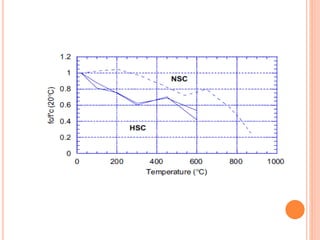
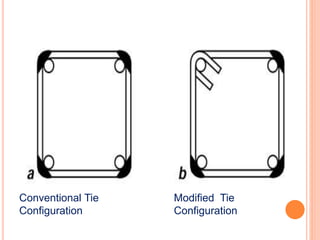
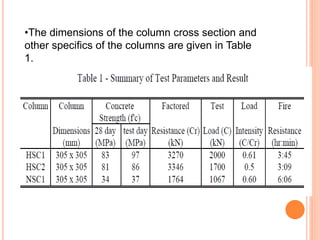
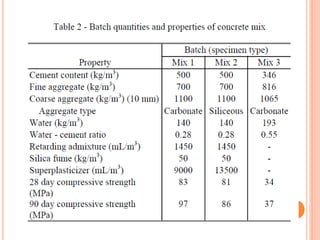
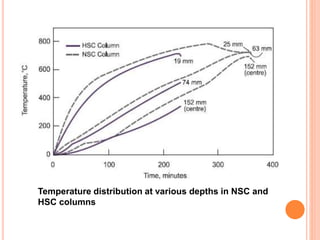
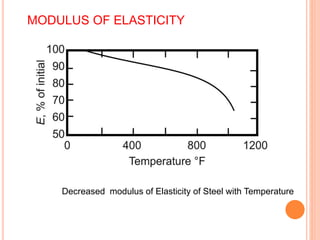
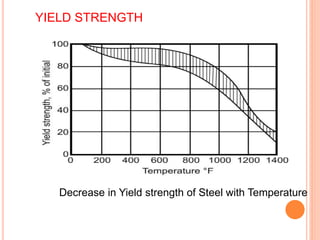
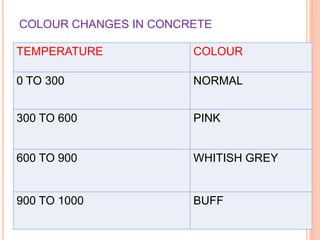
This document summarizes research on the structural behavior of high-strength concrete (HSC) columns exposed to fire. It finds that HSC columns experience more spalling than normal-strength concrete columns due to higher pore pressures developing in HSC. The fire resistance of HSC columns is affected by material properties like strength, moisture content, and aggregate type as well as structural factors like member size and reinforcement. Experimental tests showed HSC columns with carbonate aggregate had less spalling than those with siliceous aggregate. Lateral ties also improved fire resistance by limiting column expansion.