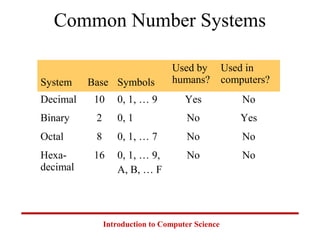
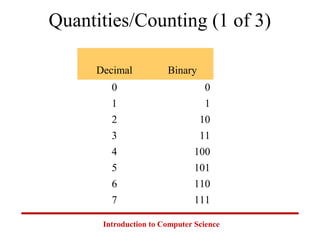
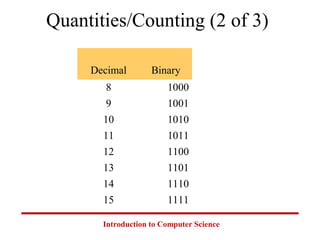
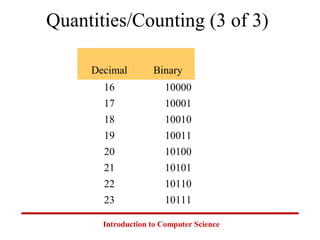
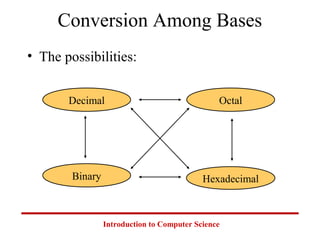
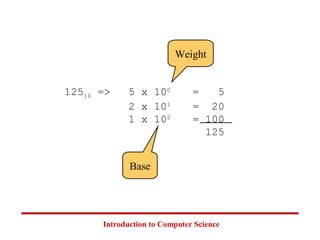
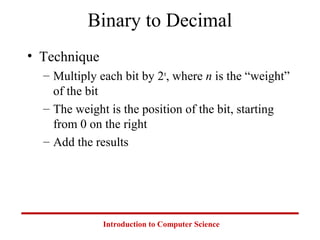
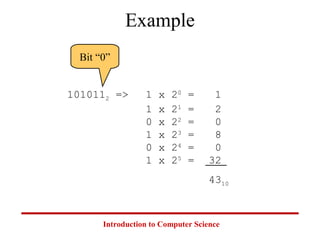
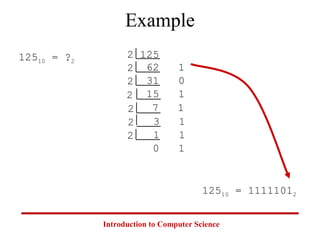
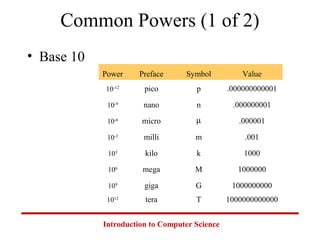
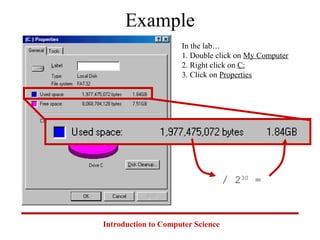
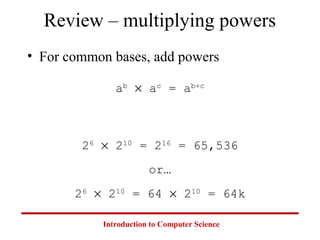
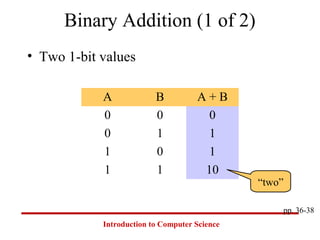
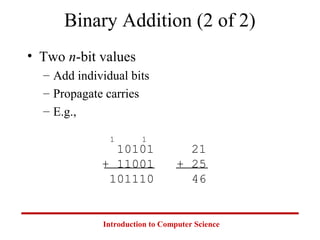
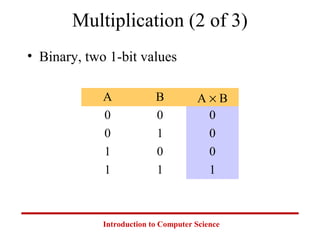
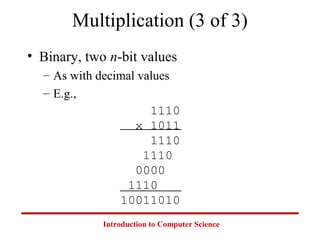
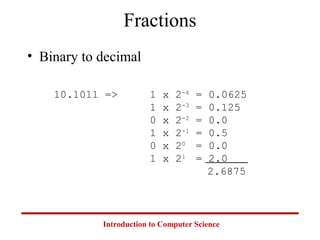
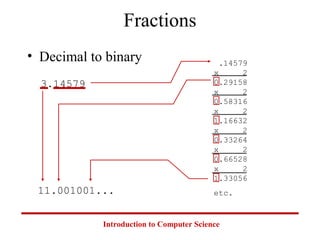
This document introduces common number systems used in computer science, including decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal. It discusses how computers use binary to represent quantities and how to convert between number bases. Key topics covered include counting in binary, converting between decimal and binary, binary addition and multiplication, common powers of 2 used in computing, and representing fractions in binary.