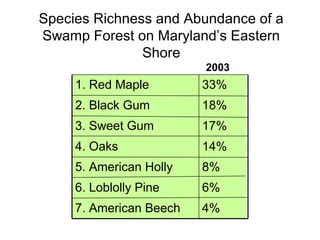
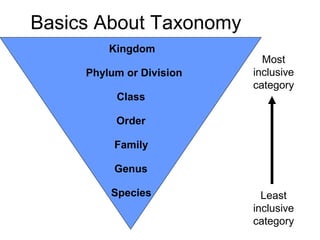
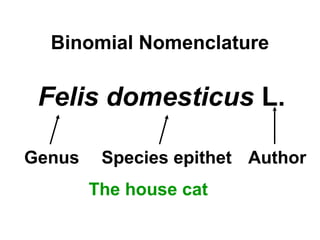
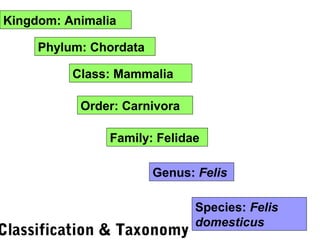
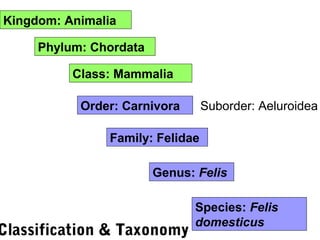
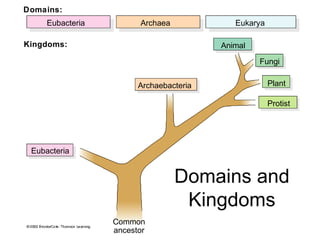
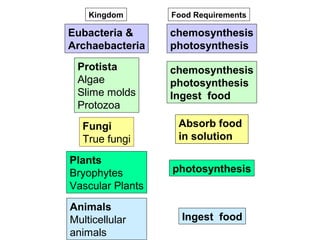
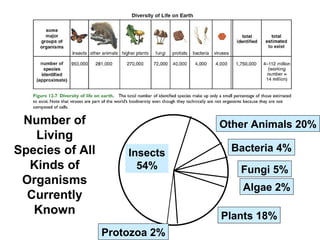
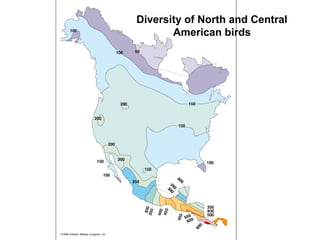
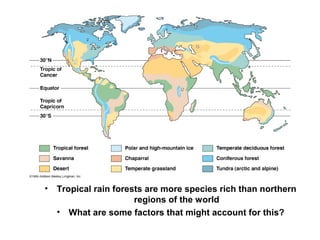
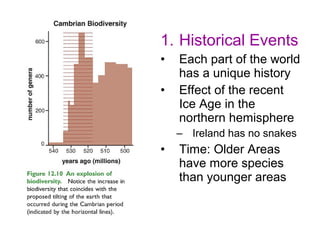
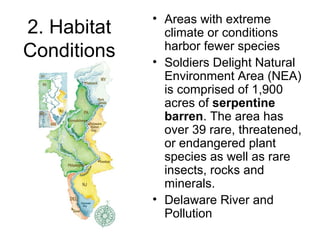
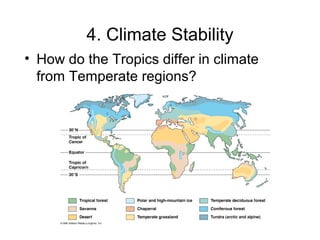
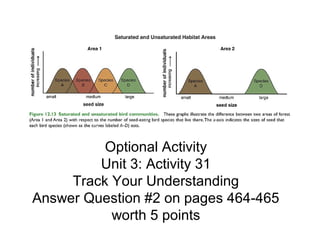
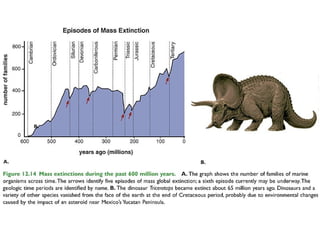
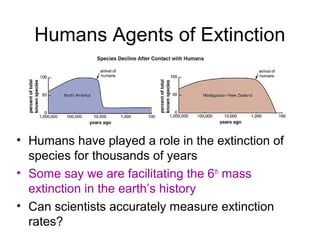
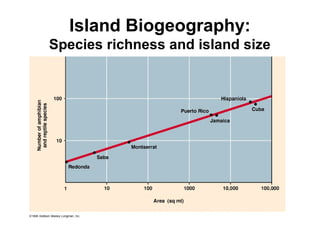
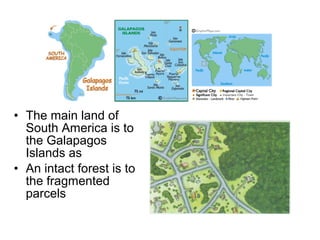
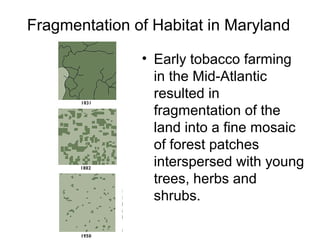
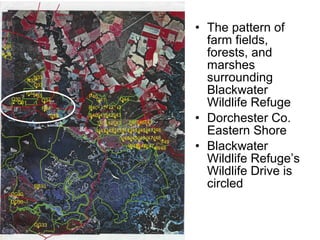
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth at all levels, from genes to ecosystems. It can be measured in five levels: genetic diversity within species; species diversity within communities; community diversity within ecosystems; ecosystem diversity within biomes; and biome diversity across the planet. Species diversity has two components - species richness, which is the number of different species, and relative species abundance, which is the number of individuals of each species. Tropical rainforests generally have higher biodiversity than temperate regions due to factors like climate stability, habitat structure, competition and disturbance regimes.