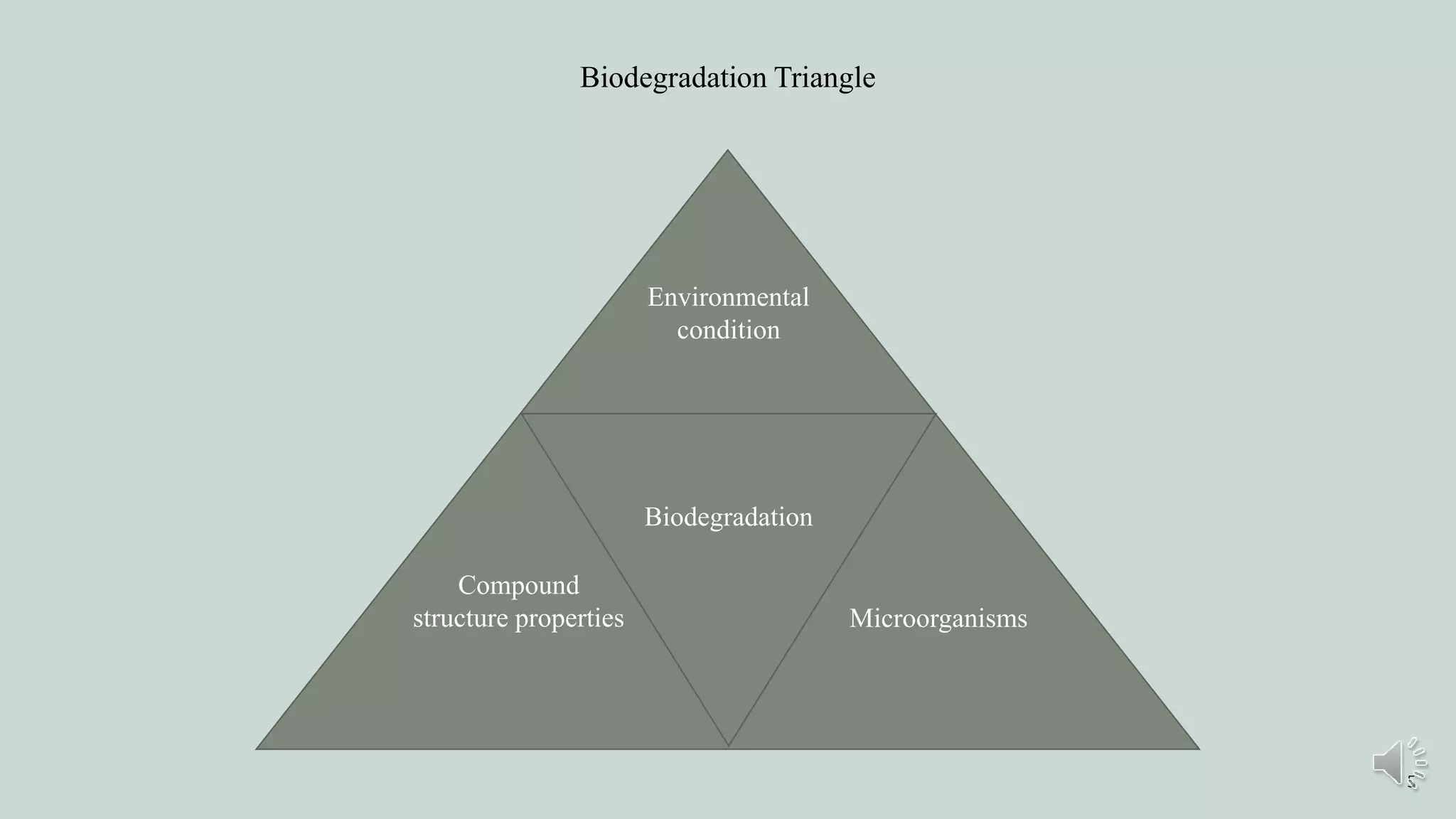
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process that differentiates it from composting. Biodegradation is defined as the process by which organic substances are decomposed by microorganisms into simpler substances like carbon dioxide, water, and ammonia. The biodegradation process is divided into three stages: biodeterioration, which weakens the structure of materials on a surface level; biofragmentation, which produces oligomers and monomers by breaking polymer bonds; and assimilation, where the resulting fragments enter microbial cells and are integrated into catabolic pathways to produce energy.