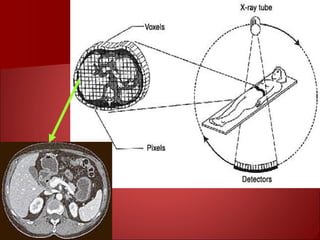
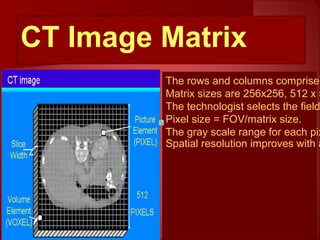
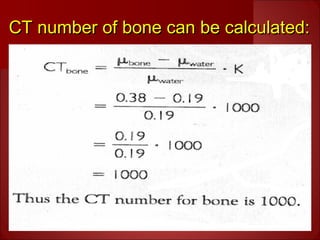
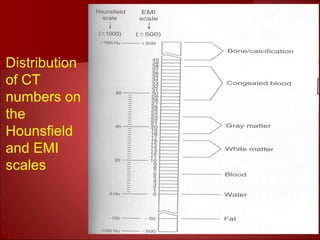
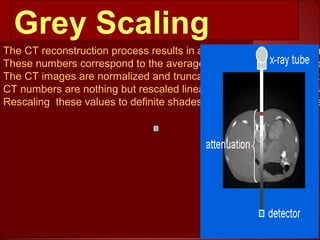
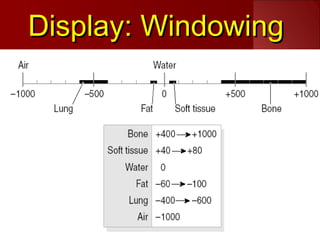
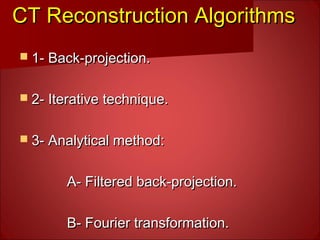
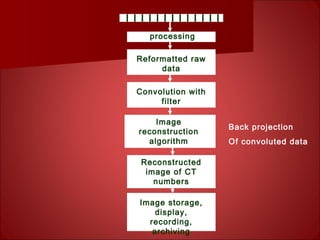
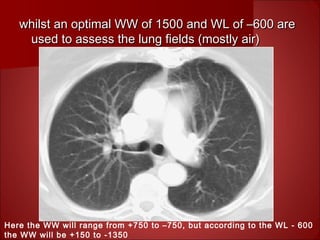
The document discusses the basics of computed tomography (CT) scanning. It explains that after measurements are taken by detectors, mathematical reconstruction techniques are used to convert the data into a CT image. The most common technique is filtered back projection. It also describes how window width and level are used to display CT images by mapping CT numbers to grayscale shades. The document provides advantages of CT over conventional radiography and gives a brief history of the technology.