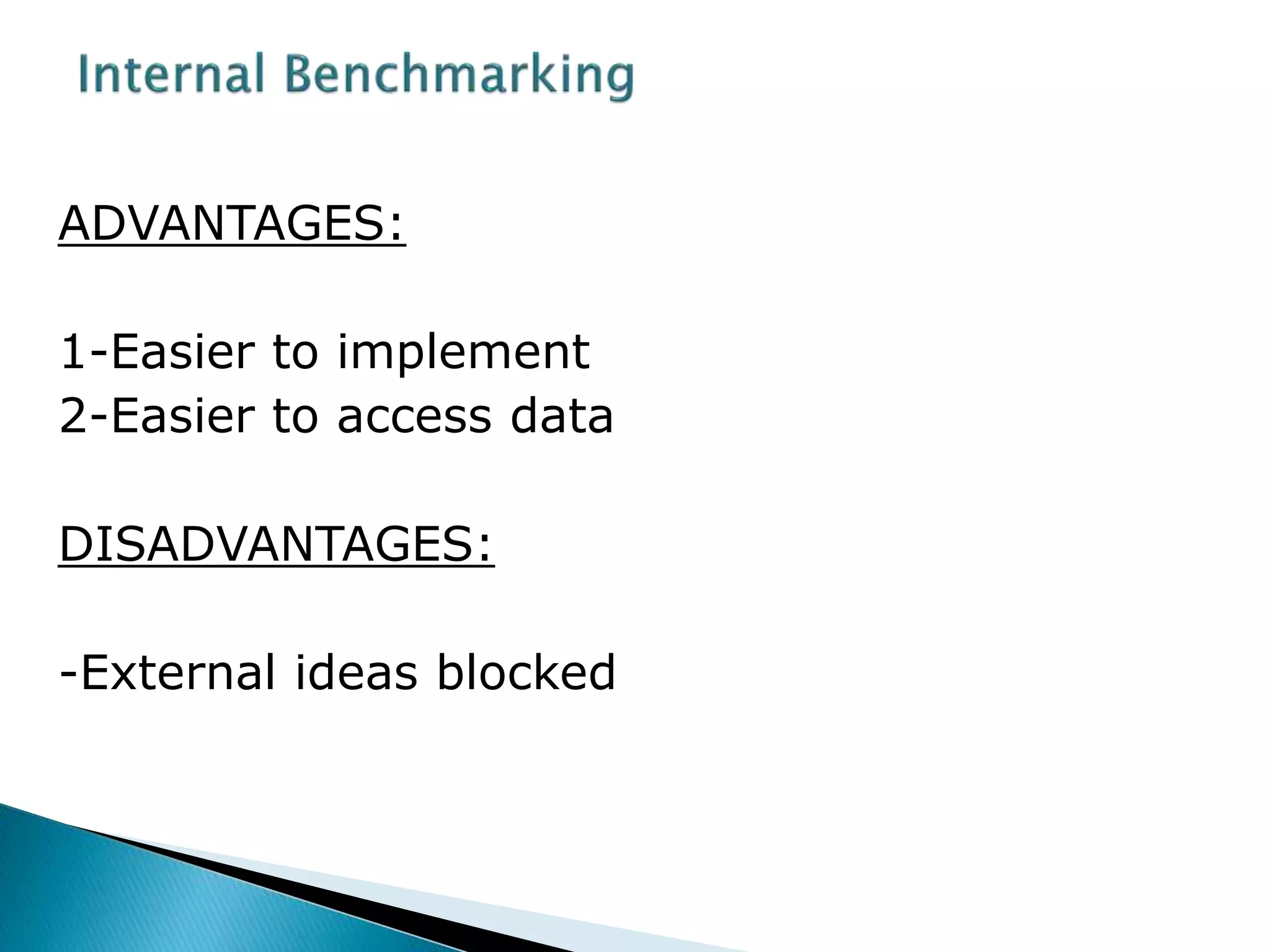
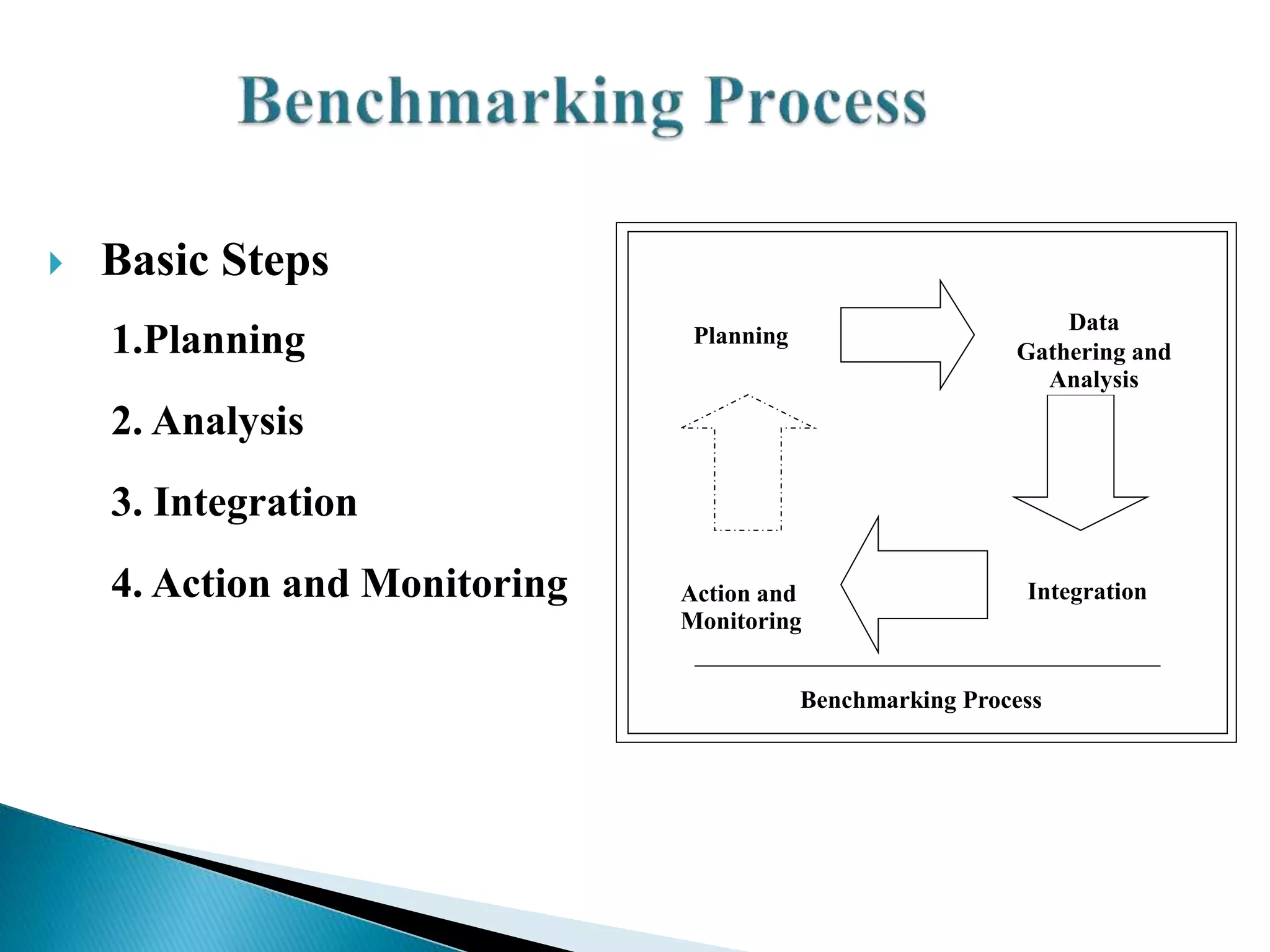
This document defines benchmarking and outlines its key principles and processes. Benchmarking is defined as identifying, understanding, and adopting outstanding practices from inside or outside an organization to improve performance. The document discusses the types of benchmarking, including internal and external benchmarking. It also outlines the basic benchmarking process of planning, analysis, integration, and action/monitoring. Finally, the advantages of identifying best practices and driving improvements are highlighted, along with some potential disadvantages like reluctance to share information.