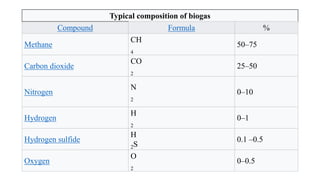
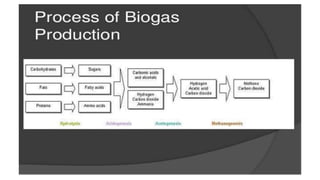
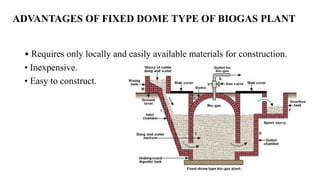
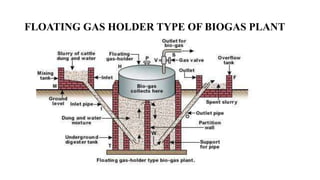
Biogas is a renewable biofuel produced from the anaerobic decomposition of organic waste, primarily consisting of methane and carbon dioxide. It serves as an eco-friendly energy source that addresses waste management and fossil fuel reliance while being useful in generating electricity and heat. Biogas production involves a series of fermentation stages, with different types of biogas plants available, each having unique advantages and disadvantages, including construction costs and operational maintenance.