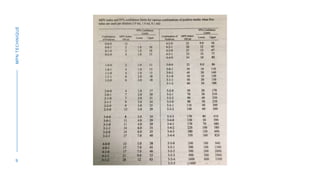
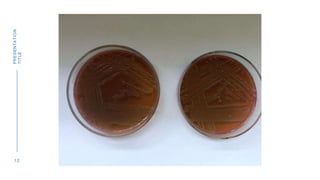
The document discusses the Most Probable Number (MPN) technique used to check water quality by testing for the presence of fecal coliform bacteria. The MPN technique involves a three step process: 1) A presumptive test where water samples are added to lactose broth tubes in different volumes and observed for gas formation, 2) A confirmatory test where cultures are streaked on EMB agar plates and observed for E. coli colonies, and 3) A complete test involving Gram staining of colonies to confirm the presence of E. coli. The number of positive lactose broth tubes corresponds to an MPN value estimate of the number of coliform bacteria per 100ml of water.