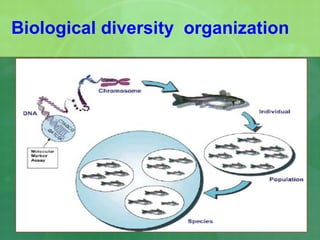
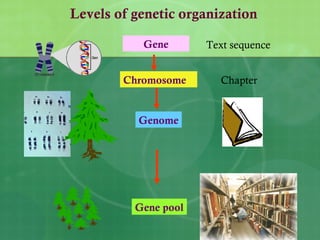
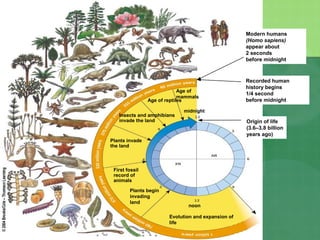
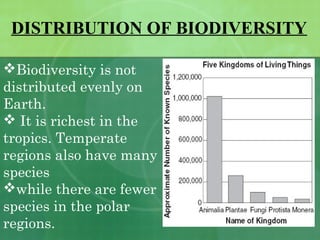
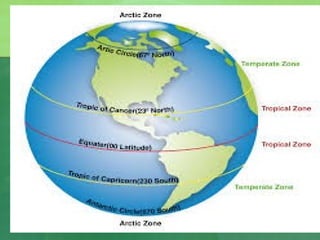
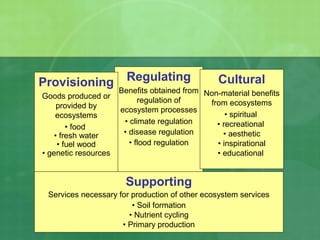
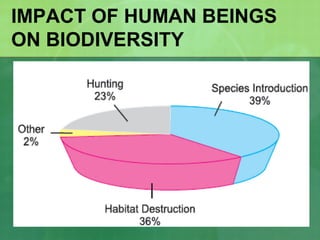
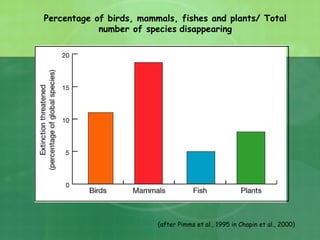
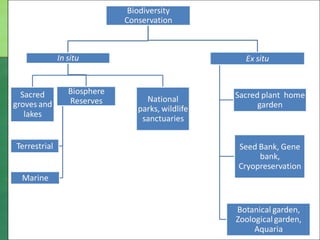
The document defines biodiversity as the variety of life on Earth, including genetic, population, species, and ecosystem diversity. It then lists the three main types of biodiversity as genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. Finally, it proposes that biodiversity needs to be protected for moral, economic, and ecological reasons, including maintaining ecosystem health and services.