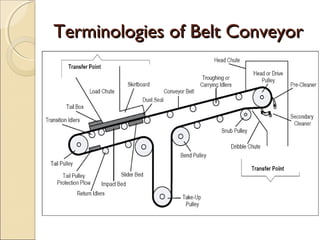
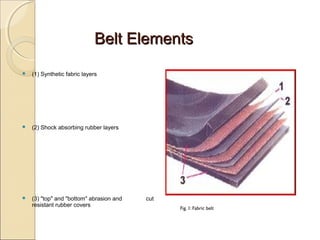
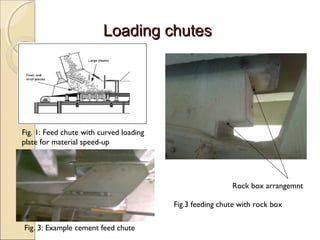
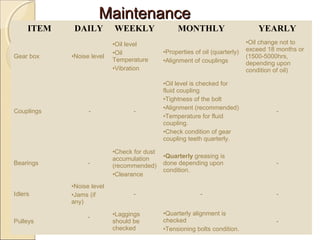
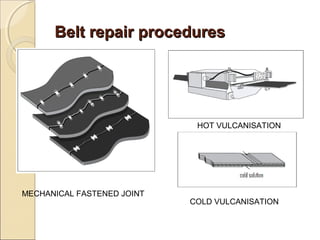
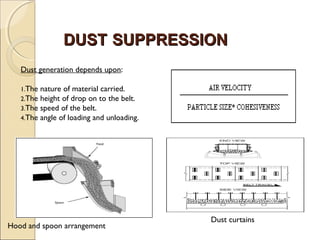
Belt conveyors transport bulk materials like crushed limestone and coal in cement plants. A belt conveyor consists of an endless rubber belt stretched over several pulleys that travels constantly. It includes belt elements, idlers, pulleys, take-ups, and other components. Proper loading conditions and regular maintenance are important to prevent belt wear and failures. Safety precautions must also be followed when working with belt conveyors.