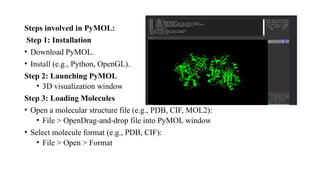
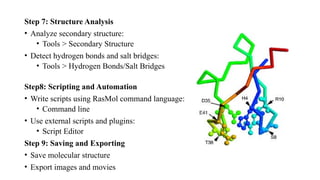
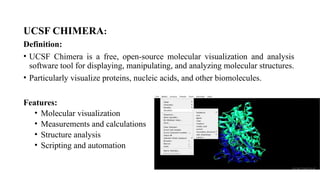
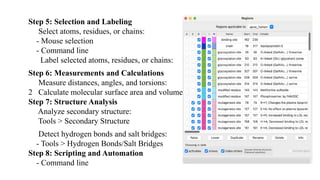
The document discusses protein structure visualization tools essential for analyzing the 3D structures of proteins and biomolecules, highlighting popular software like PyMOL, Rasmol, and UCSF Chimera. Each tool has unique features, installation procedures, and capabilities for molecular visualization, structure manipulation, and analysis. Detailed steps for using each software are provided, emphasizing their importance in drug and vaccine design.