Basic Mathematics contains information about various charts and graphs:
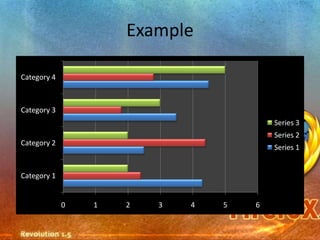
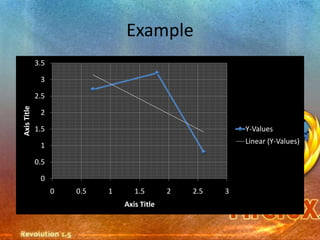
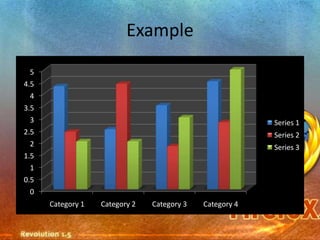
Pie charts and bar charts illustrate proportions and comparisons using wedges or bars divided based on quantities. Scatter plots show the relationship between two variables through data points on Cartesian axes. Histograms bin categorical data into intervals to show distributions, while line graphs connect data points over time or categories. Pictograms represent quantities pictorially through symbols.