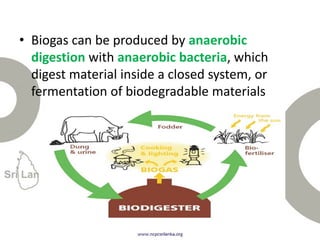
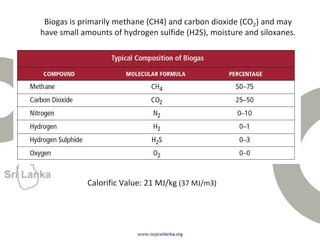
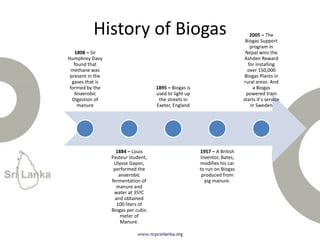
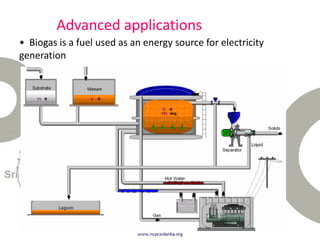
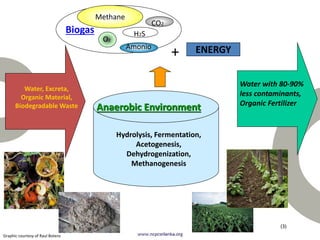
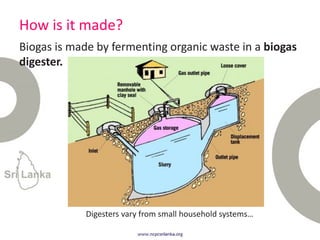
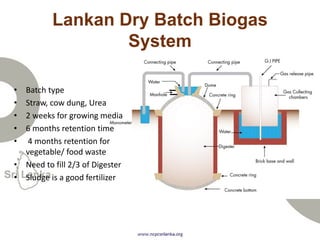
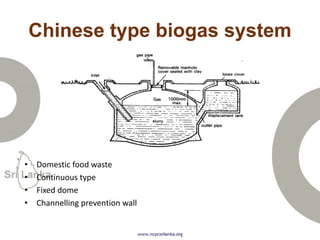
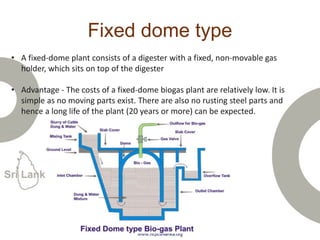
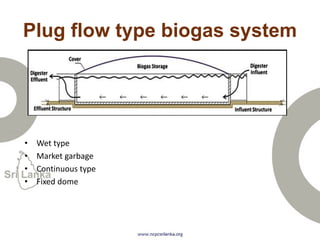
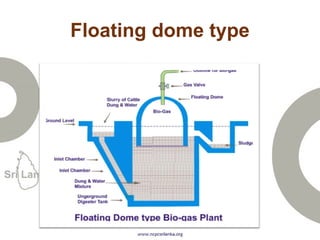
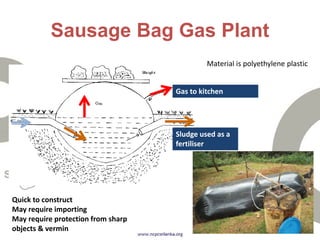
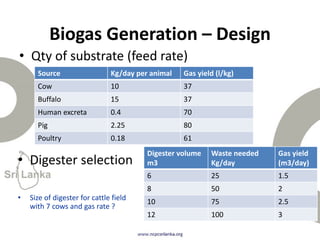
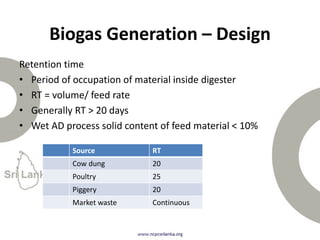
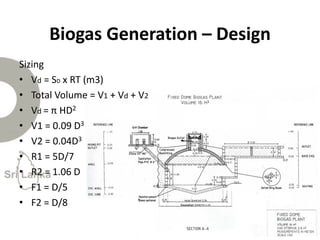
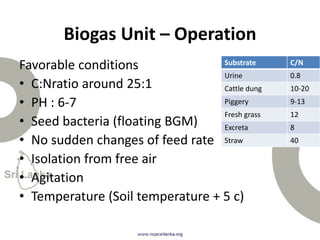
Biogas is produced by the breakdown of organic waste by bacteria during anaerobic digestion. It is a mixture of gases, primarily methane and carbon dioxide. A biogas plant consists of a digester where the waste decomposes and a gas holder that captures the gases produced. Biogas can be used as a fuel for cooking, lighting, electricity generation, and transportation. While biogas has benefits such as being renewable and reducing pollution, some challenges to biogas adoption include plant failures and lack of technology advancement to produce cleaner gas.