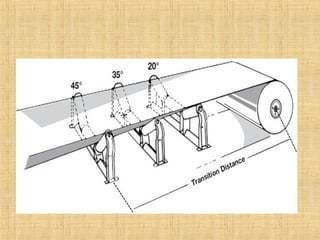
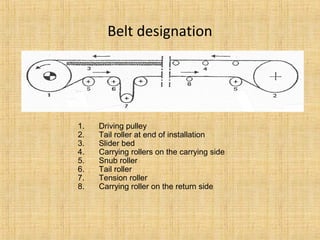
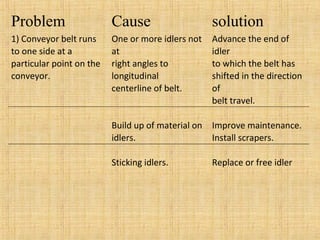
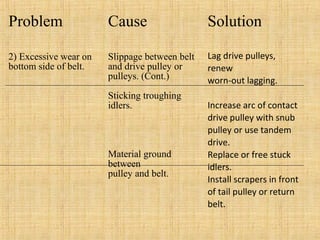
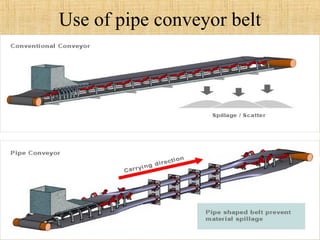
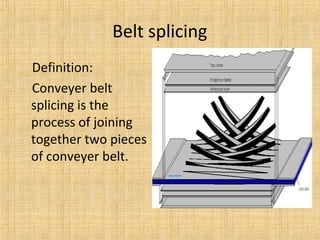
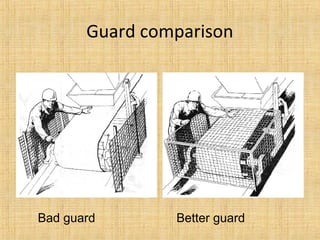
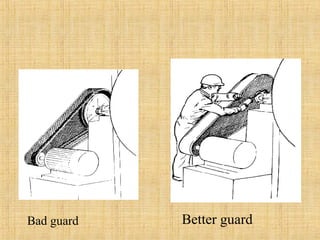
The document provides a comprehensive overview of conveyor belts, including their definition, types (troughed, flat, and pipe belts), and components. It explores various belt types like steel cord and textile belts, their typical failures, troubleshooting tips, and maintenance procedures to prevent issues. Additionally, it outlines safety measures and best practices for operating and maintaining conveyor systems efficiently.