Embed presentation
Download to read offline





![6
INIT(G, s)
for each v V do
d[v] ← ∞
π[v] ← NIL
d[s] ← 0
RELAX(u, v)
if d[v] > d[u]+w(u,v)
then
d[v] ← d[u]+w(u,v)
π[v] ← u](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellmanfordwithnegativecyclejs-150927004142-lva1-app6892/75/Bellmanfordwith-negative-cycle-js-6-2048.jpg)

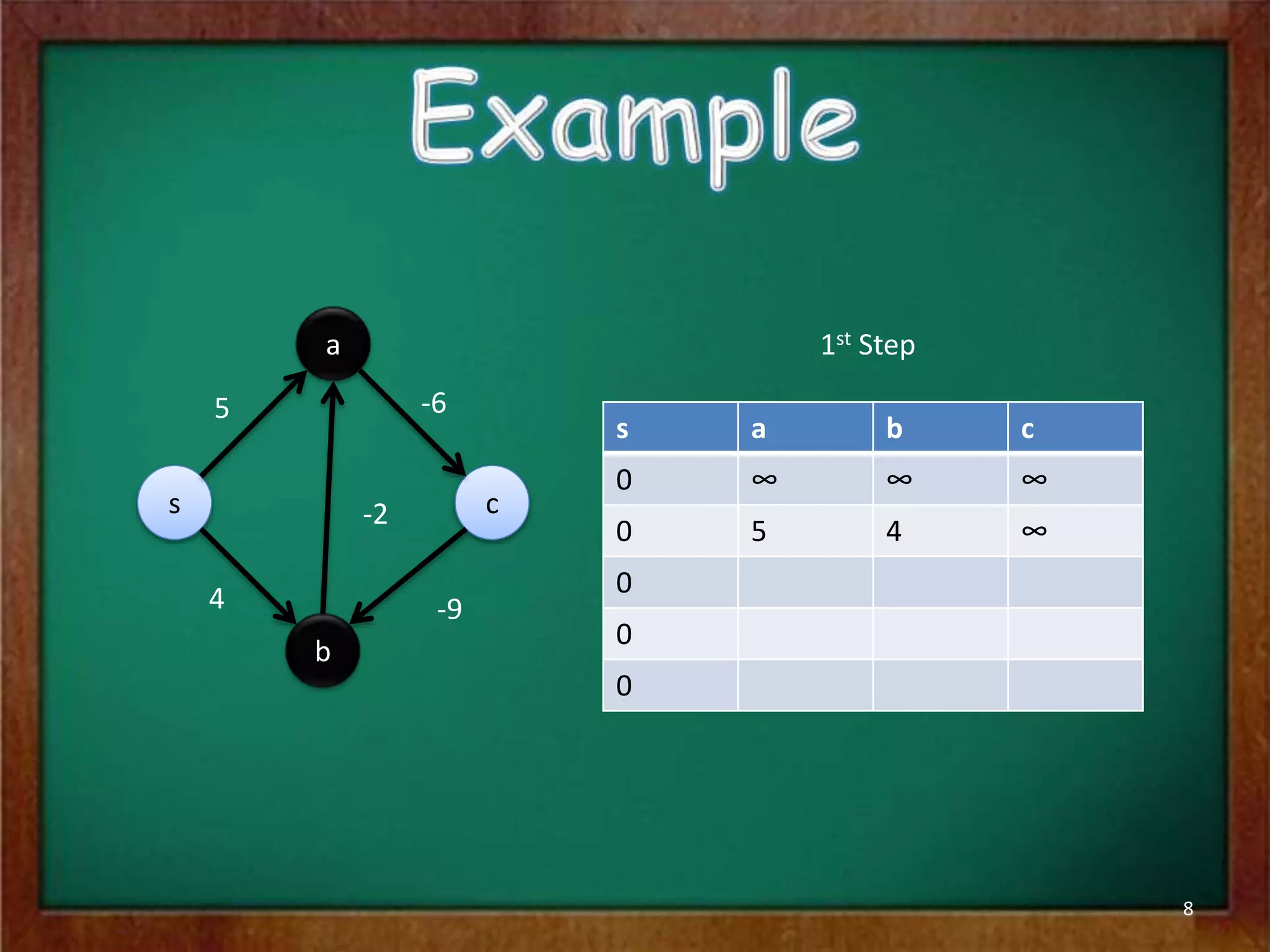
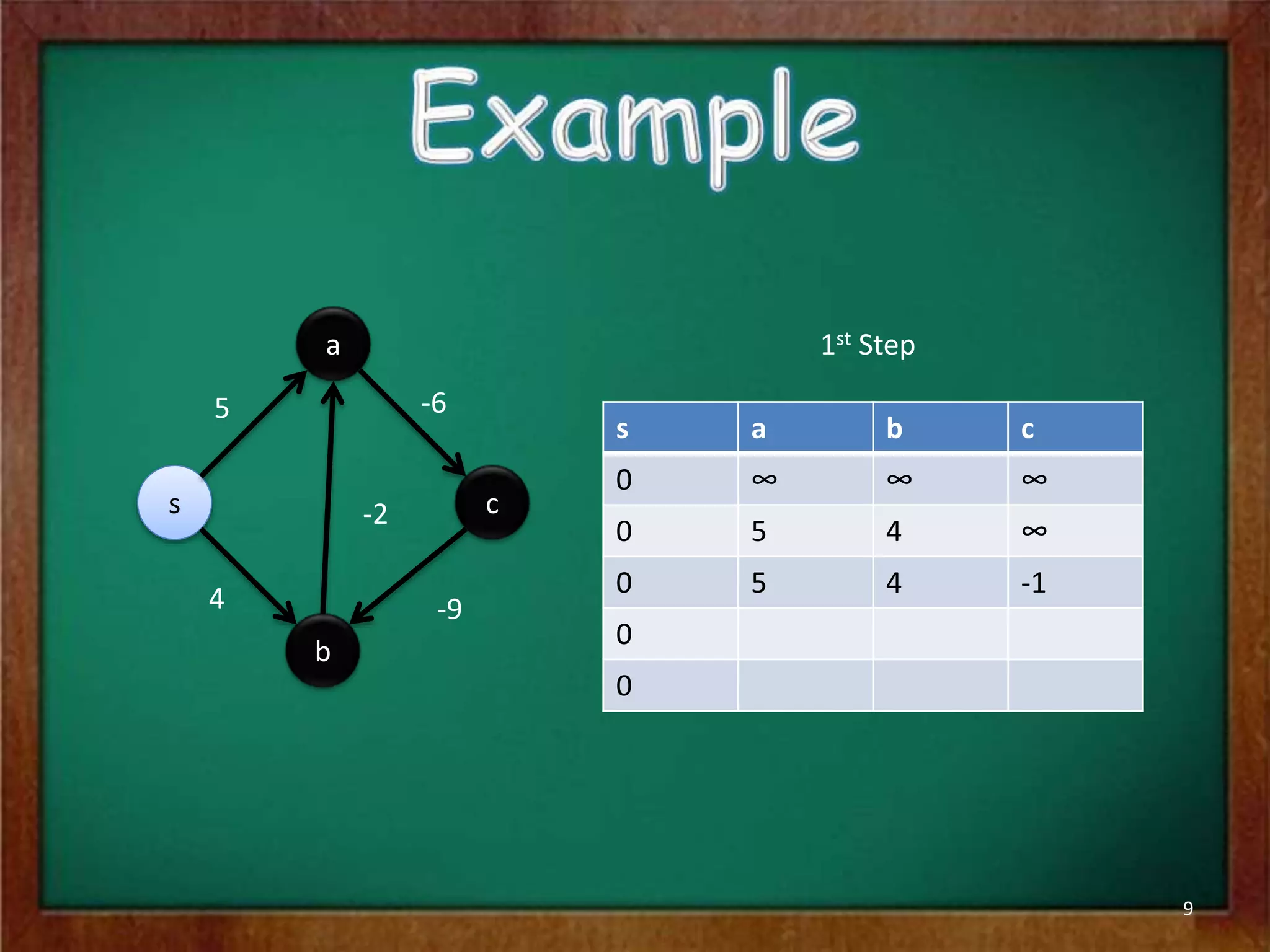
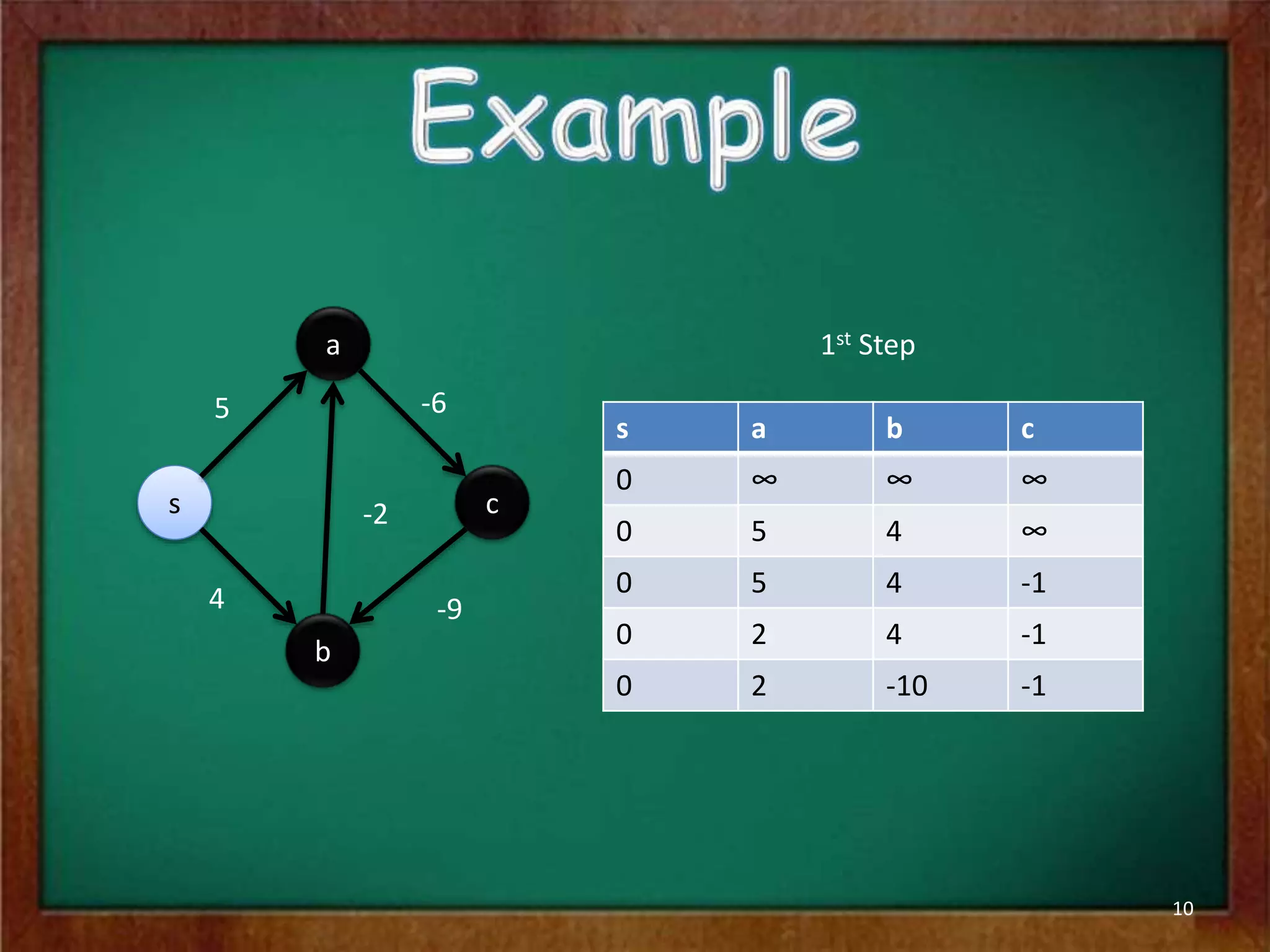
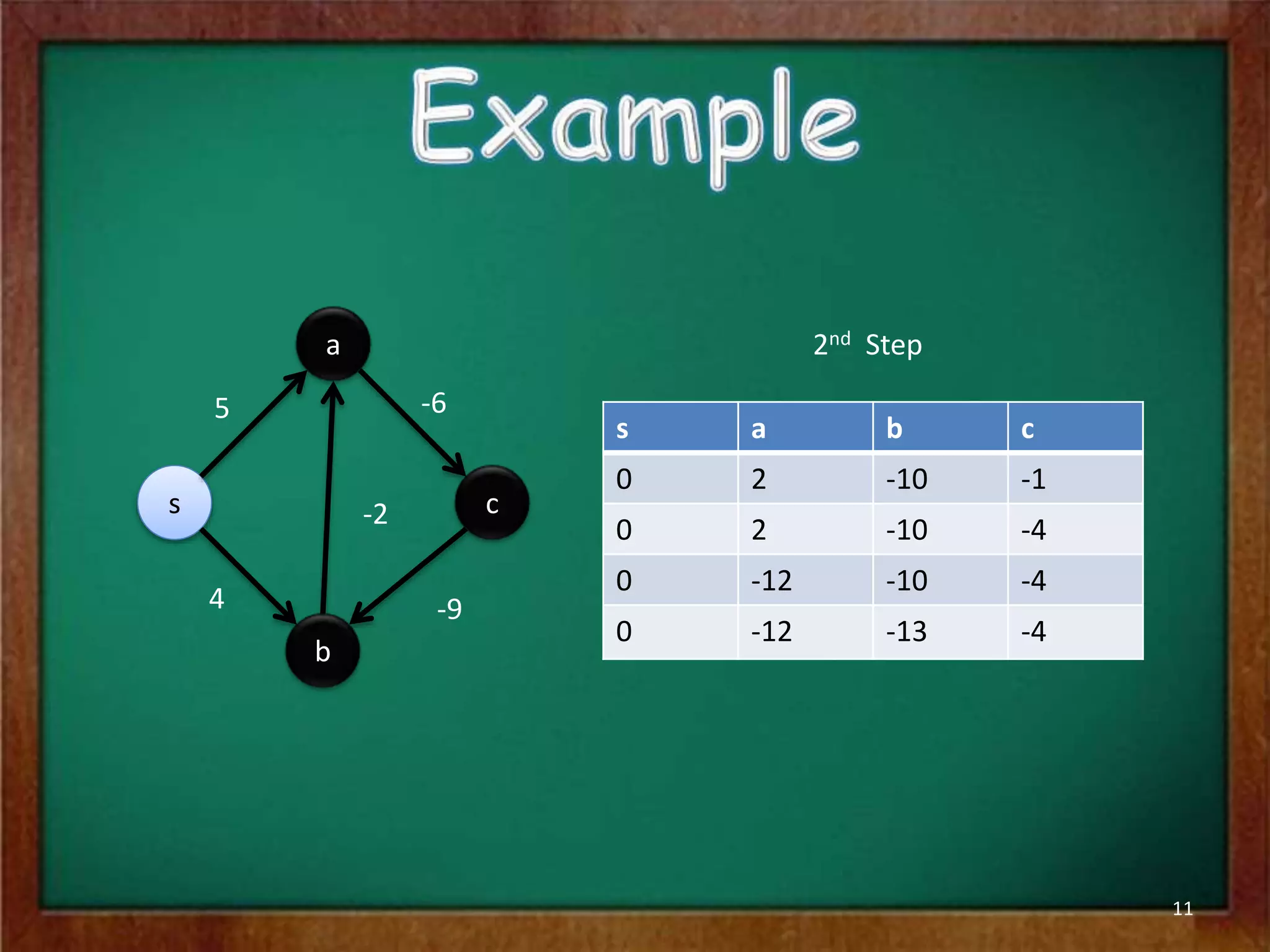
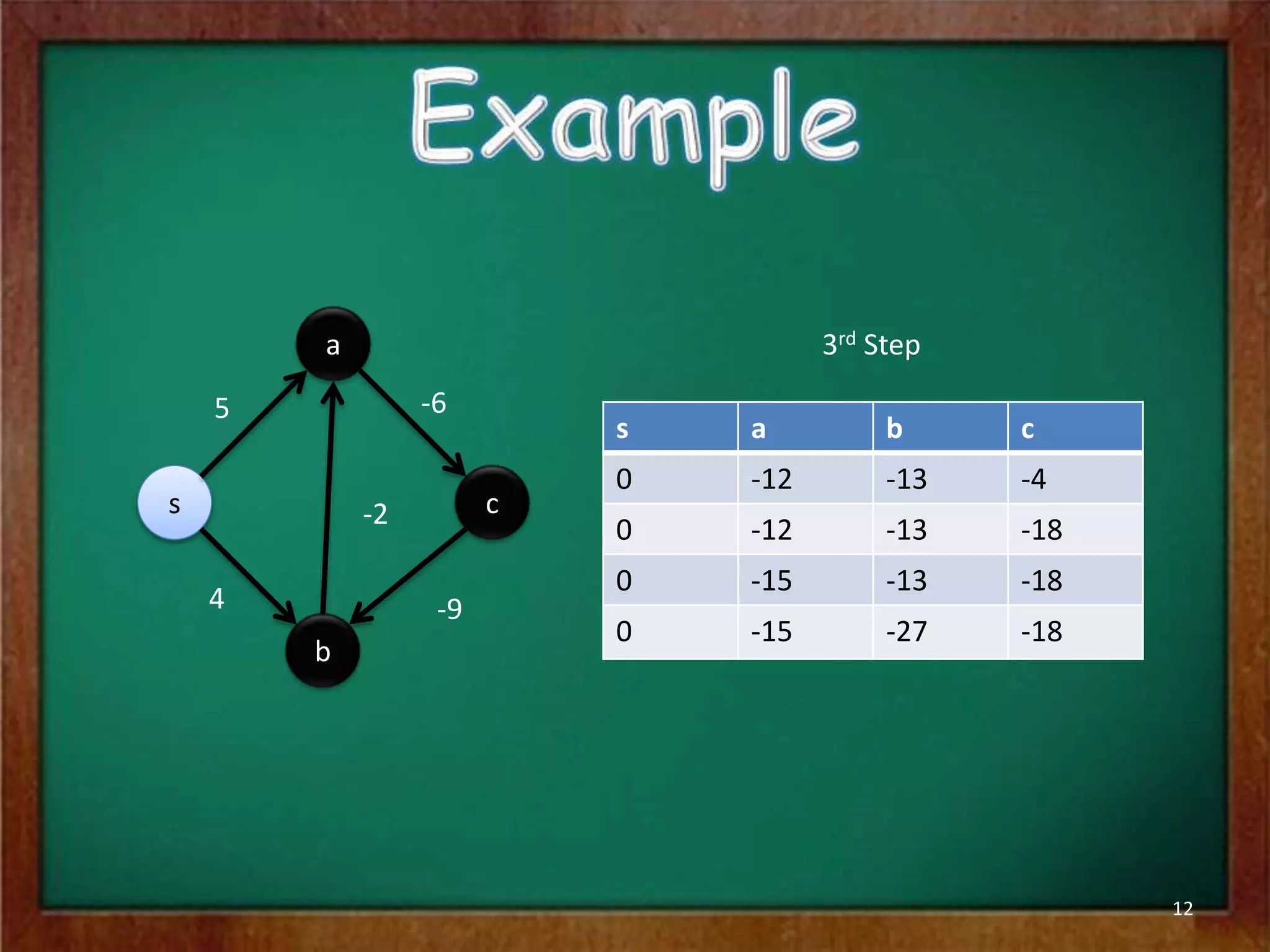
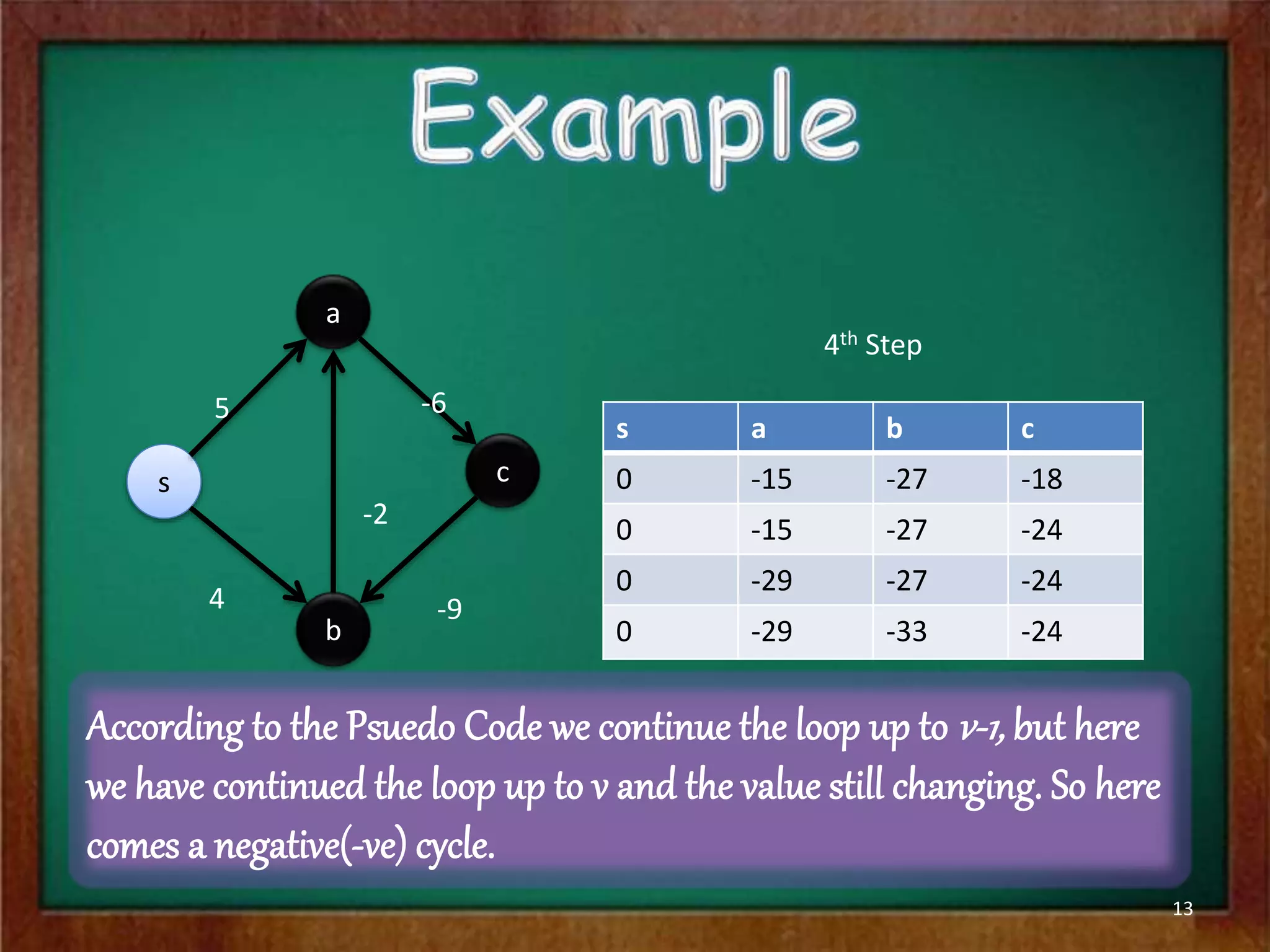




The Bellman-Ford algorithm is used to find the shortest paths from a single source vertex to all other vertices in a graph that may contain negative edge weights. It iterates through all edges |V|-1 times to detect and handle negative cycles, running in O(|V||E|) time. The algorithm initializes distances and predecessors, then repeatedly relaxes edges to update distance values until it converges on the shortest paths or finds a negative cycle.





![6
INIT(G, s)
for each v V do
d[v] ← ∞
π[v] ← NIL
d[s] ← 0
RELAX(u, v)
if d[v] > d[u]+w(u,v)
then
d[v] ← d[u]+w(u,v)
π[v] ← u](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bellmanfordwithnegativecyclejs-150927004142-lva1-app6892/75/Bellmanfordwith-negative-cycle-js-6-2048.jpg)









