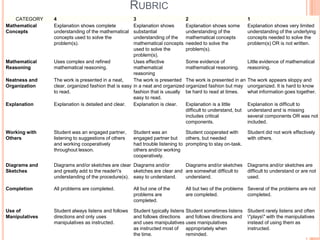
This document provides guidance for teaching addition and subtraction to elementary school students. It recommends having students write math problems for peers to solve and incorporating math into other subjects like language arts. The document also lists technologies and apps that can be used, such as Kidspiration and coolmath-games.com. It provides tips for English language learners and students with disabilities. Teachers should assess student knowledge through board work, tests, and allowing students to teach addition and subtraction problems.