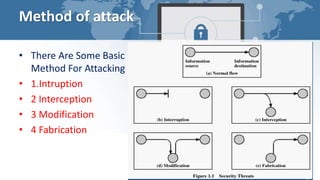
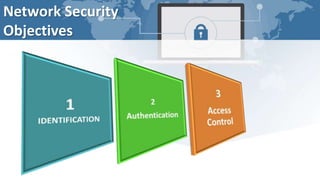
This document provides an introduction to network security. It discusses the history of network security, including early networks in universities and government and the Morris Worm in 1988. The document outlines common security threats like intrusion, interception, and modification and their countermeasures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and education. It defines network security objectives including identification, authentication, and access controls. Finally, the document lists elements of a comprehensive security program and advantages of network security like protecting data, information, and physical computers from external attacks.