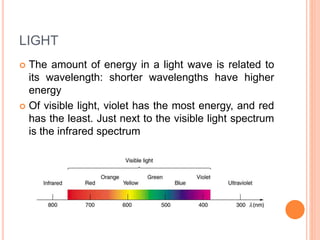
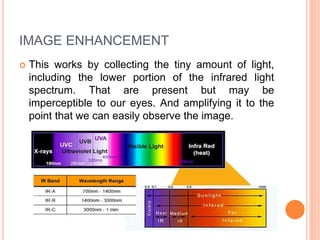
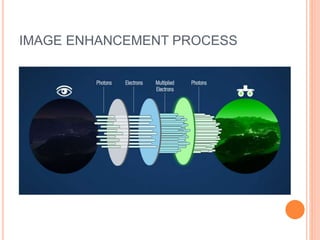
The document outlines night vision technology, explaining its two principal methods: image enhancement and thermal imaging, which operate on different portions of the infrared light spectrum. Image enhancement amplifies low levels of light, while thermal imaging detects heat emitted by objects. The technology is utilized in various applications including military, hunting, security, and wildlife observation.