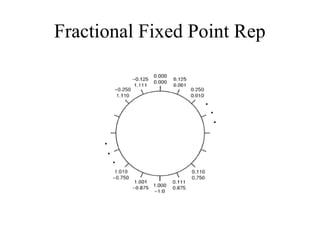
1) Fixed point numbers represent integers in a binary format using a fixed number of bits. They have limited range but are fast and inexpensive to implement. Floating point numbers use exponents to represent a wider range of values with varying precision levels.
2) Common data types include short (16-bit integer), int (32-bit integer), float (32-bit floating point), and double (64-bit floating point). Floating point values follow IEEE standards and use significands and exponents.
3) Single precision floating point uses 32 bits with 24 bits for the significand, while double precision uses 64 bits with 53 bits for the significand, allowing wider ranges of values to be represented.

![Fixed point numbers[1]
• Fast and inexpensive implementation
• Limited in the range of numbers
• Susceptible to problems of overflow
•In a fixed-point processor, numbers are represented in integer
format.
• Fixed-point numbers and their data types are
characterized by their -
word size in bits
binary point
and
whether they are signed or unsigned](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bca-2ndsem-u-1-150317050313-conversion-gate01/85/Bca-2nd-sem-u-1-9-digital-logic-circuits-digital-component-floting-and-fixed-point-2-320.jpg)


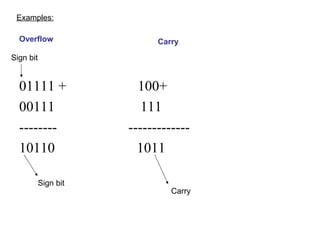
![• Carry applies to unsigned numbers — when adding or
subtracting, result is incorrect.
• Overflow applies to signed numbers — when adding or
subtracting, result is incorrect.
Carry and Overflow[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bca-2ndsem-u-1-150317050313-conversion-gate01/85/Bca-2nd-sem-u-1-9-digital-logic-circuits-digital-component-floting-and-fixed-point-5-320.jpg)

![Data types[3]
1.Short:
it is of size 16 bits represented as 2’s complement with a
range from -215
to (215
-1)
2.Int or signed int:
it is of size 32 bits represented as 2’s complement with a
range from -231
to ( 231
-1)
3.Float:
it is of size 32 bits represented as IEEE 32 bit with a range
from 2-126
(1.175494x10-38
) to 2+128
(3.40282346x1038
)
4.Double:
it is of size 64 bits represented as IEEE 64 bit with a range
from 2-1022
(2.22507385x10-308
) to 2 1024
(1.79769313x10308
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bca-2ndsem-u-1-150317050313-conversion-gate01/85/Bca-2nd-sem-u-1-9-digital-logic-circuits-digital-component-floting-and-fixed-point-9-320.jpg)






