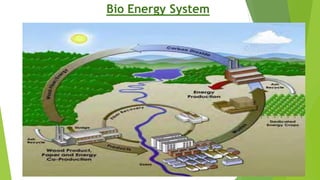
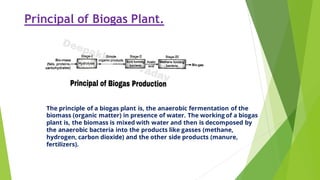
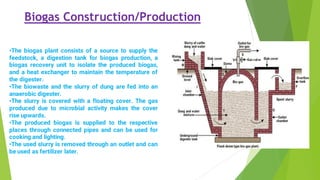
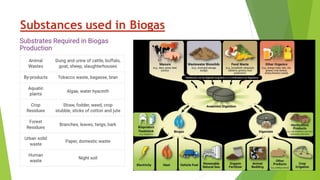
SITU PAUL is an 8th semester student studying Mechanical Engineering. The document discusses biogas, including what it is, its properties, composition, how it is produced, and its uses. Biogas is a combustible gas produced through anaerobic digestion of organic waste. It is lighter than air, has a calorific value of 18.7 to 26 MJ, and can be used as a fuel for cooking, electricity generation, vehicles, and more. The production of biogas involves feeding organic waste into an anaerobic digester where bacteria break it down to produce methane gas and fertilizer byproduct.