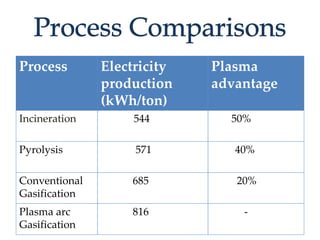
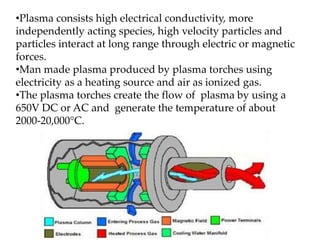
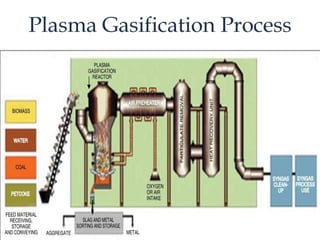
The document discusses challenges and opportunities related to solid waste management. Global solid waste is projected to double by 2025, with India generating 100,000 metric tons per day. This waste can be used to generate energy. Plasma gasification is highlighted as a unique opportunity to mitigate waste challenges by converting waste into syngas and vitrified slag at very high temperatures without greenhouse gas emissions. It produces more electricity per ton of waste than other waste-to-energy methods like incineration and gasification. The document then provides details on the plasma gasification process and its advantages over other waste treatment options.