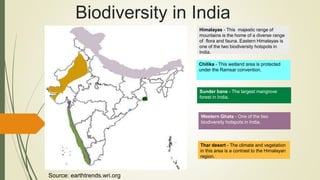
This document discusses biodiversity, defining it as the variety of life in an area determined by the number of different species. It notes that biodiversity increases ecosystem stability and health. It then lists the main types of biodiversity as genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. The document emphasizes the importance of biodiversity for maintaining ecosystem balance, providing biological resources, and social benefits. It explains the need to conserve biodiversity to protect natural functions, for aesthetic and moral reasons, and to preserve potential material and economic benefits. Finally, it outlines some of India's biodiversity hotspots and the government's efforts to establish protected areas and enact wildlife protection laws.