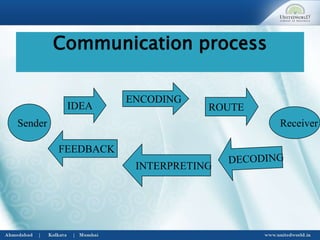
This document discusses barriers to effective communication. It begins by defining communication and outlining the basic communication process. It then examines several types of barriers, including environmental barriers, personal barriers, administrative/financial barriers, and time barriers. Specific barriers can occur due to issues with the sender, such as poor planning or using the wrong language. Receiver barriers include inattention or different perceptions than the sender. Barriers common to both include a lack of shared understandings or information overload. The document concludes by recommending ways to overcome these barriers, such as eliminating differences in perception, active listening, and choosing the proper media.