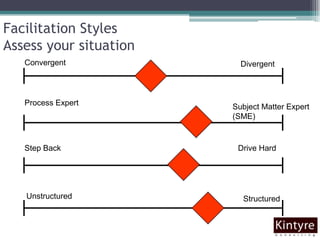
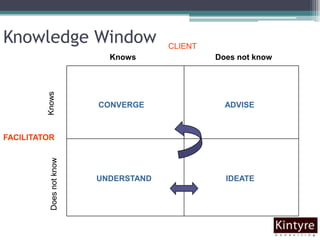
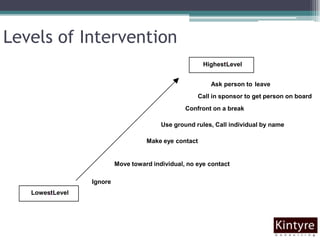
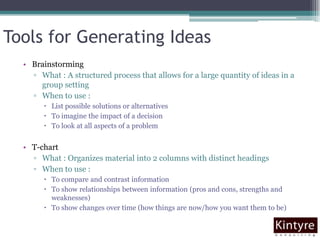
This document provides an overview of facilitation best practices. It discusses the role of the facilitator in guiding discussion and managing group dynamics. Key parts of preparation include creating an agenda with objectives and deliverables. During sessions, the facilitator should ask questions to guide participation, capture content, and deal with challenging behaviors diplomatically. A variety of tools are presented for generating, organizing, and evaluating ideas as a group. The overall goal is for the facilitator to help diverse participants develop shared solutions efficiently.