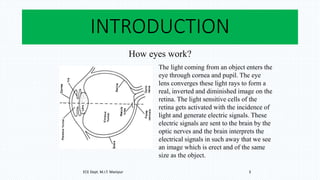
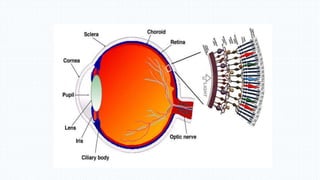
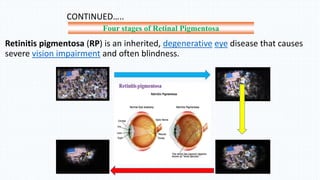
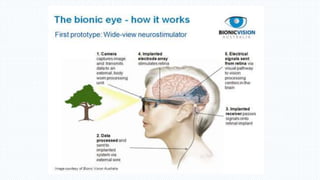
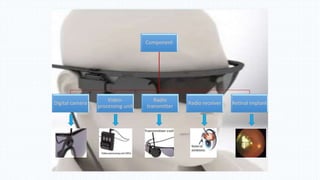
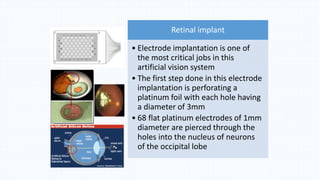
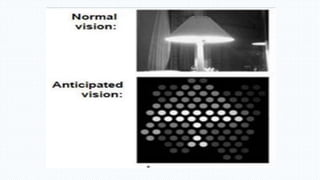
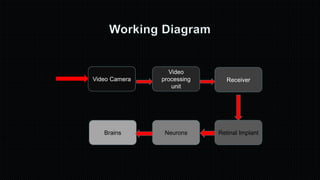
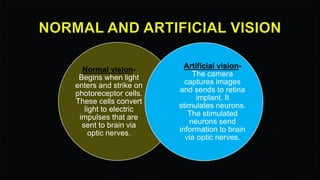
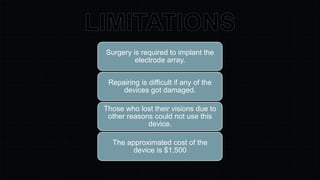
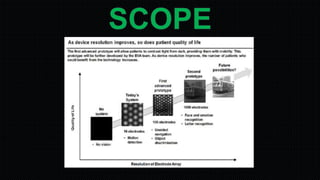
The document discusses the development and implications of artificial and bionic eyes, highlighting their potential to restore vision for individuals with retinal diseases like age-related macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa. It details the technology involved, including a camera system, video processing, and a retinal implant that stimulates the optic nerve, allowing users to recognize objects and read simple text. Despite its advantages, the high cost and challenges of maintenance are noted as significant barriers to accessibility for those in need.