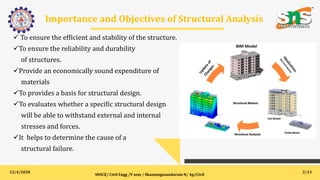
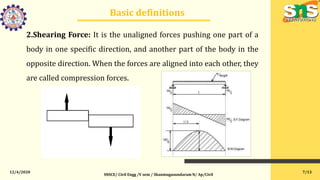
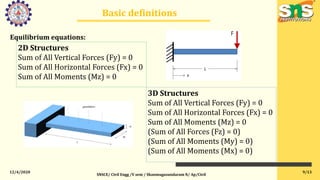
This document provides an overview of structural analysis for a course on the topic at SNS College of Engineering. It defines key terms like bending moment, shearing force, and equilibrium. It explains the objectives of studying structural analysis, including introducing classical analysis methods. It outlines the outcomes students will achieve in learning to analyze different structural elements like continuous beams and rigid frames using various techniques. The first unit focuses on the strain energy method and how to apply it to continuous beams, frames, and trusses with up to two degrees of redundancy.