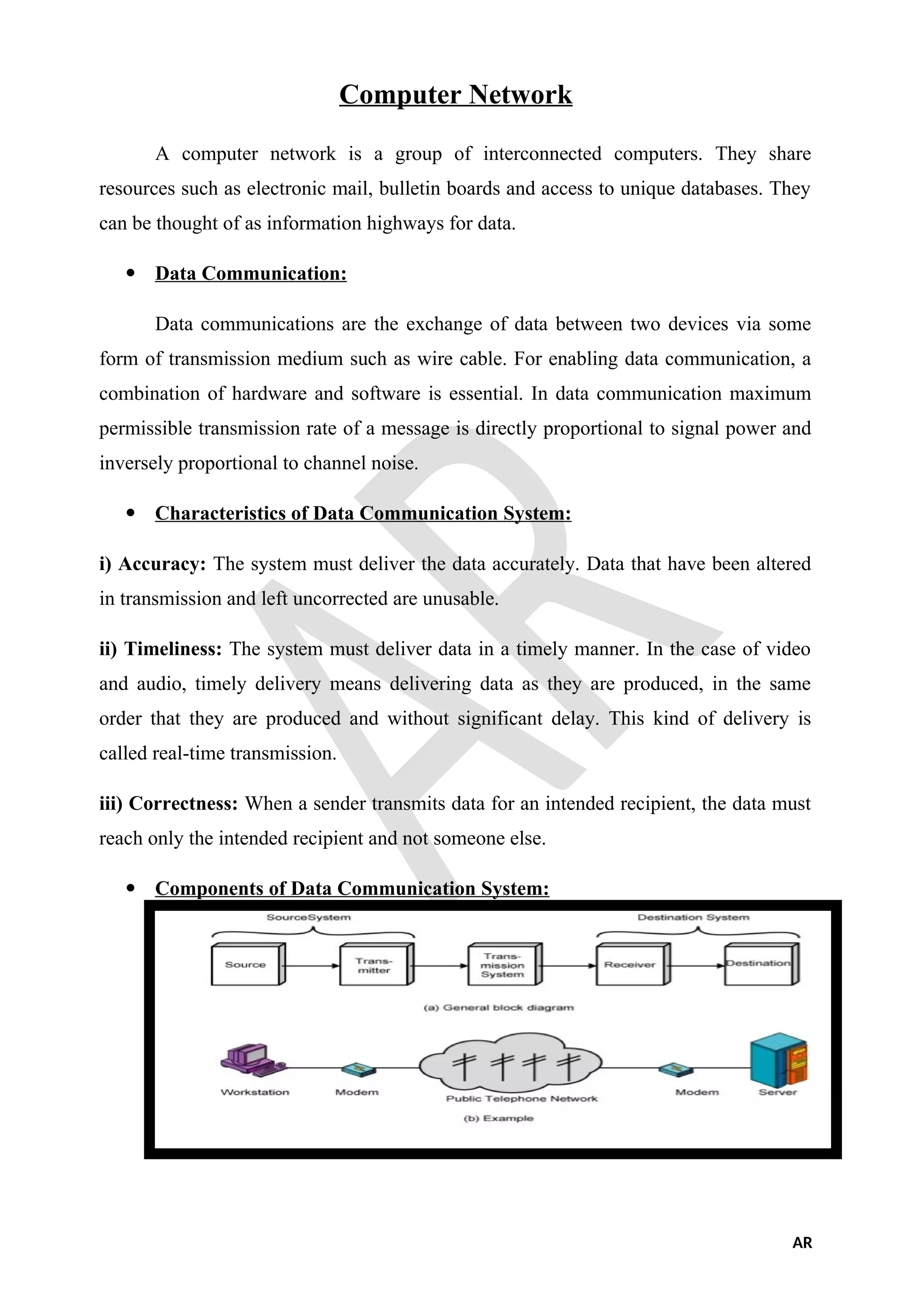
A computer network is a collection of interconnected computers that share resources like email and databases, functioning as information highways for data exchange. Data communication involves the exchange of information between devices through transmission mediums, emphasized by the accuracy, timeliness, and correctness of the conveyed data. The system comprises various components, including terminals, communication processors, telecommunication channels, host computers, and relevant software which facilitate the effective transmission and reception of data.