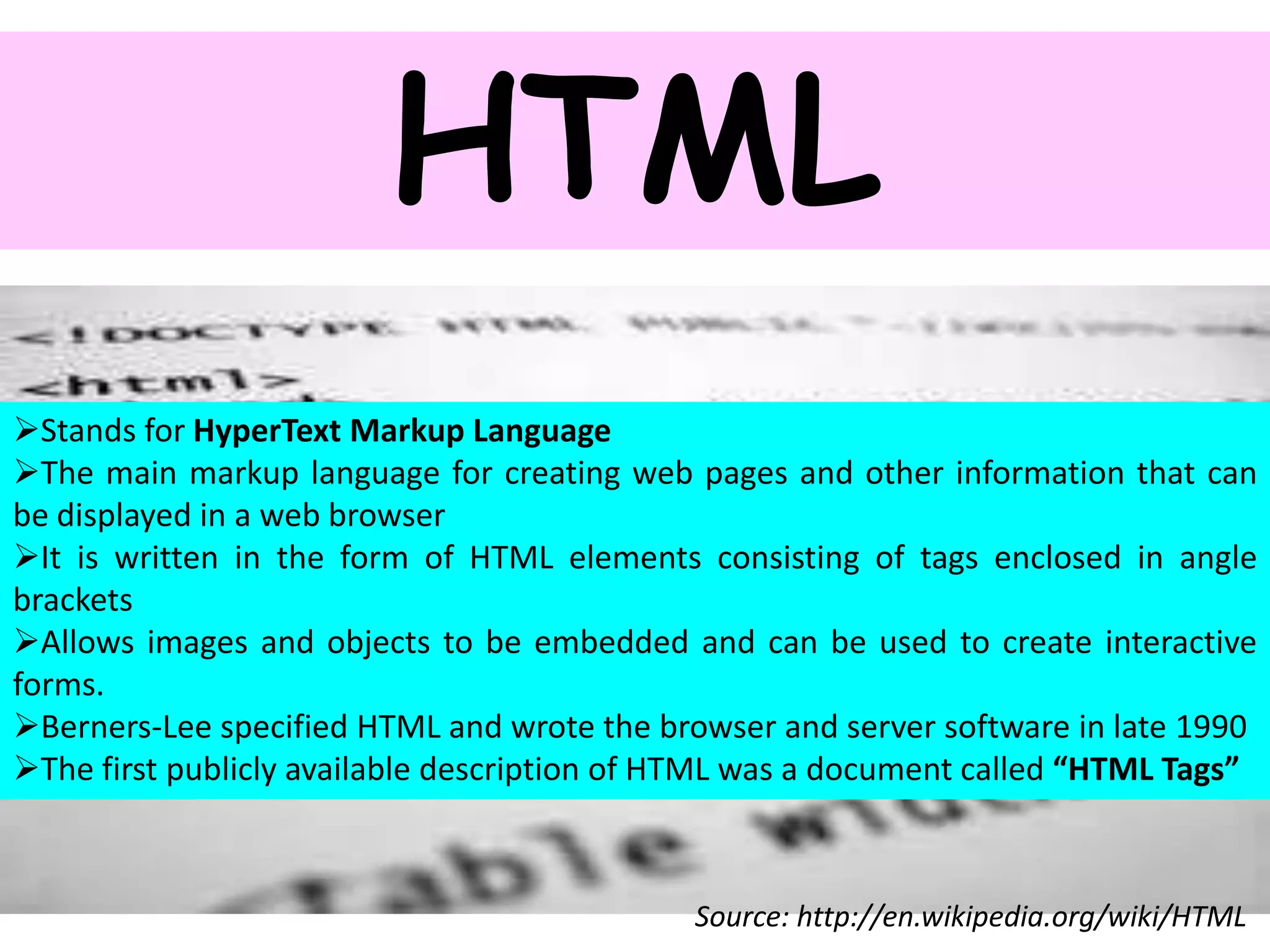
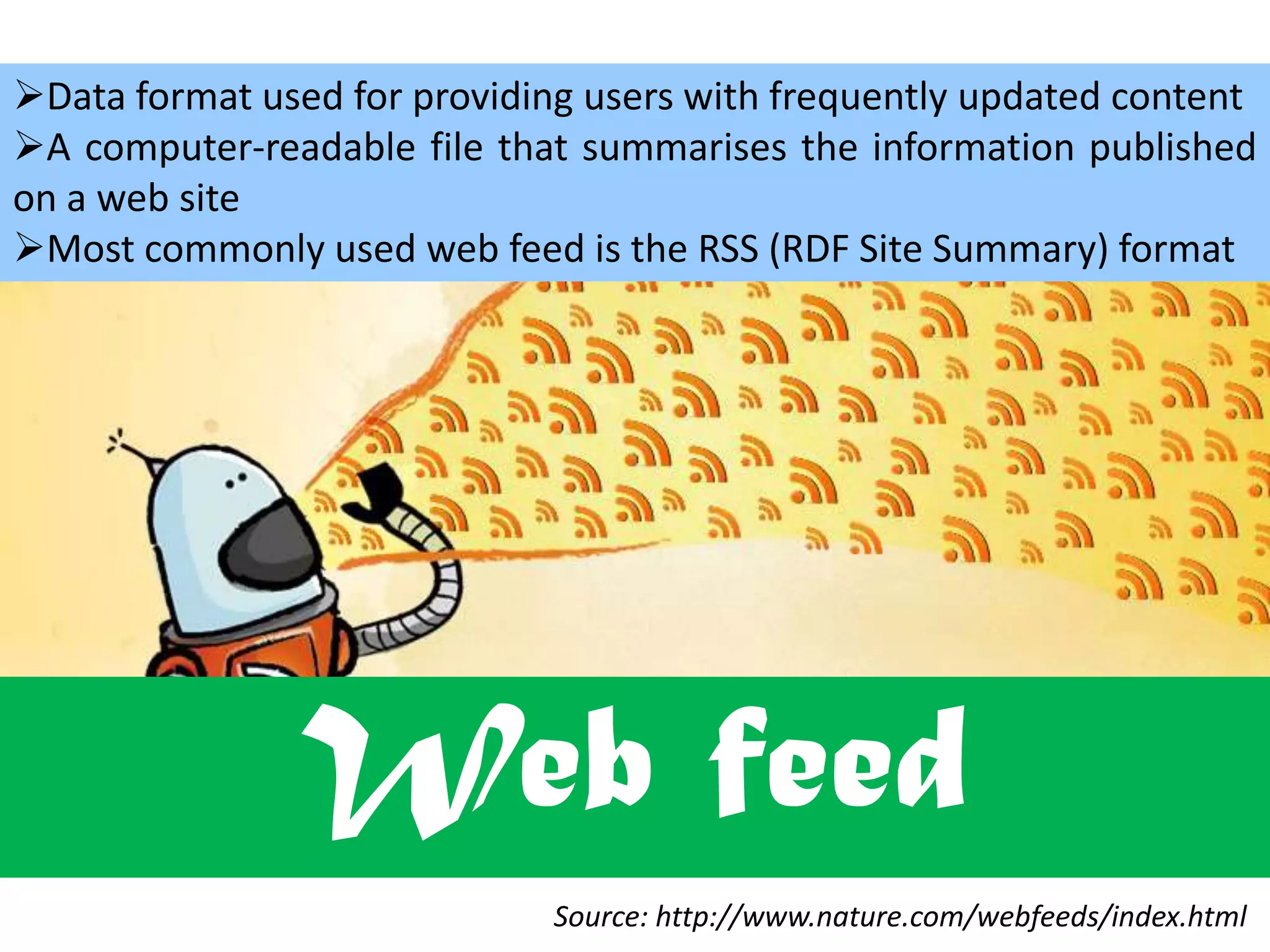
The document defines common online terminology used on the internet and world wide web. It provides definitions for terms like email, blogs, wikis, social networking, hashtags, URLs, HTML, web feeds, podcasts, VoIP, online chat, WWW, and streaming. The definitions are sourced from online references like Wikipedia and dictionaries.