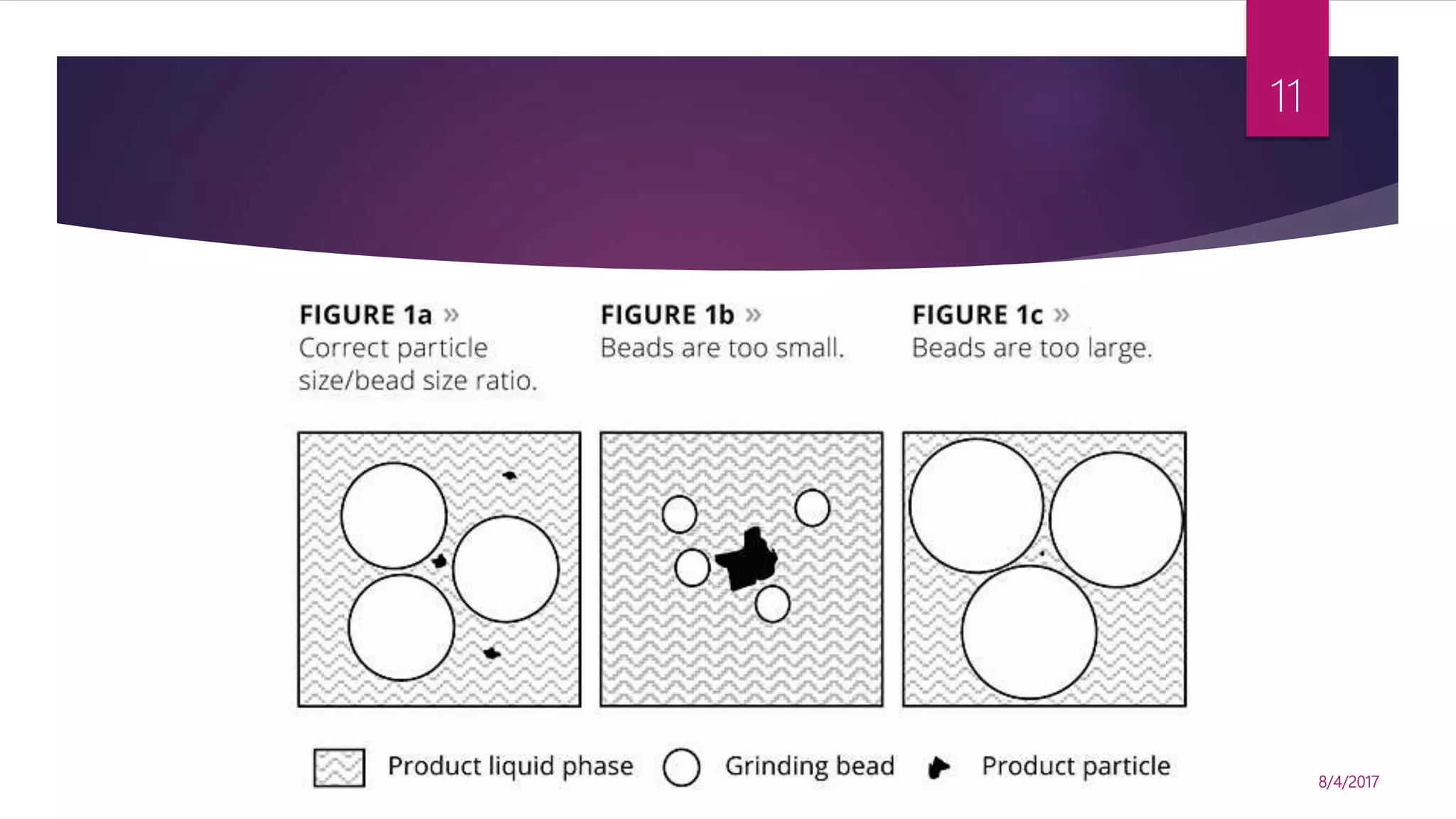

![ The kinetics of protein release from bead mills follows the relationship with
respect to the time (t) that a particle spends in the mill.
Ln[ Pm/Pm – Pr] = kt
P represents the protein content remaining associated with cells.
t is the time.
k is a release constant dependent on the system.
Pm is the maximum possible protein releasable.
8/4/2017
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/celldisruption-170804163251/75/Cell-disruption-methods-13-2048.jpg)