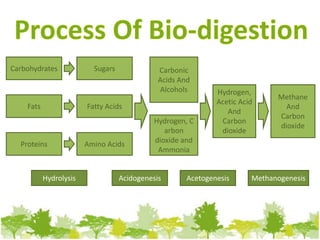
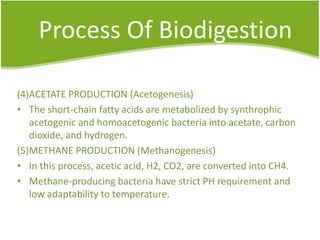
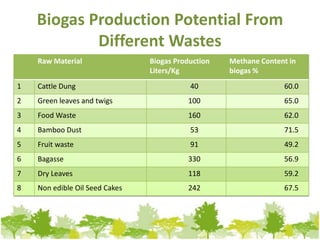
Biogas can be generated from organic wastes through anaerobic digestion to provide a renewable source of energy. It has the benefits of dealing with waste management issues while also producing a clean fuel for cooking, lighting, electricity and transportation. The biogas production process involves several steps of hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis by which bacteria break down biomass into methane and carbon dioxide gas. Common feedstocks and their expected biogas yields are listed to evaluate production potential from various resources.


![Biogas
• Biogas is clean environment friendly fuel.
• Biogas is generated when bacteria degrade biological material in
the absence of oxygen, in a process known as anaerobic
digestion.
• Biogas generally comprise of 55-65 % methane, 35-45 % carbon
dioxide, 0.5-1.0 % hydrogen sulfide and traces of water vapour.
• The heating value of biogas is about 60% of natural gas and
about 25% of propane. [Average calorific value of biogas is 20
mj/m3].
• Biogas has corrosive nature and storage of biogas is not
practical.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biogas-140110032925-phpapp01/85/Bio-gas-3-320.jpg)