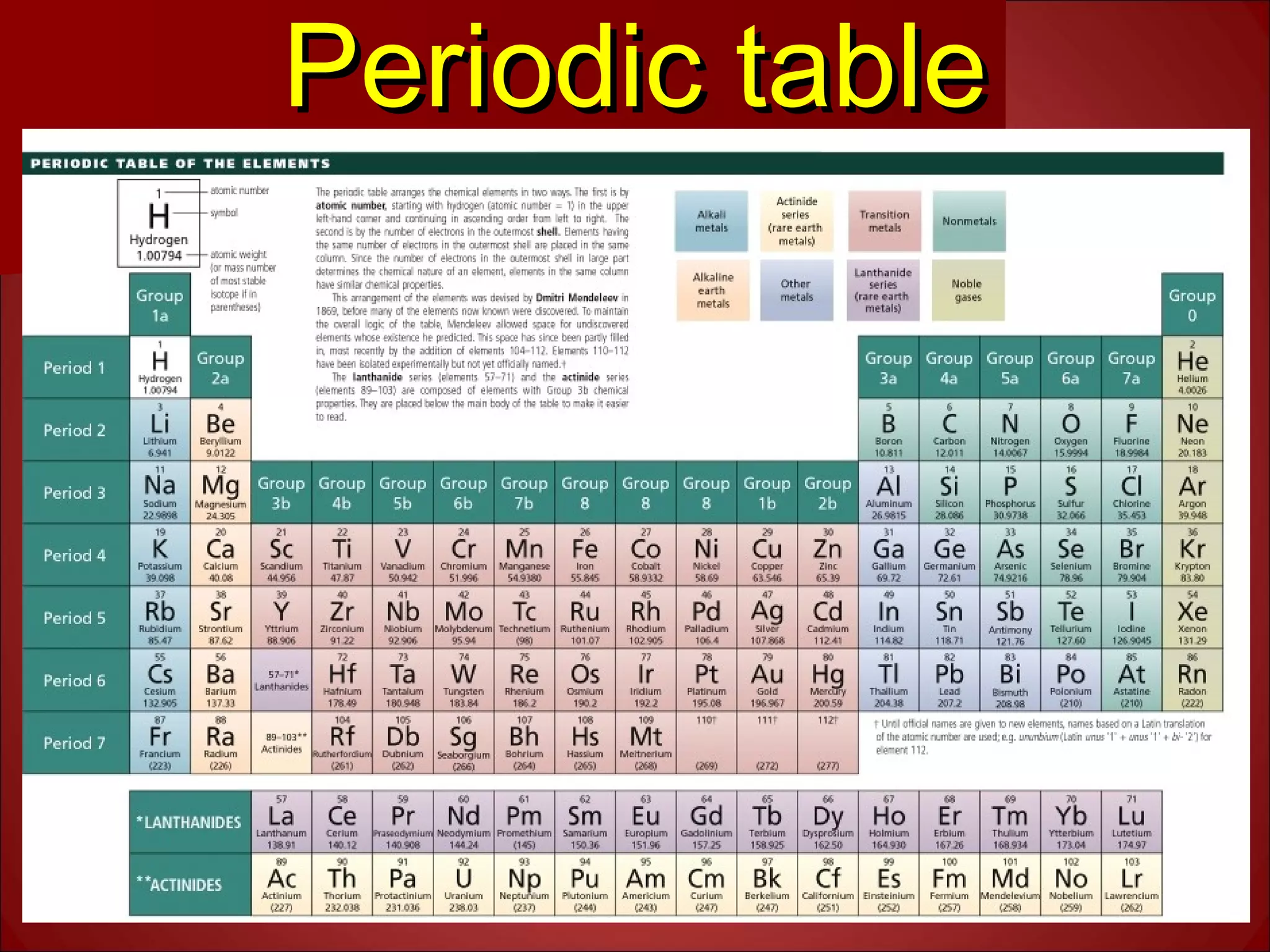
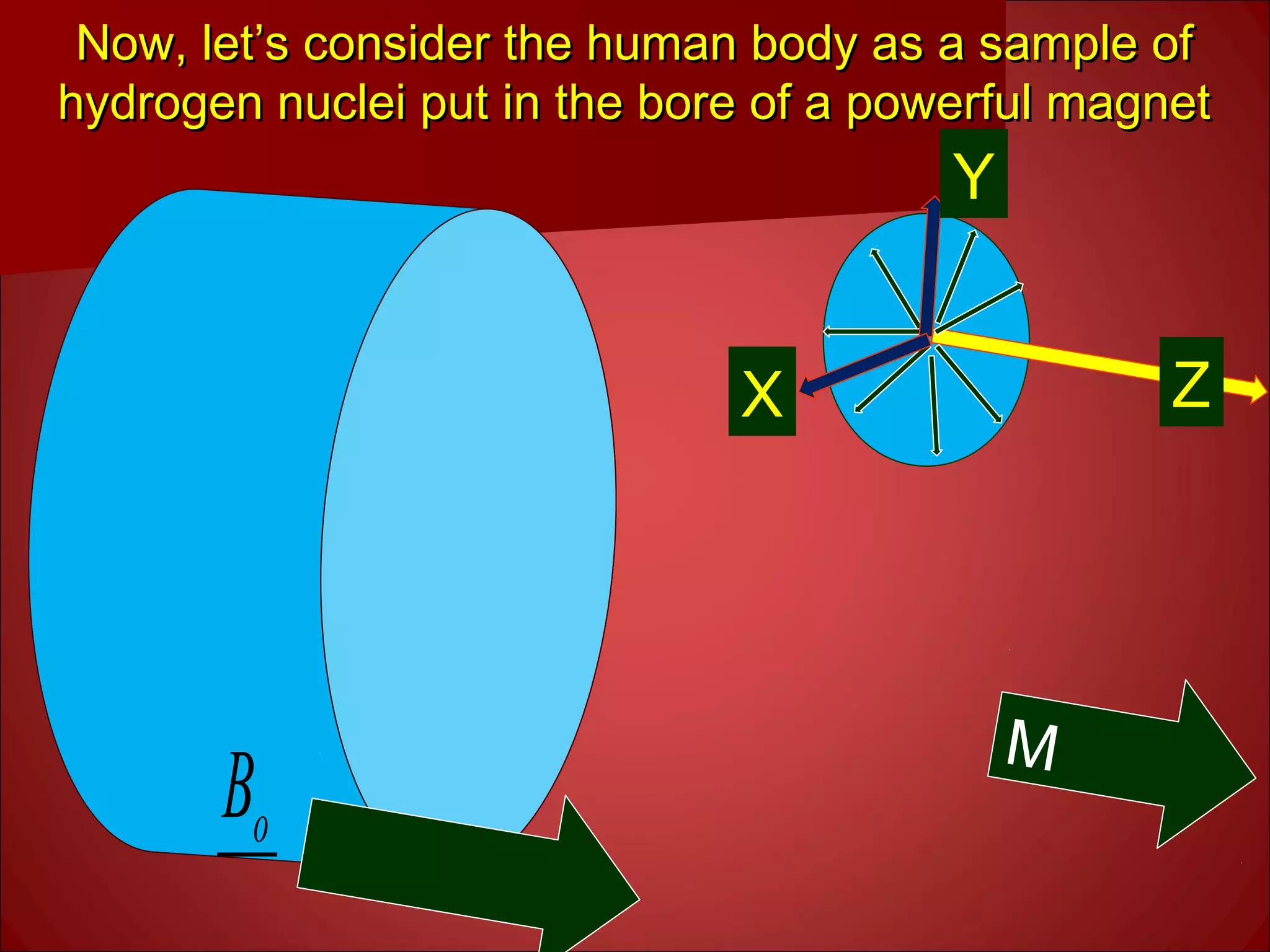
1. The document discusses the basics of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It explains that MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radiofrequency waves to align hydrogen proton spins in the body and produce signals that are used to generate images.
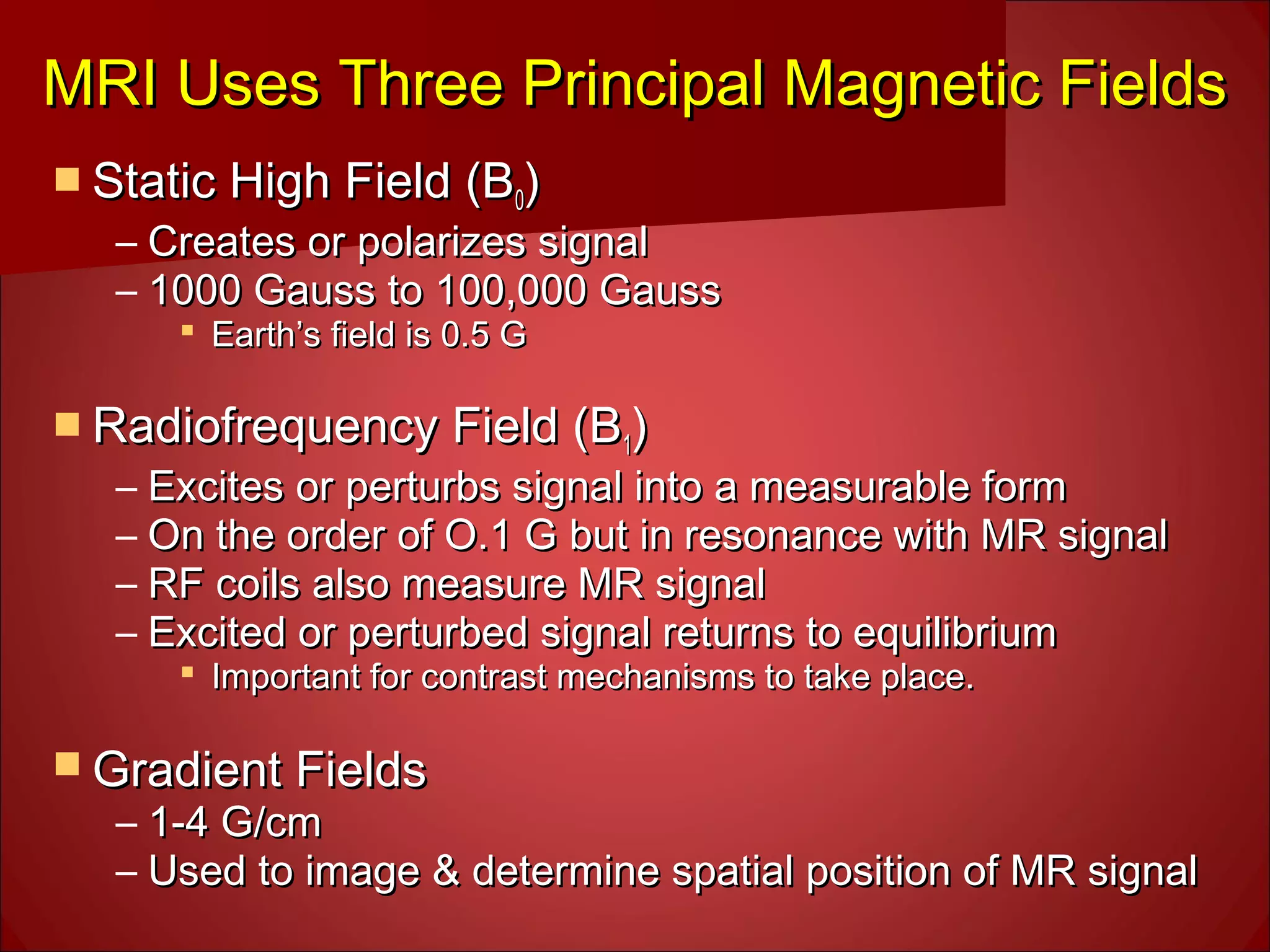
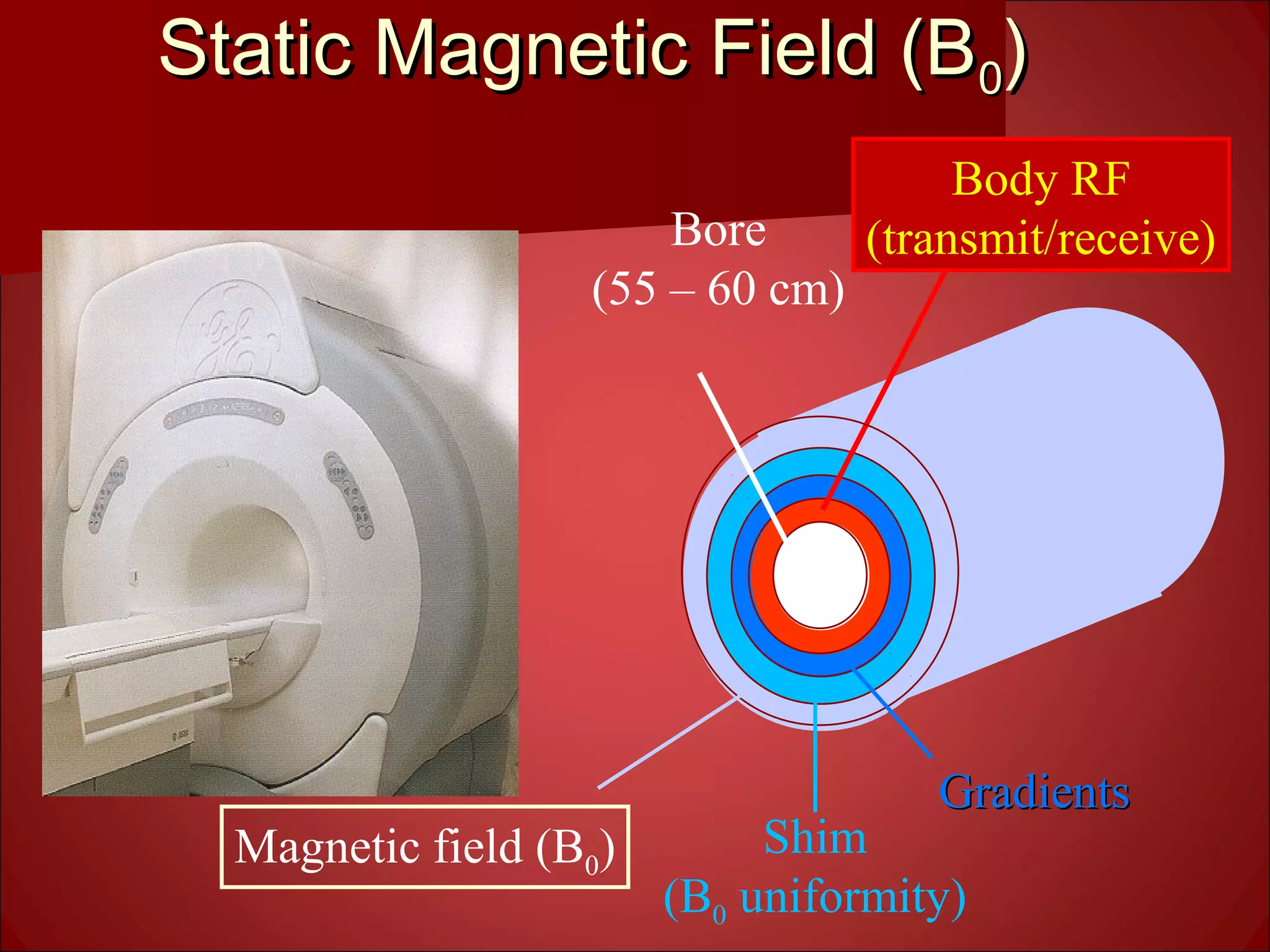
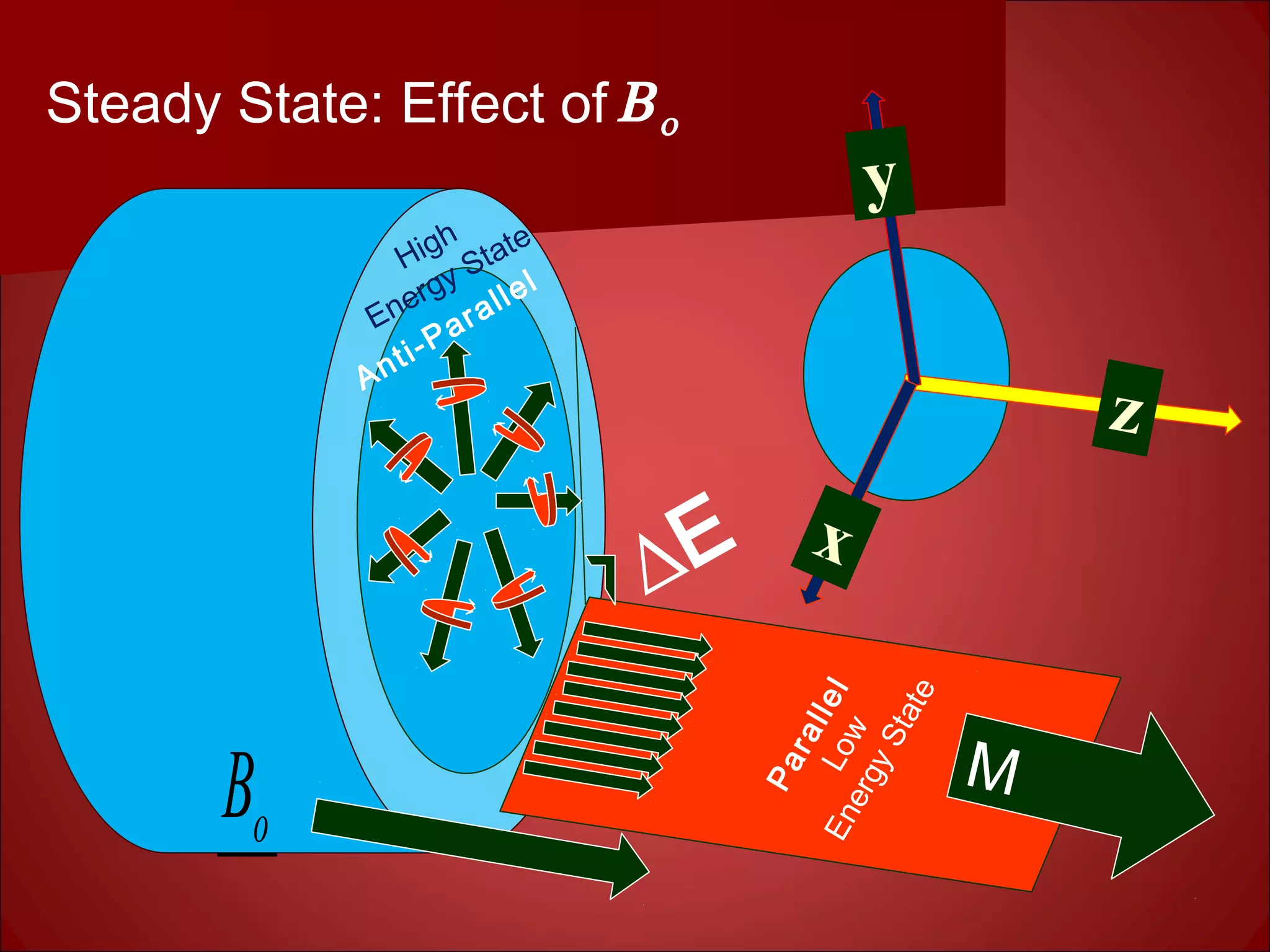
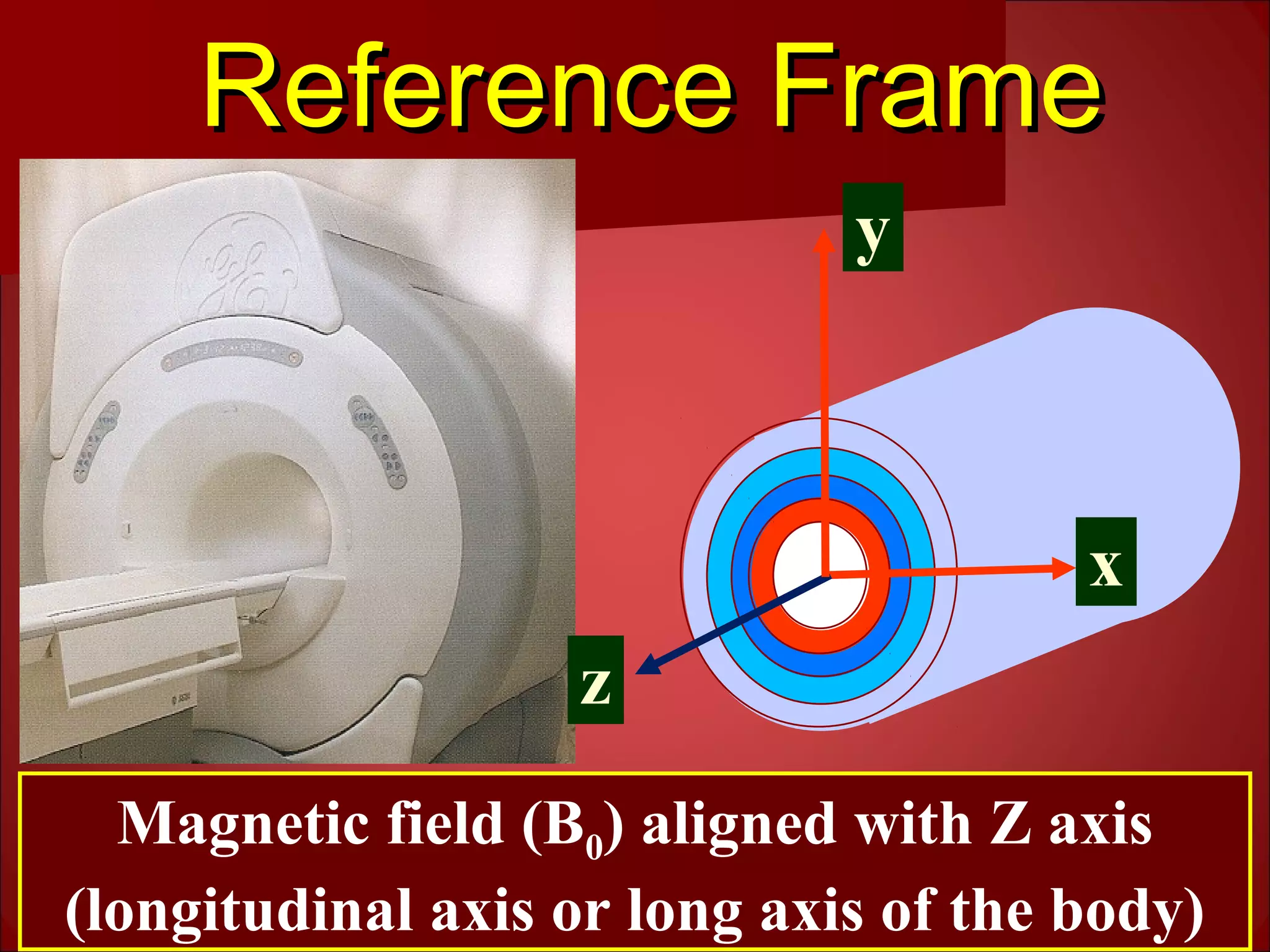
2. The static magnetic field polarizes proton spins. Radiofrequency waves excite the spins, causing them to emit radio signals that are measured to form an image. Gradient magnetic fields are used to spatially encode the signals.
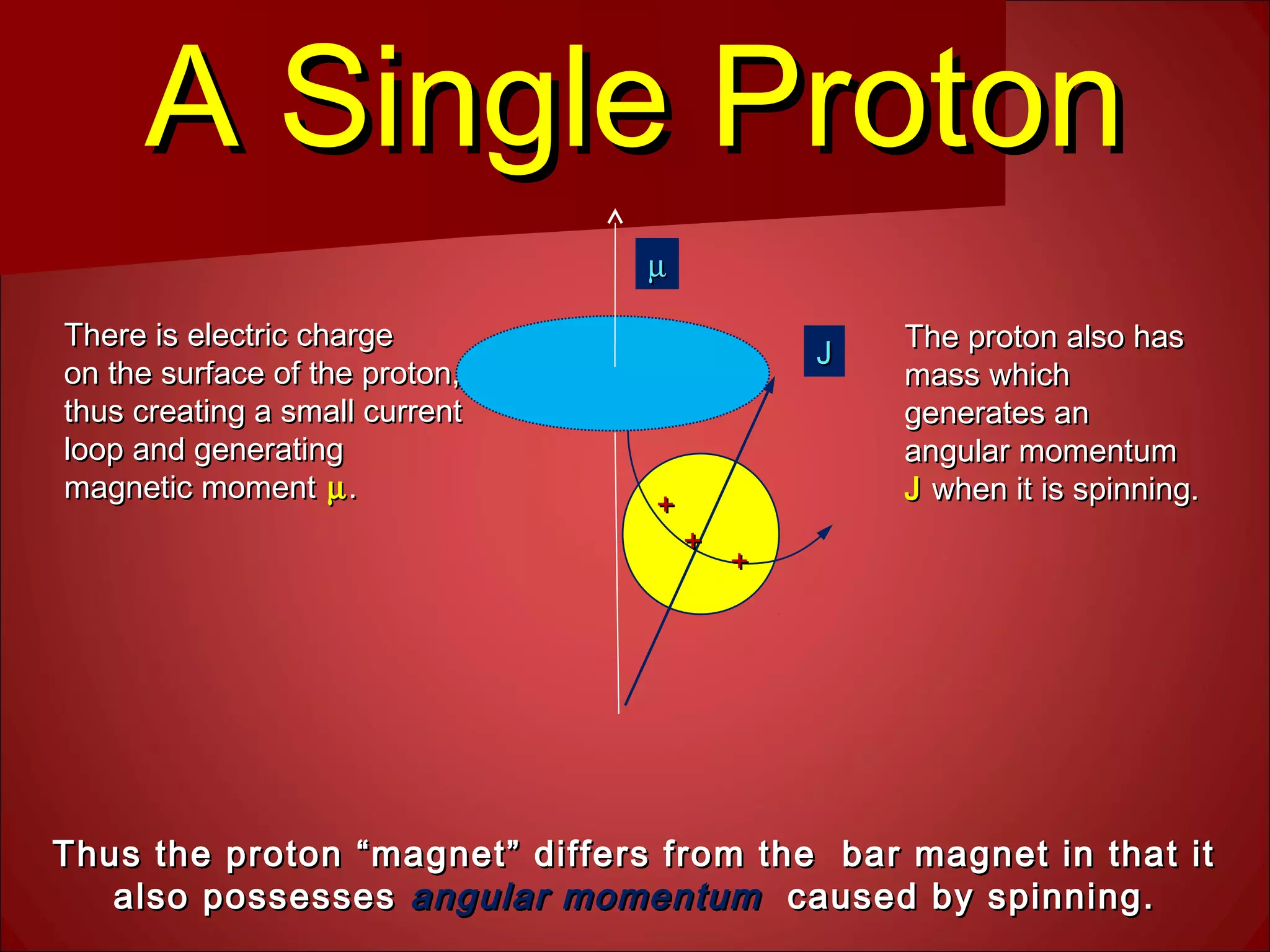
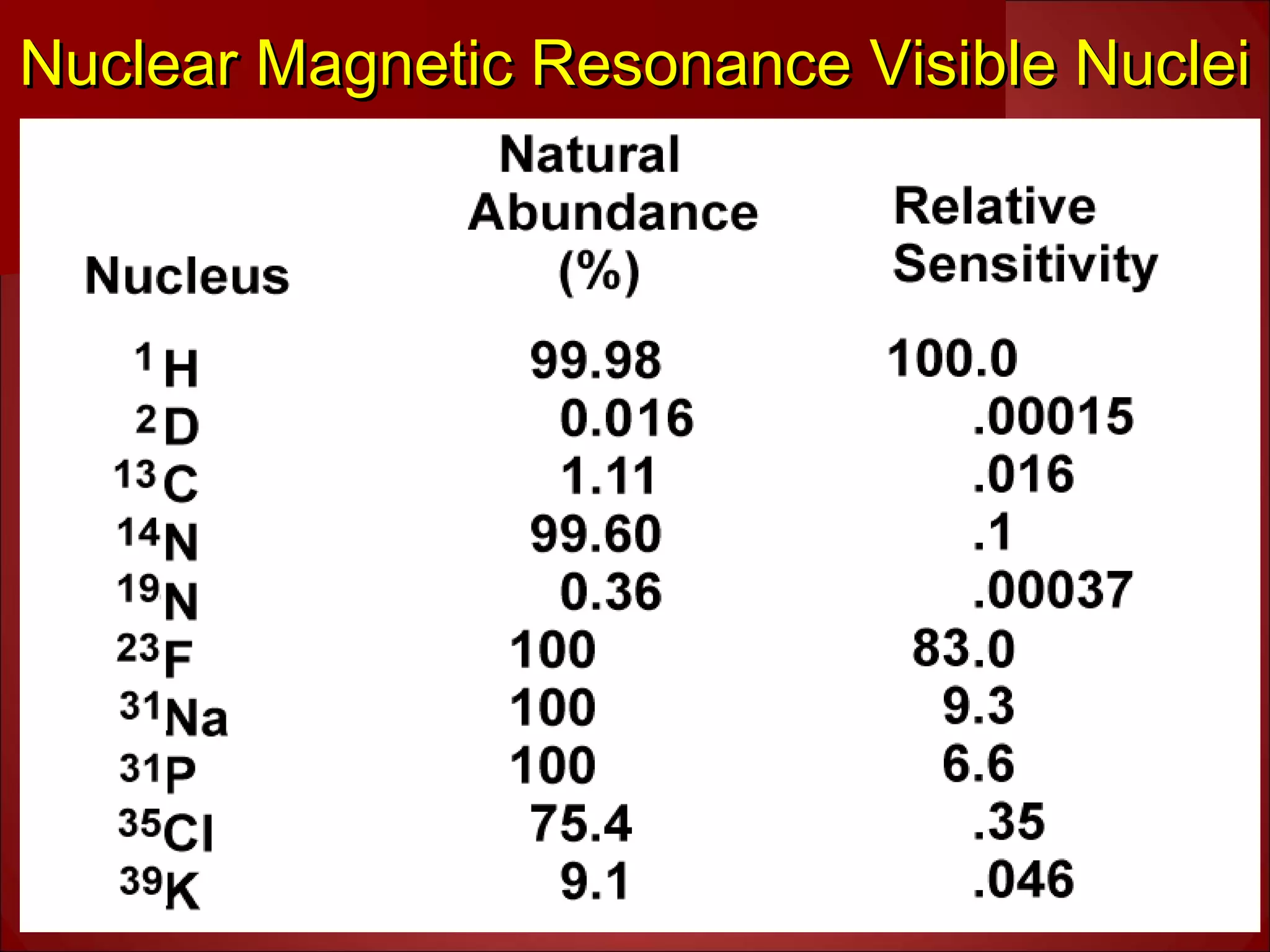
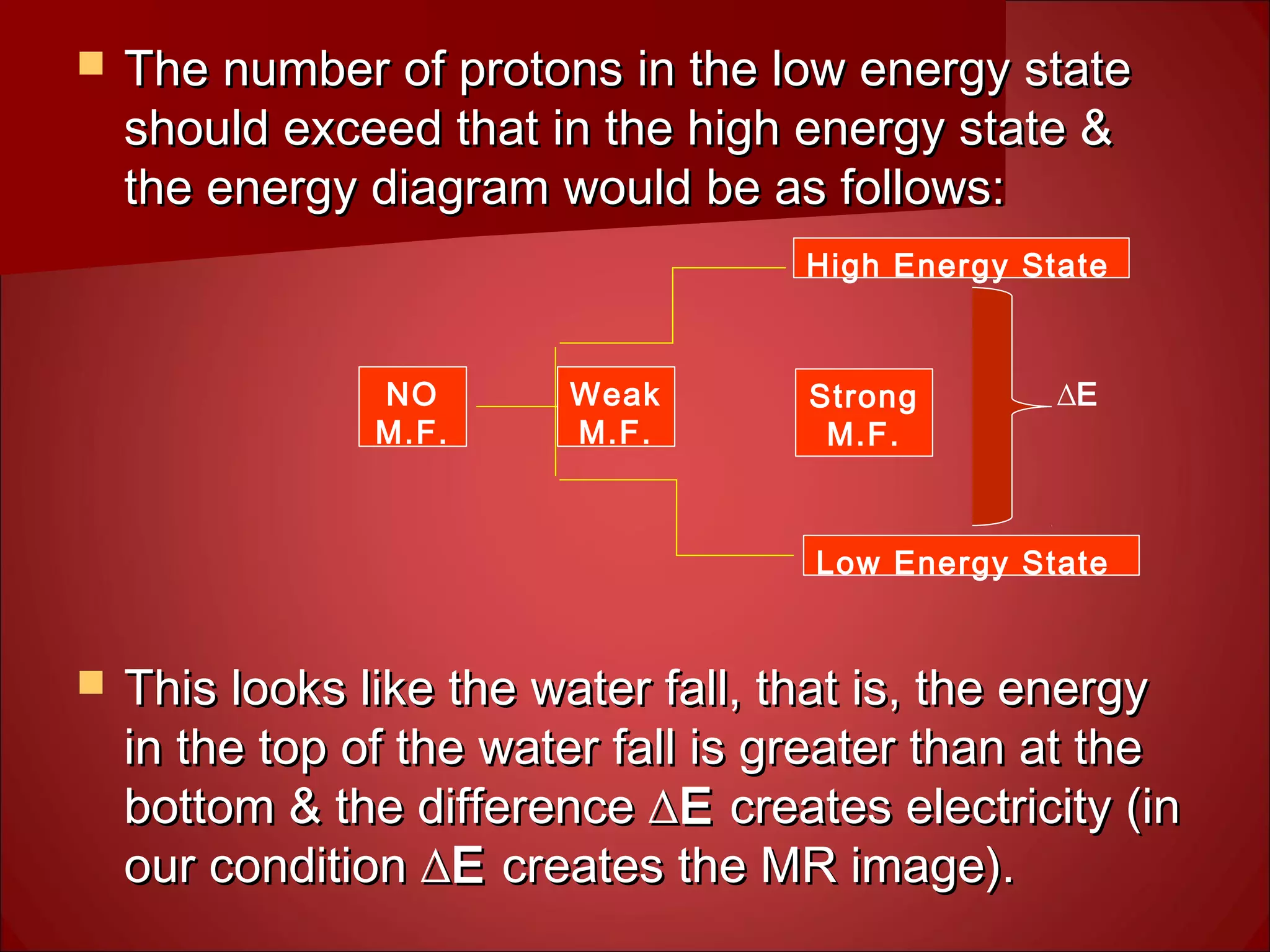
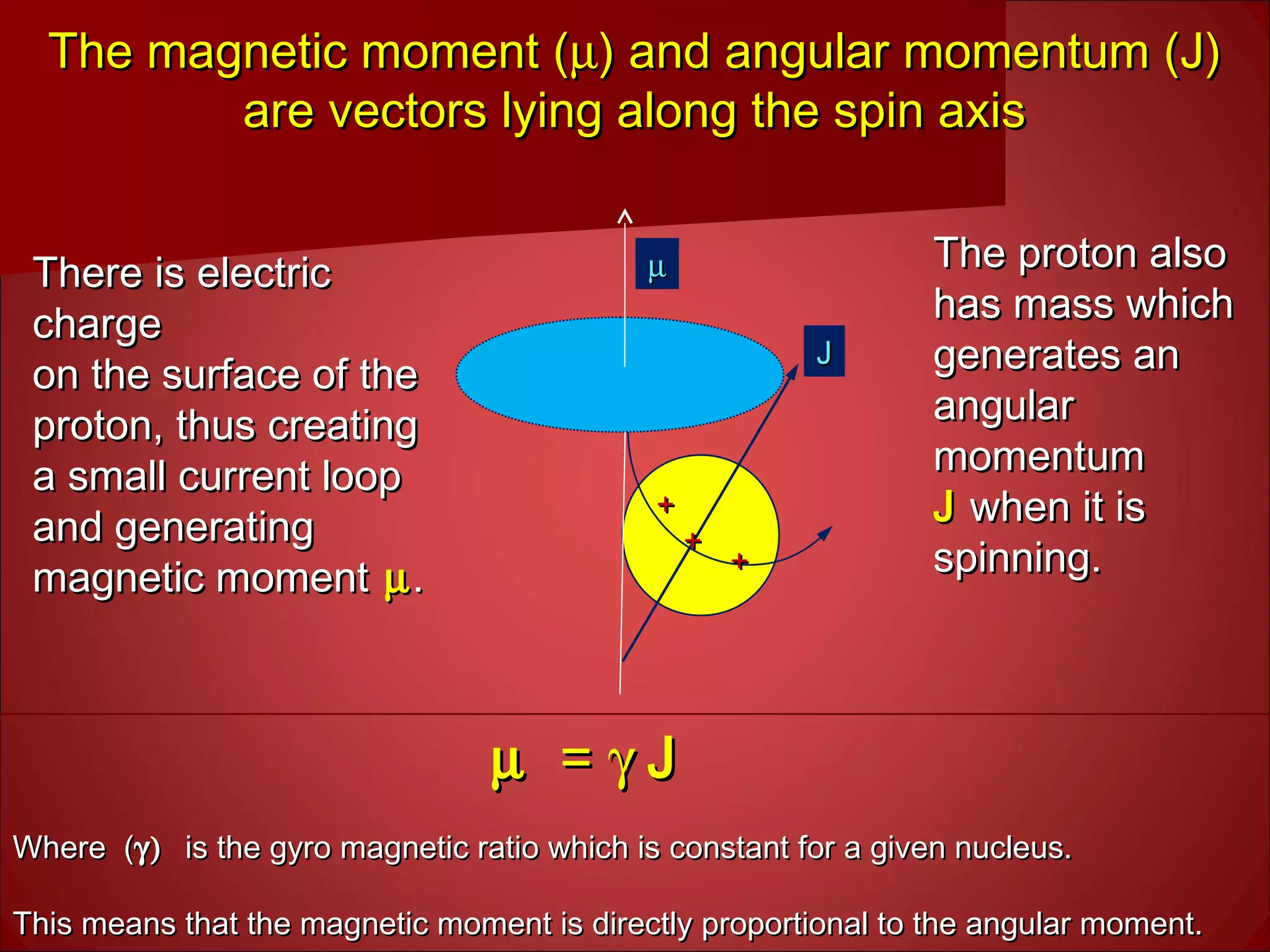
3. Hydrogen protons are ideal for MRI because they are highly abundant in the body and have a simple structure. When placed in a magnetic field, their spins can exist in either a high or low energy state. The energy difference between the states produces the signal measured in


![Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
A pilot look on the events occurring in MRI:A pilot look on the events occurring in MRI:
1)1) Patient is put into the bore of a strongPatient is put into the bore of a strong
magnet.magnet.
2)2) Radiofrequency waves are transmitted intoRadiofrequency waves are transmitted into
the patient for a extremelythe patient for a extremely shortshort time [2~10time [2~10
ms], then turned off.ms], then turned off.
3)3) Radio waves re-transmitted by the patientRadio waves re-transmitted by the patient
are then received in the Receive coil.are then received in the Receive coil.
4)4) Measured RF data are then transformed toMeasured RF data are then transformed to
image.image.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicsofmri-lecture1-151007174910-lva1-app6891/75/Basics-of-mri-lecture-1-3-2048.jpg)