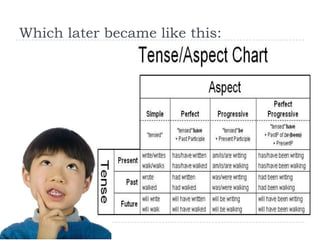
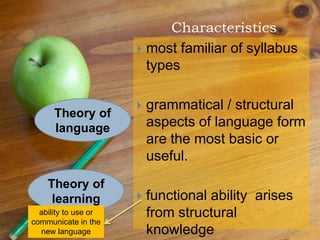
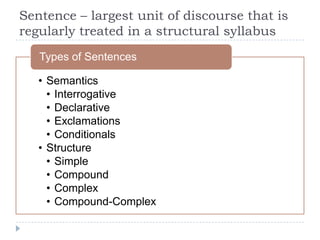
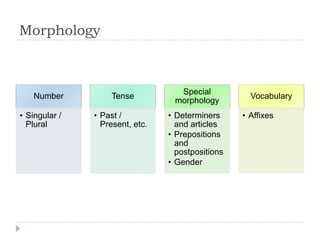
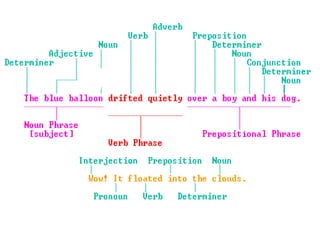
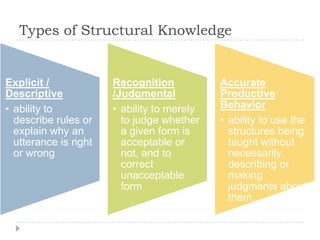
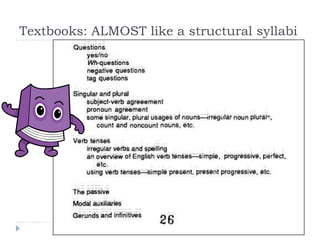
The document discusses the structural syllabus approach to language teaching. It defines the structural syllabus as one that focuses on the grammatical and structural aspects of a language by analyzing and isolating language elements. This approach believes that functional language ability arises from structural knowledge. The summary then lists some key characteristics of the structural syllabus, including that it focuses on language form and traditional grammatical classifications. It also notes both positive characteristics, such as serving as a basis for learner self-correction, and negative characteristics, such as lack of applicability and transferability of structural knowledge alone.