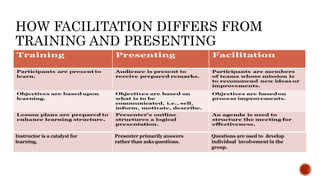
The document discusses basic facilitation skills. It explains that a facilitator leads discussions but does not provide answers, instead acting as a tour guide. Effective facilitation relies on skills like active listening, summarizing, and recognizing progress. Facilitation differs from training in that the facilitator asks questions to develop involvement while presenters primarily answer questions. Tips are provided for facilitating discussions, communicating effectively, and handling difficult team members.