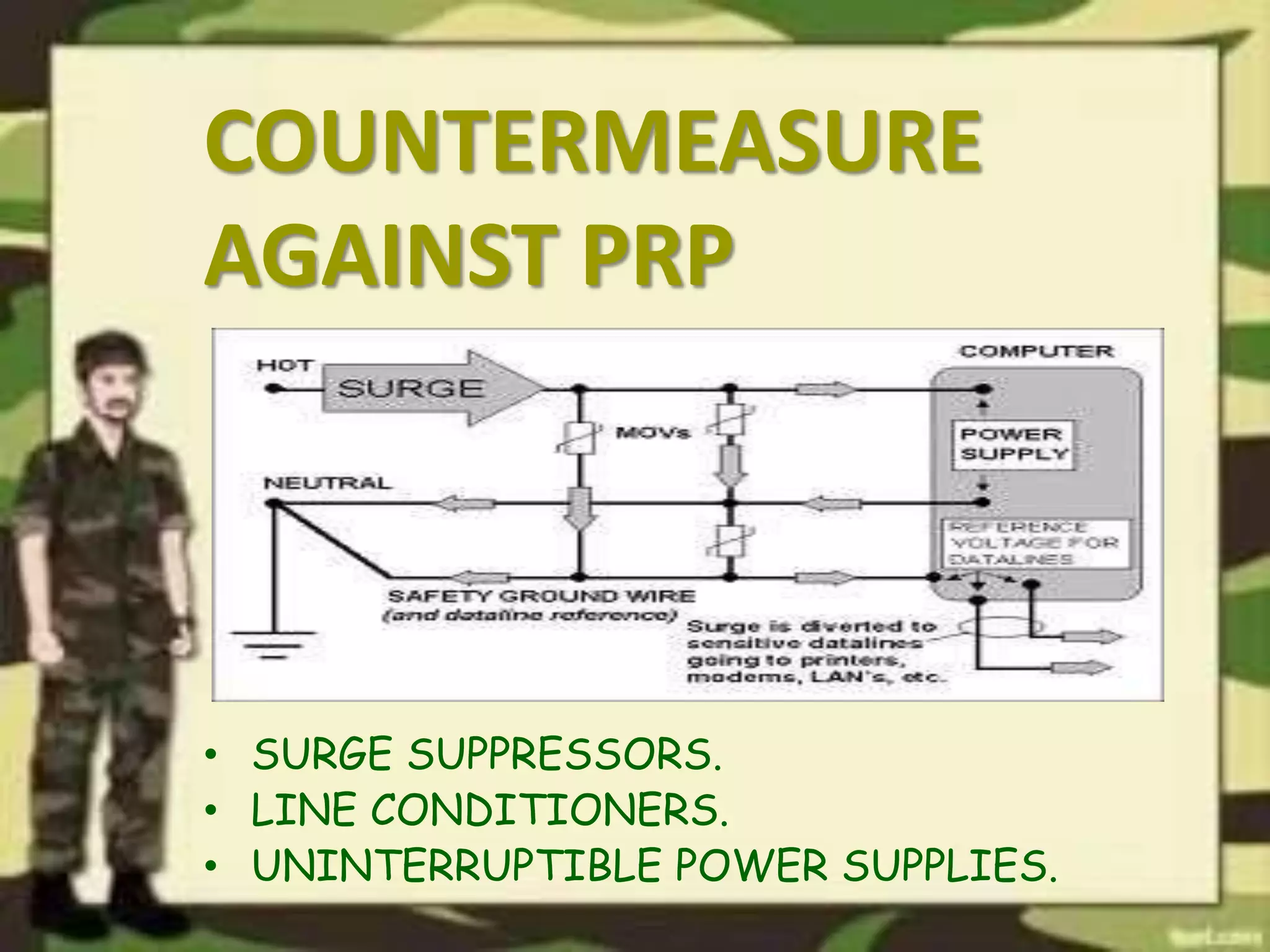
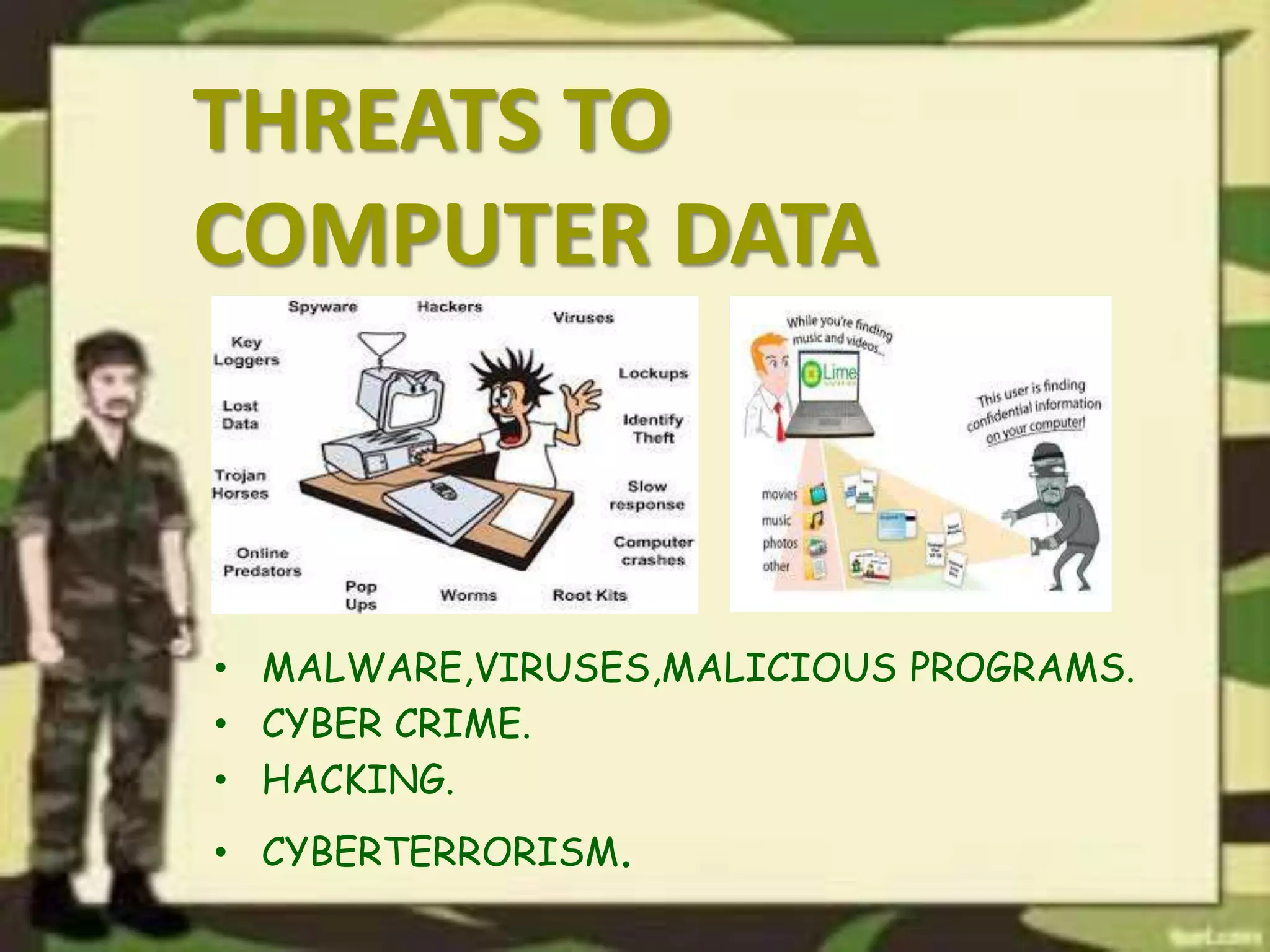
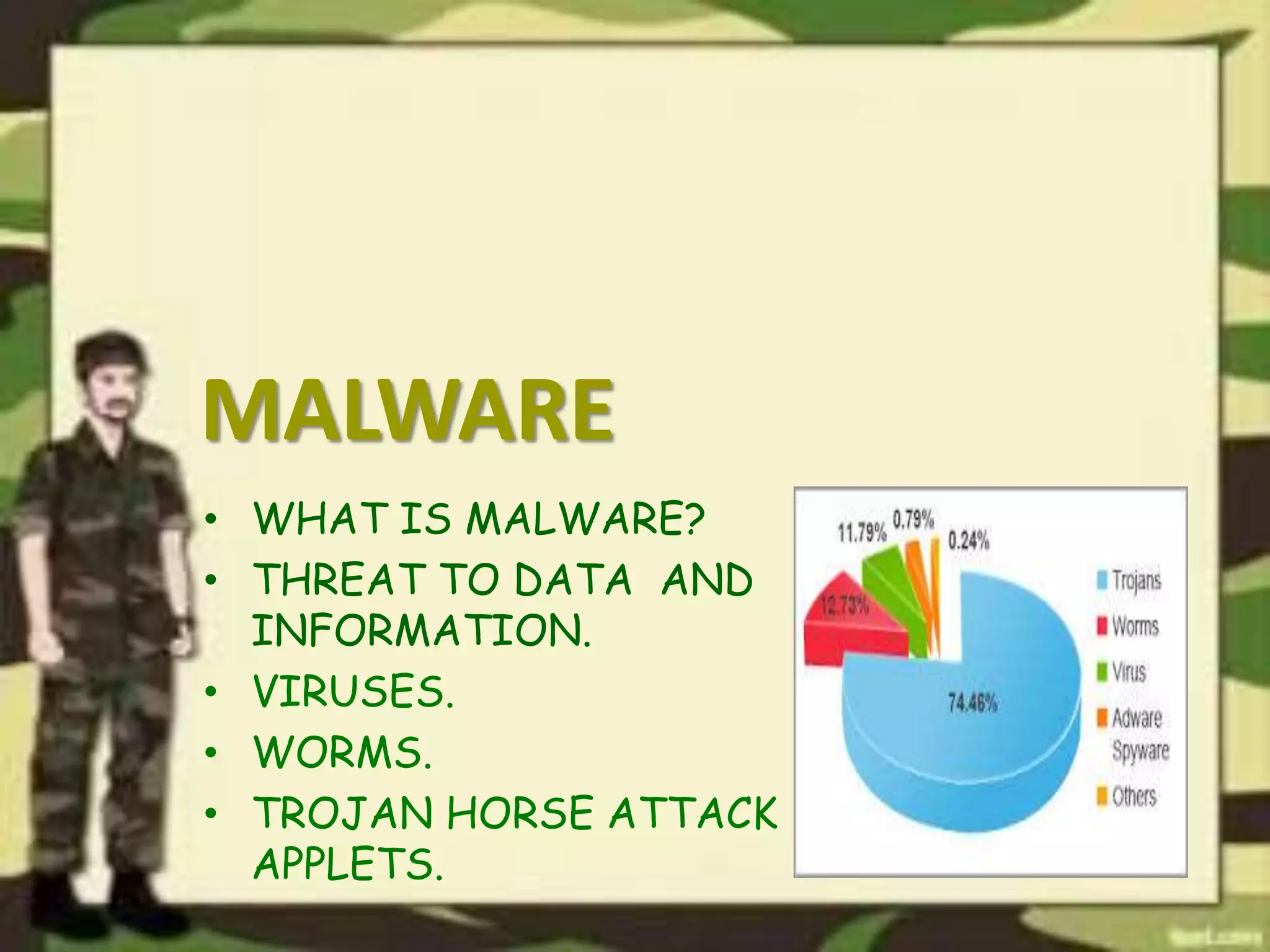
The document outlines a presentation on computer security, detailing various threats to hardware, users, and data, along with countermeasures to mitigate these risks. It covers the basic concepts of computer security, including types of software and the importance of software security in protecting against attacks. Additionally, it discusses vulnerabilities and best practices for maintaining security in computer systems.