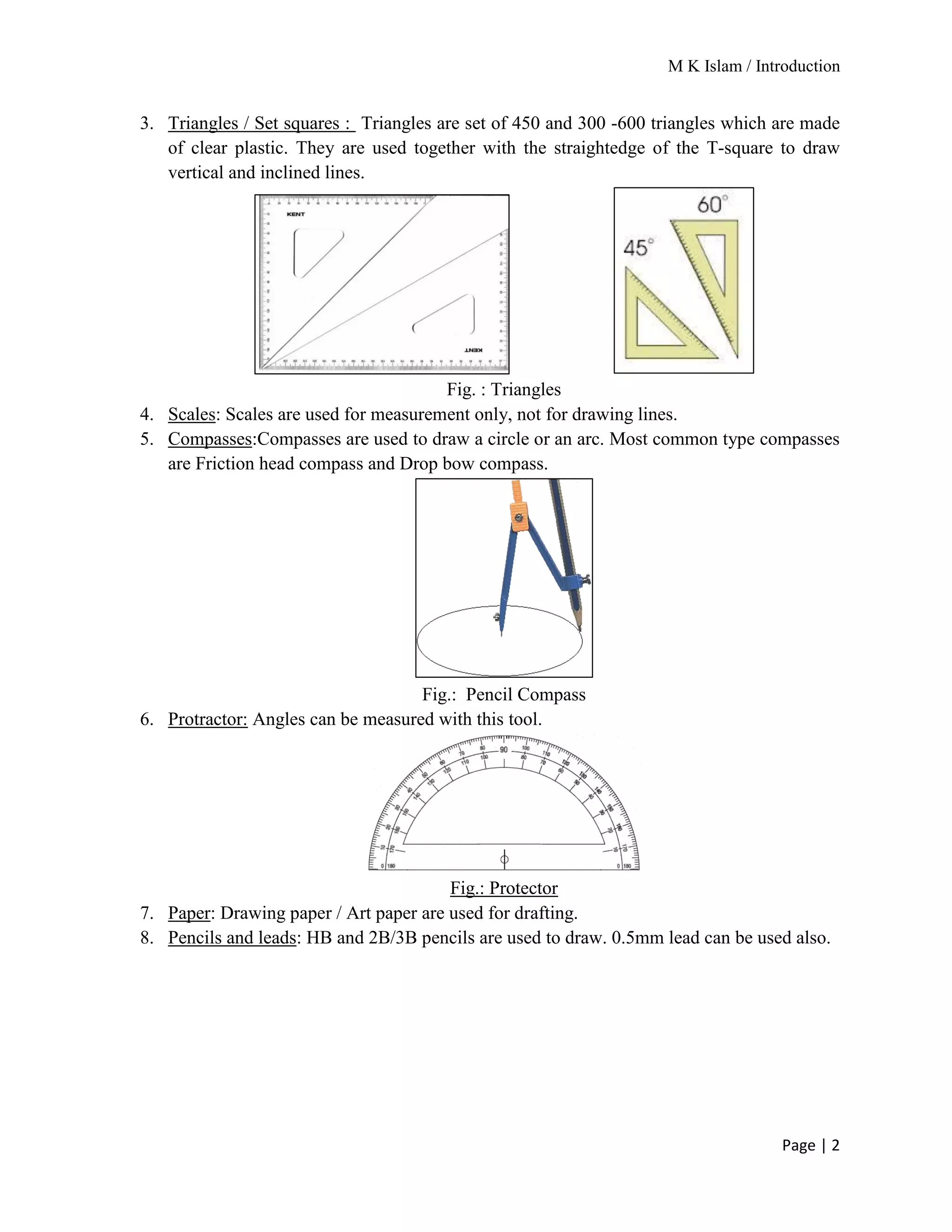
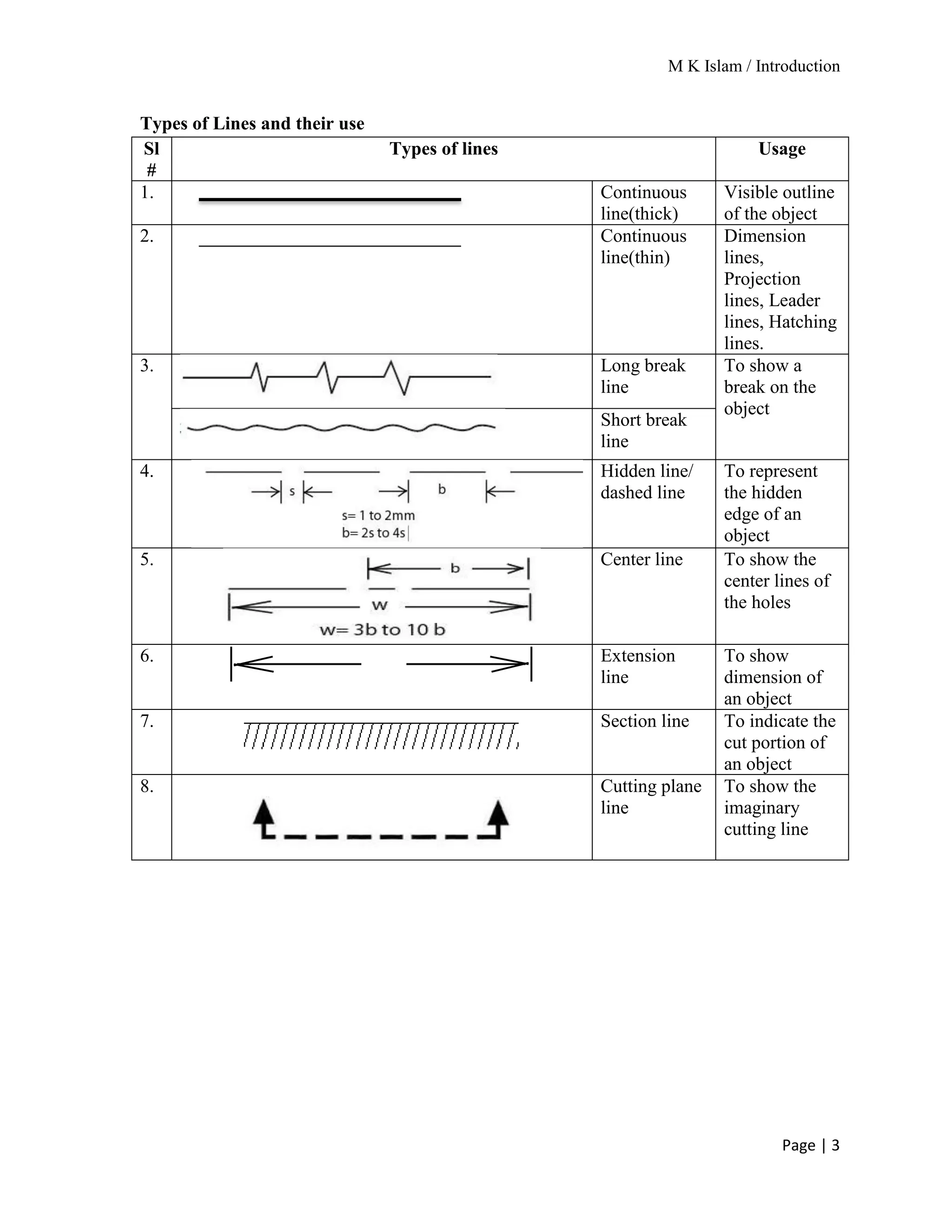
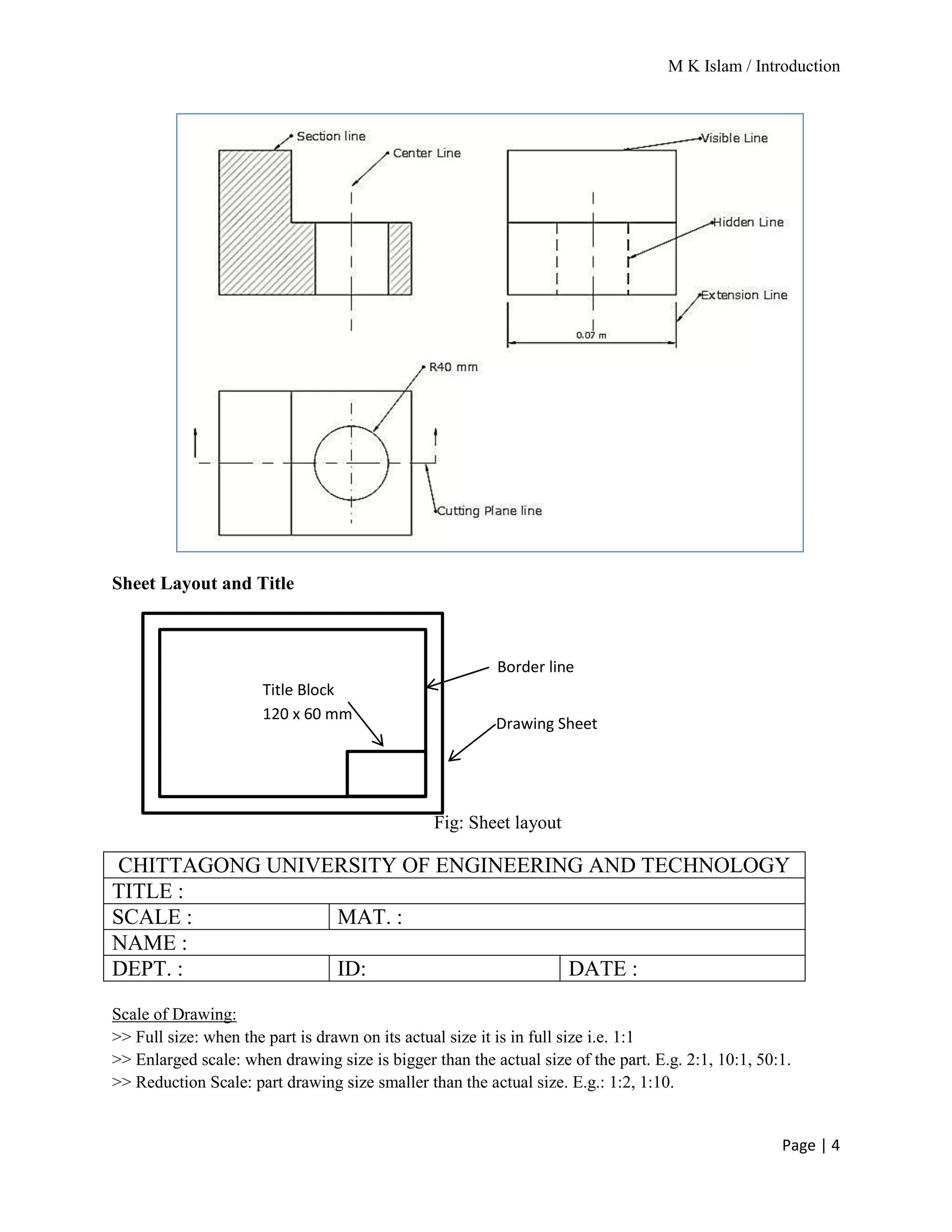
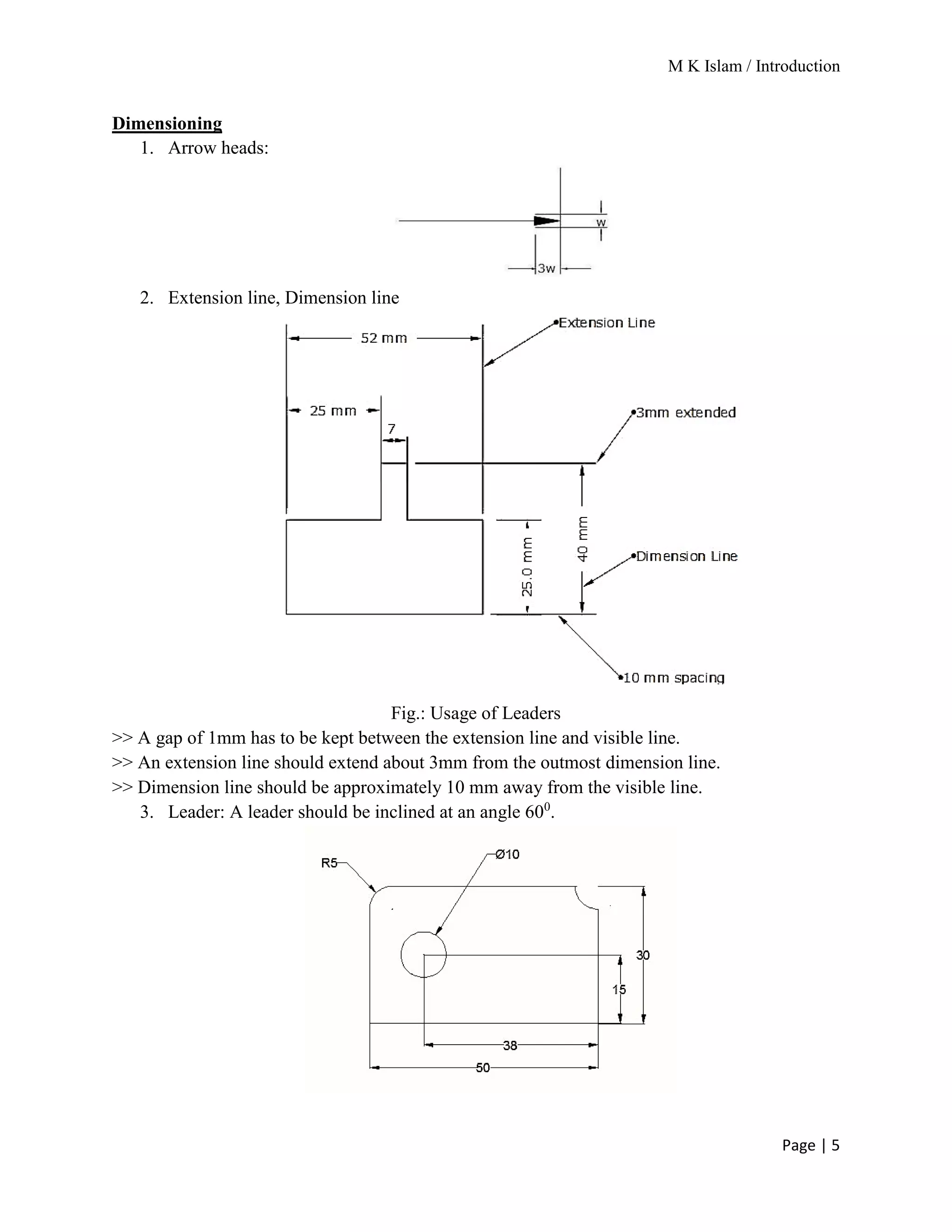
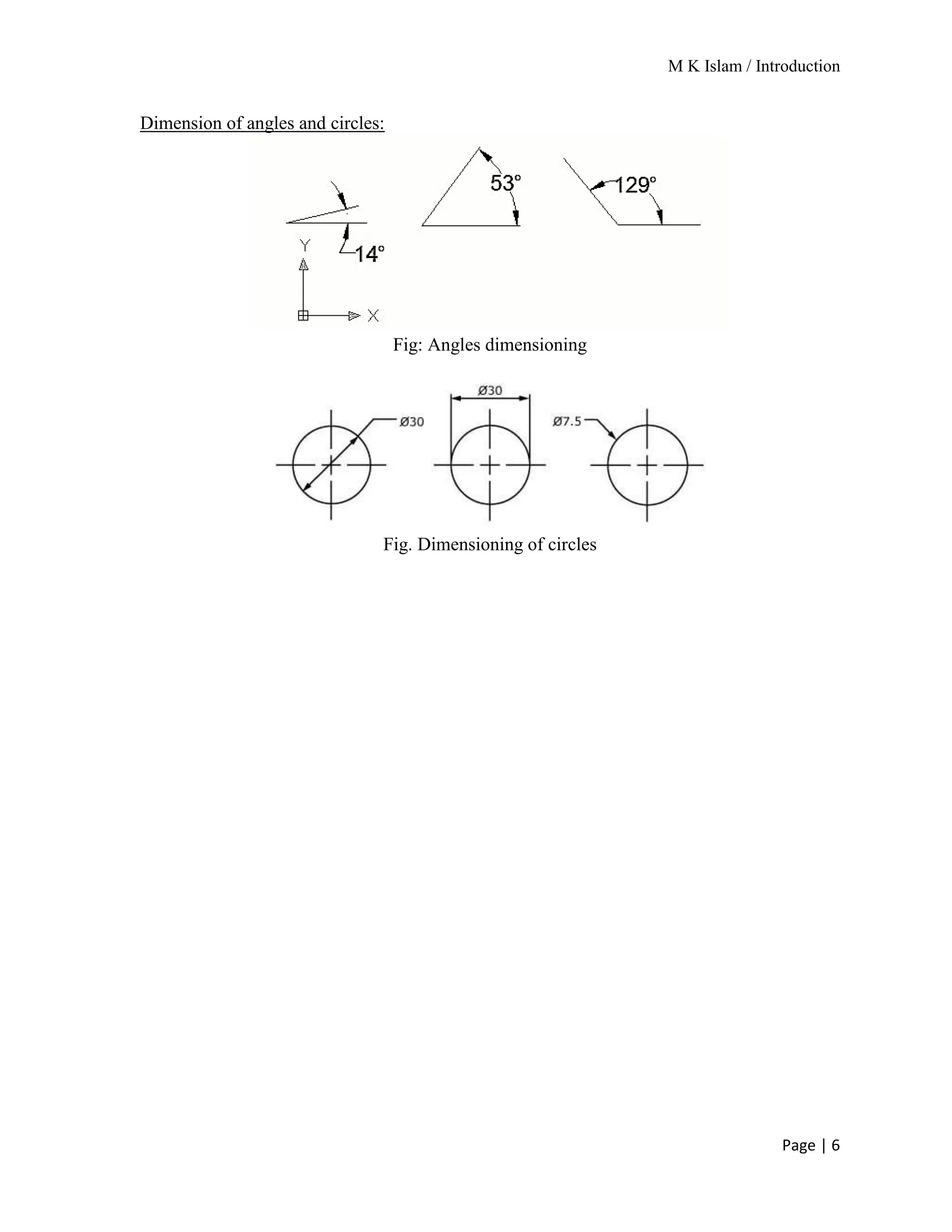
The document provides an overview of mechanical drawing, emphasizing its role as a communication medium in engineering for manufacturing and design. It outlines essential drawing instruments and techniques, including the types of lines used in drawings and the proper layout for dimensioning. Additionally, it details the different scales of drawing and the requirements for dimensioning techniques.