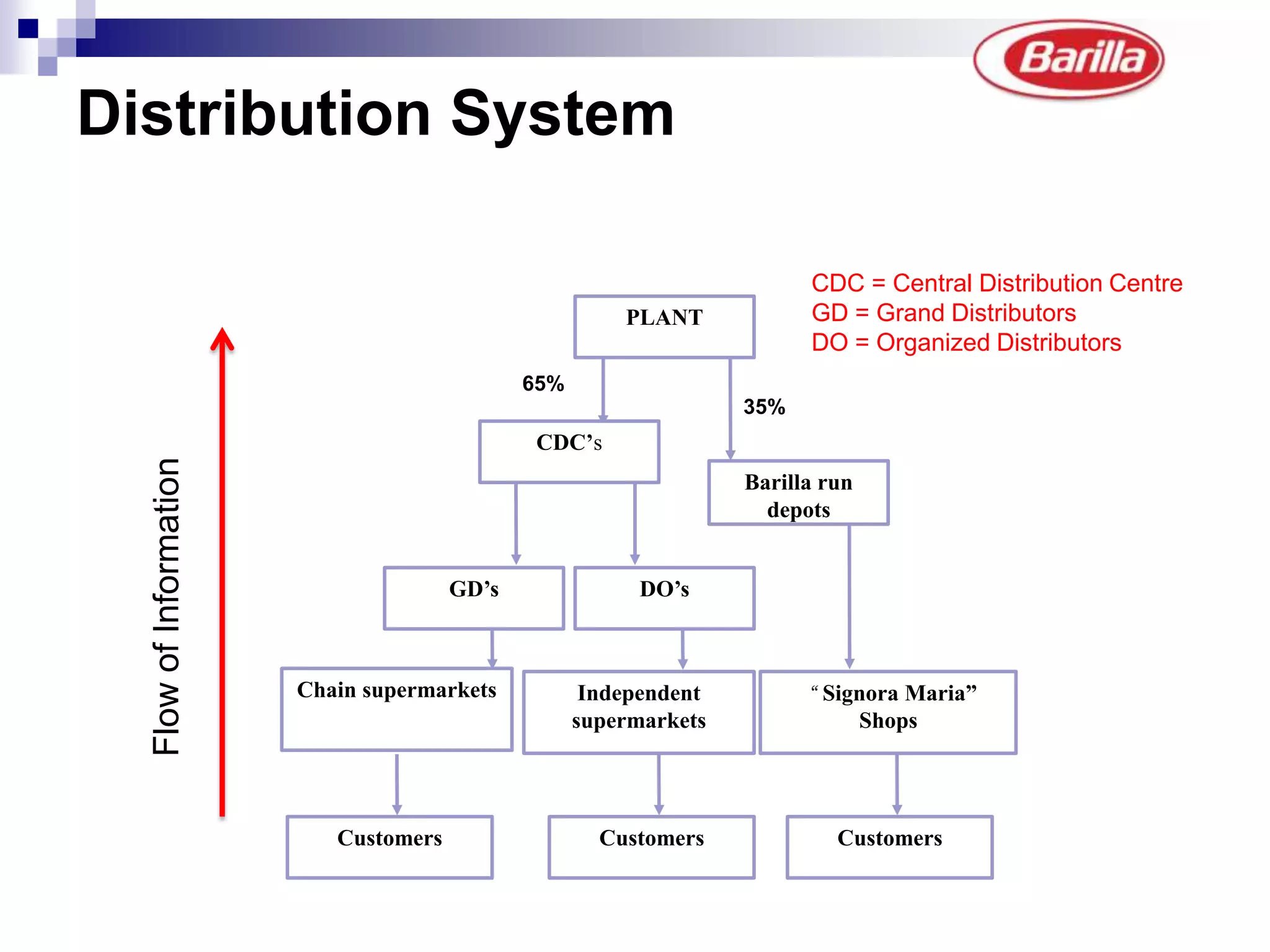
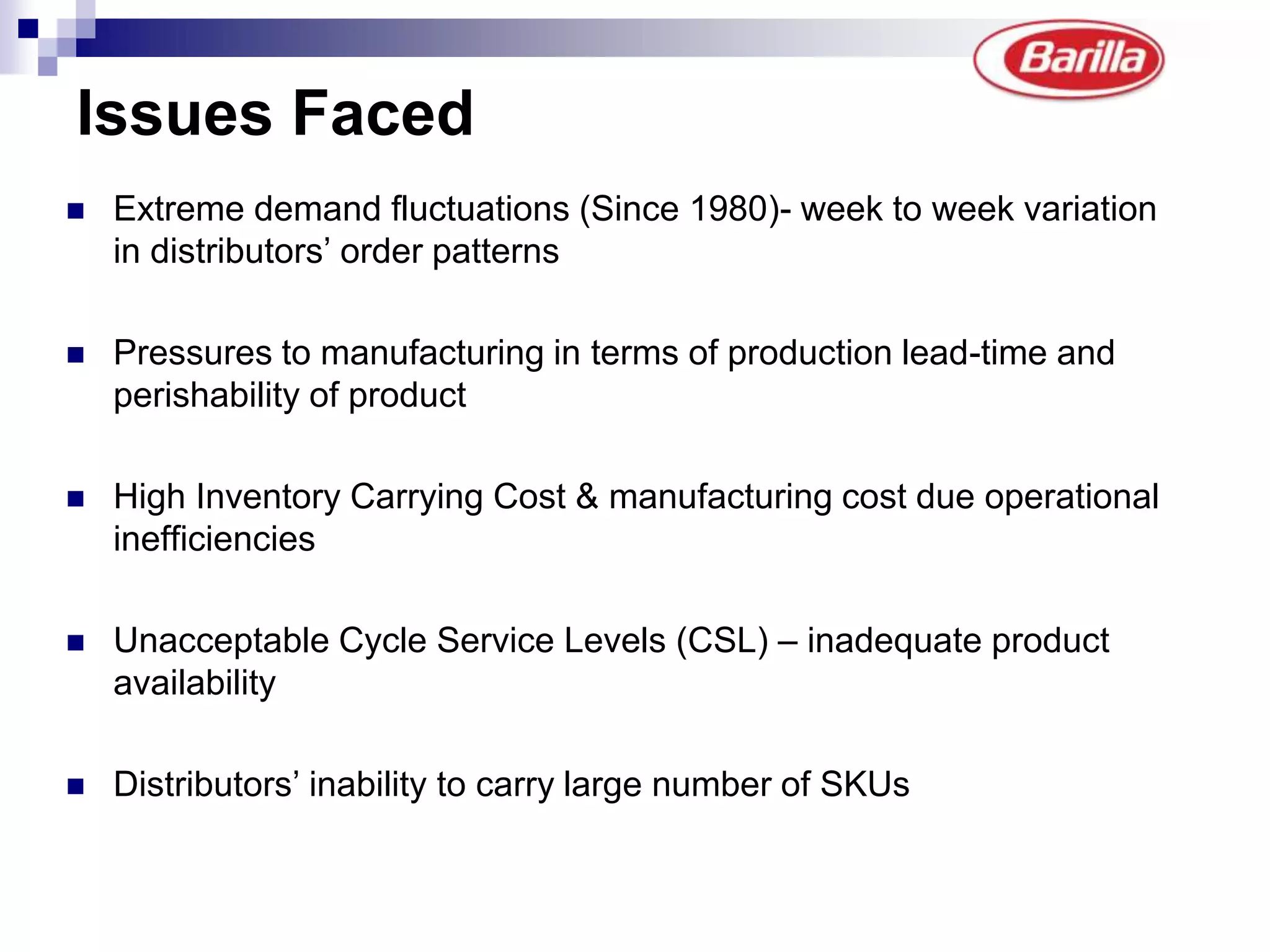
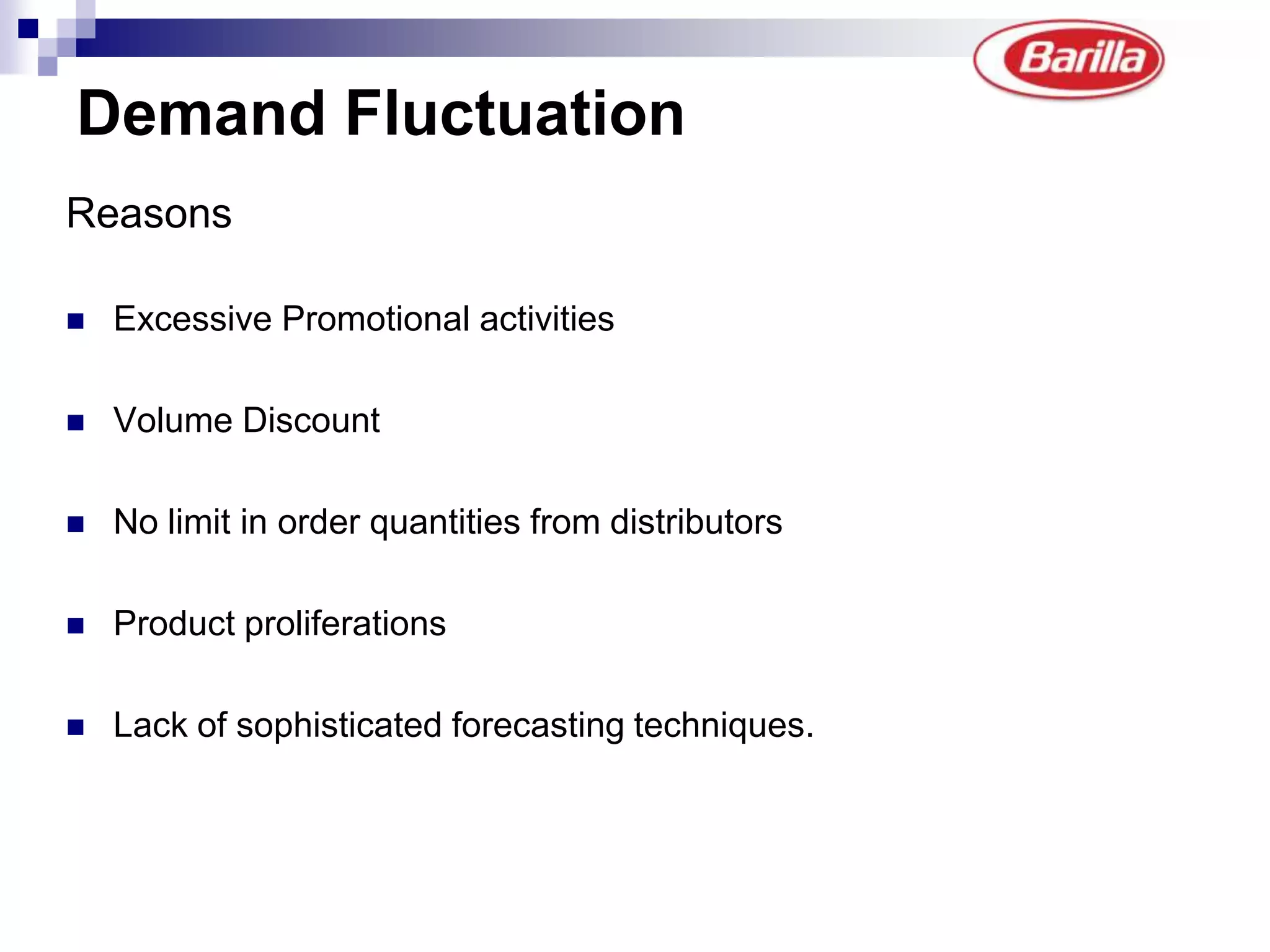
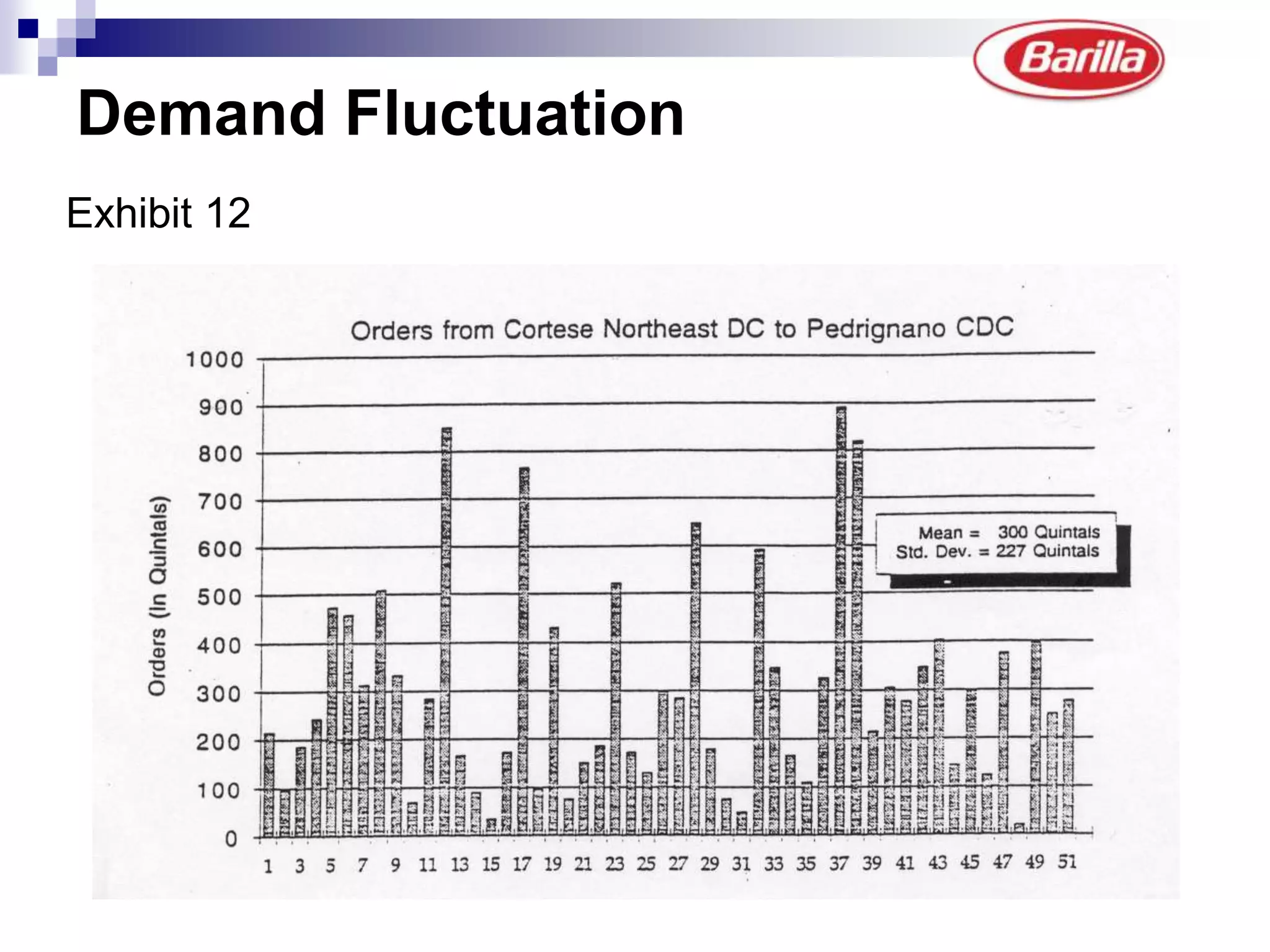
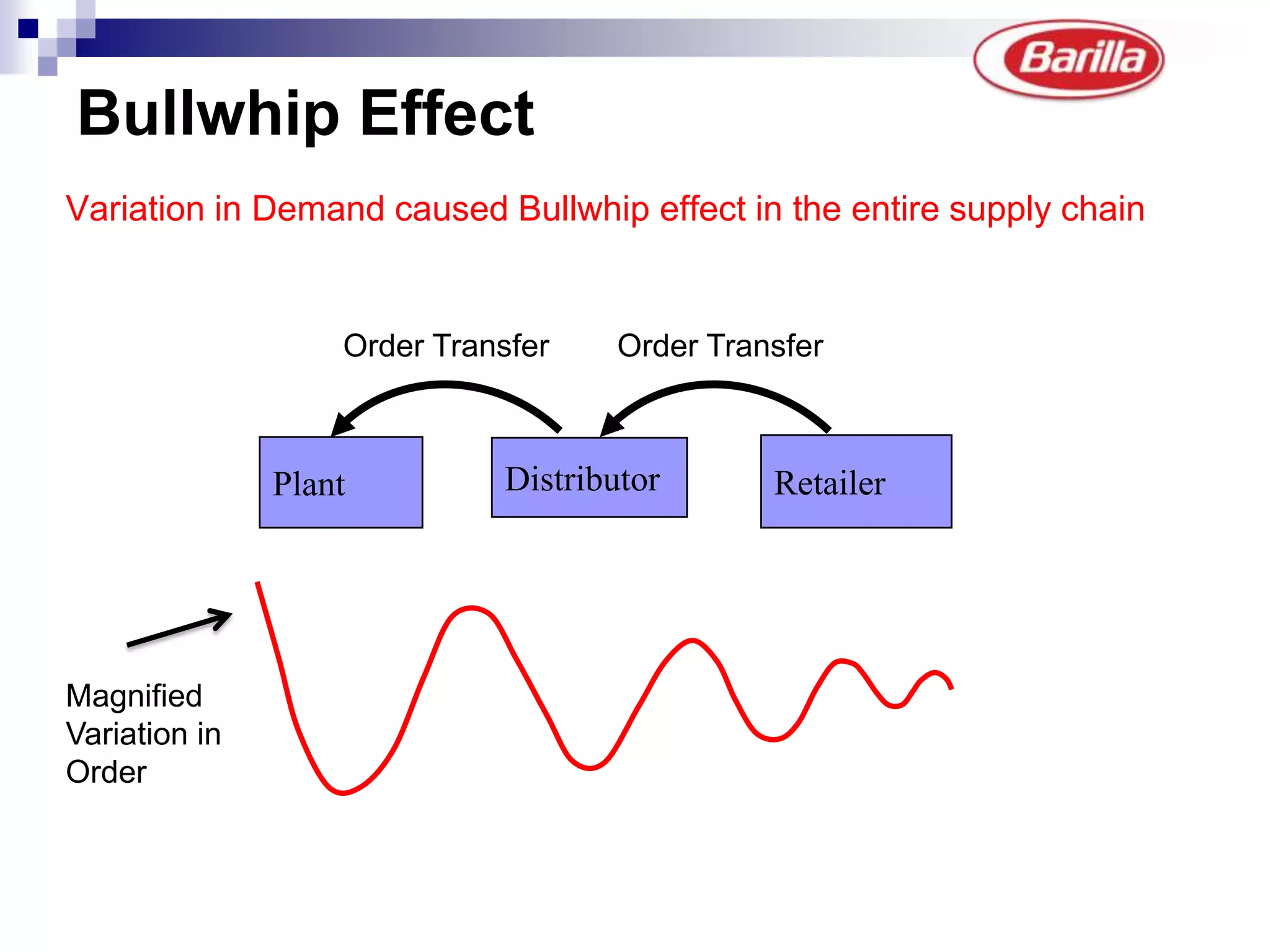
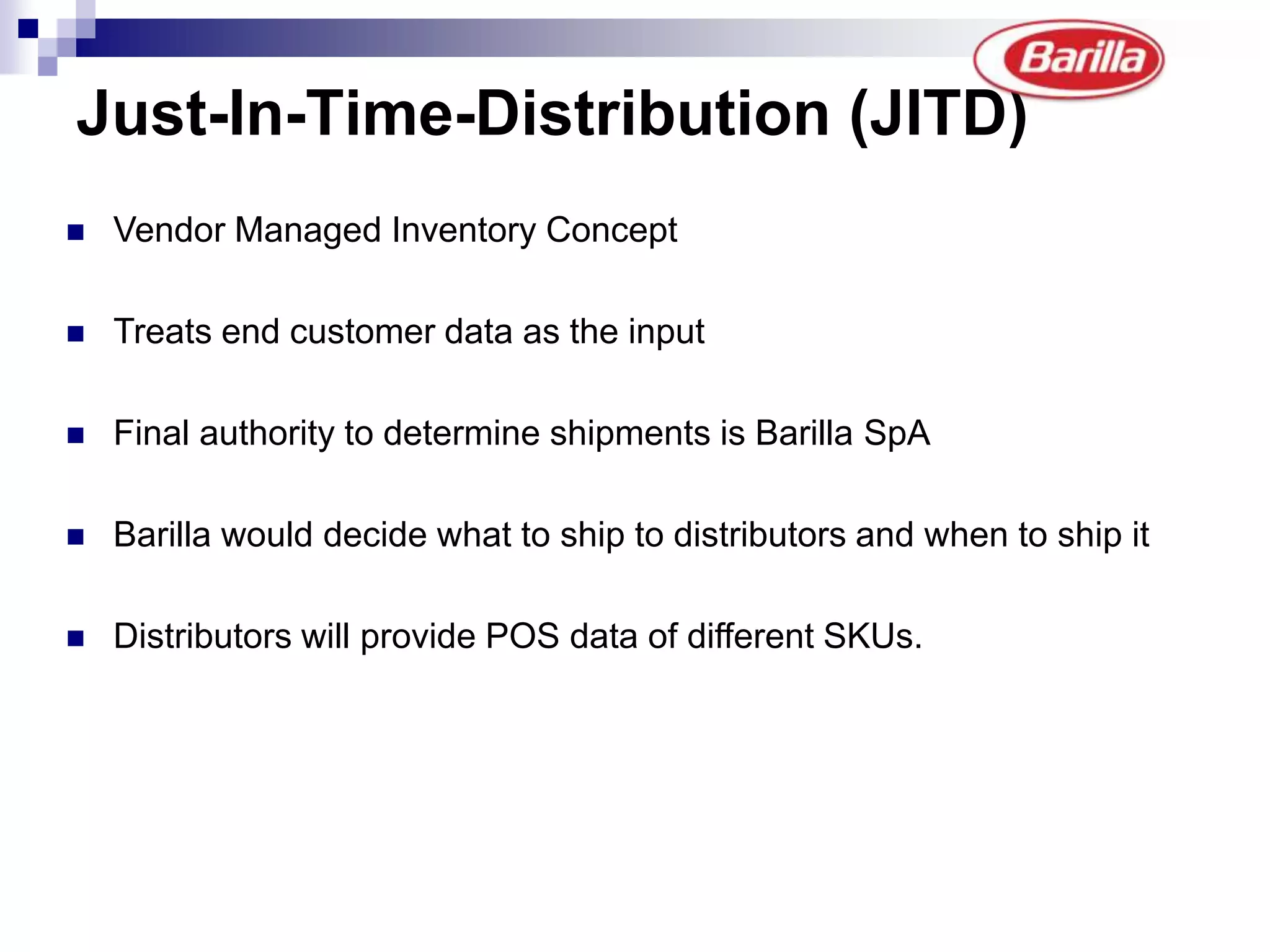
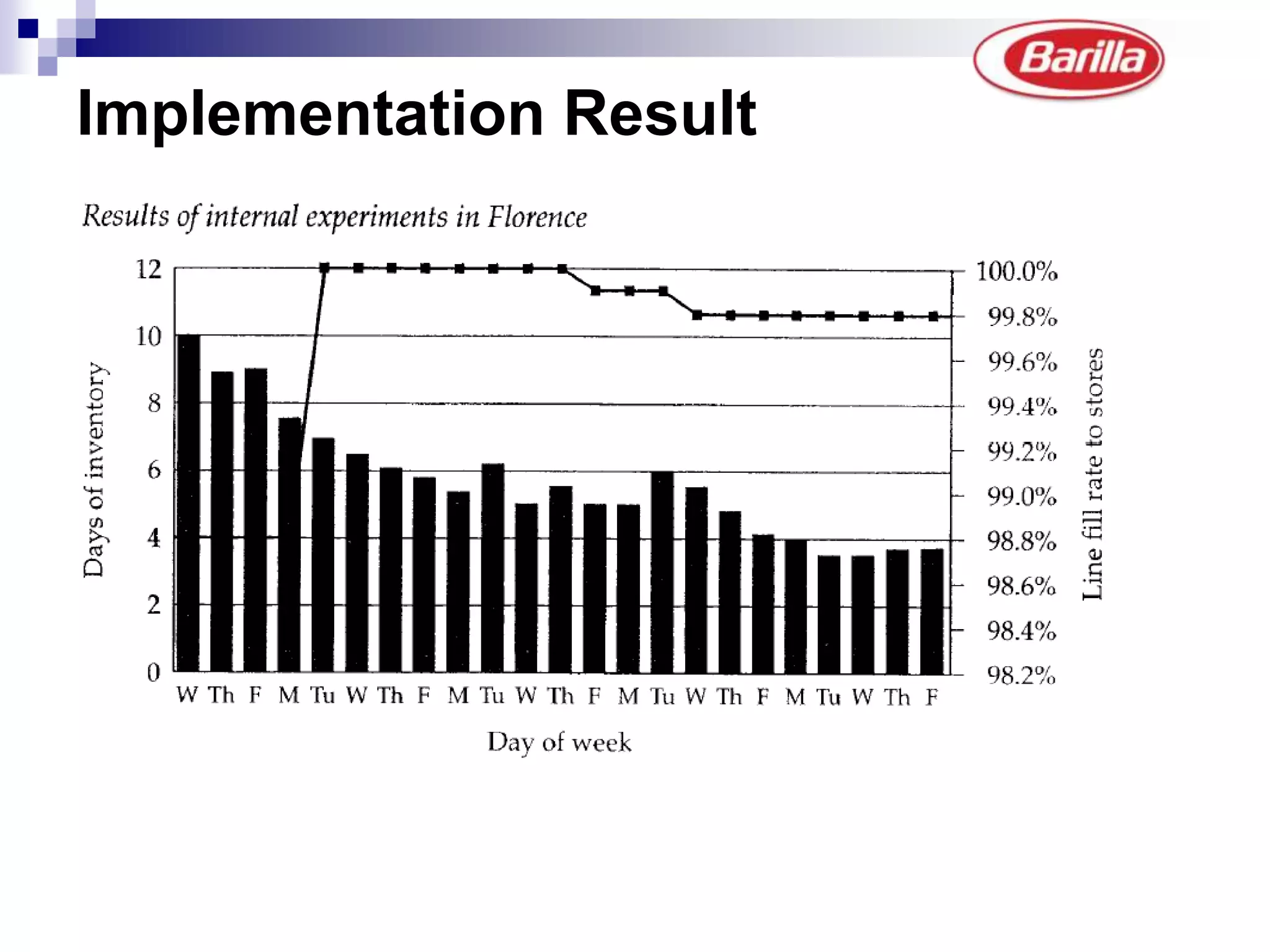
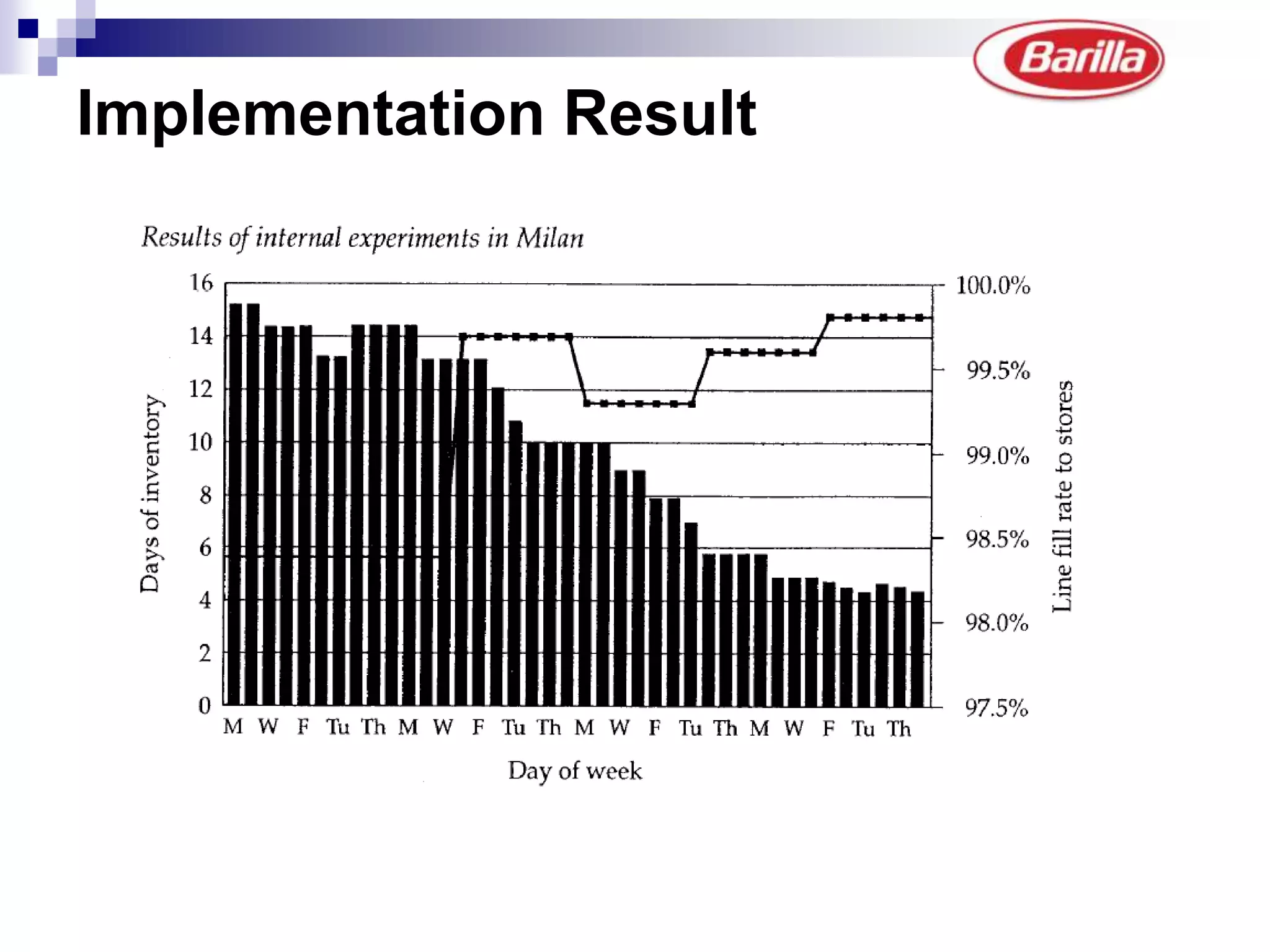
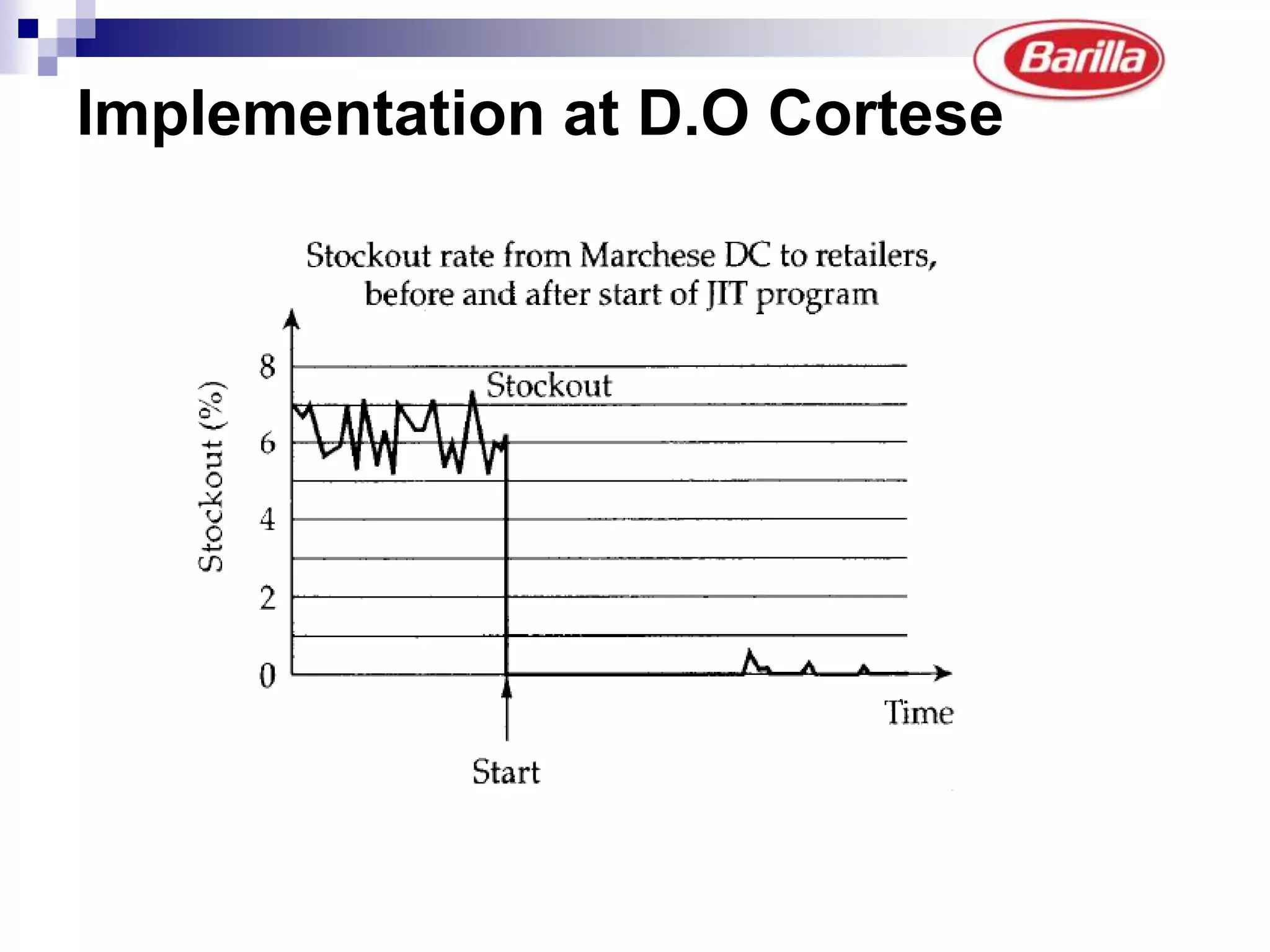
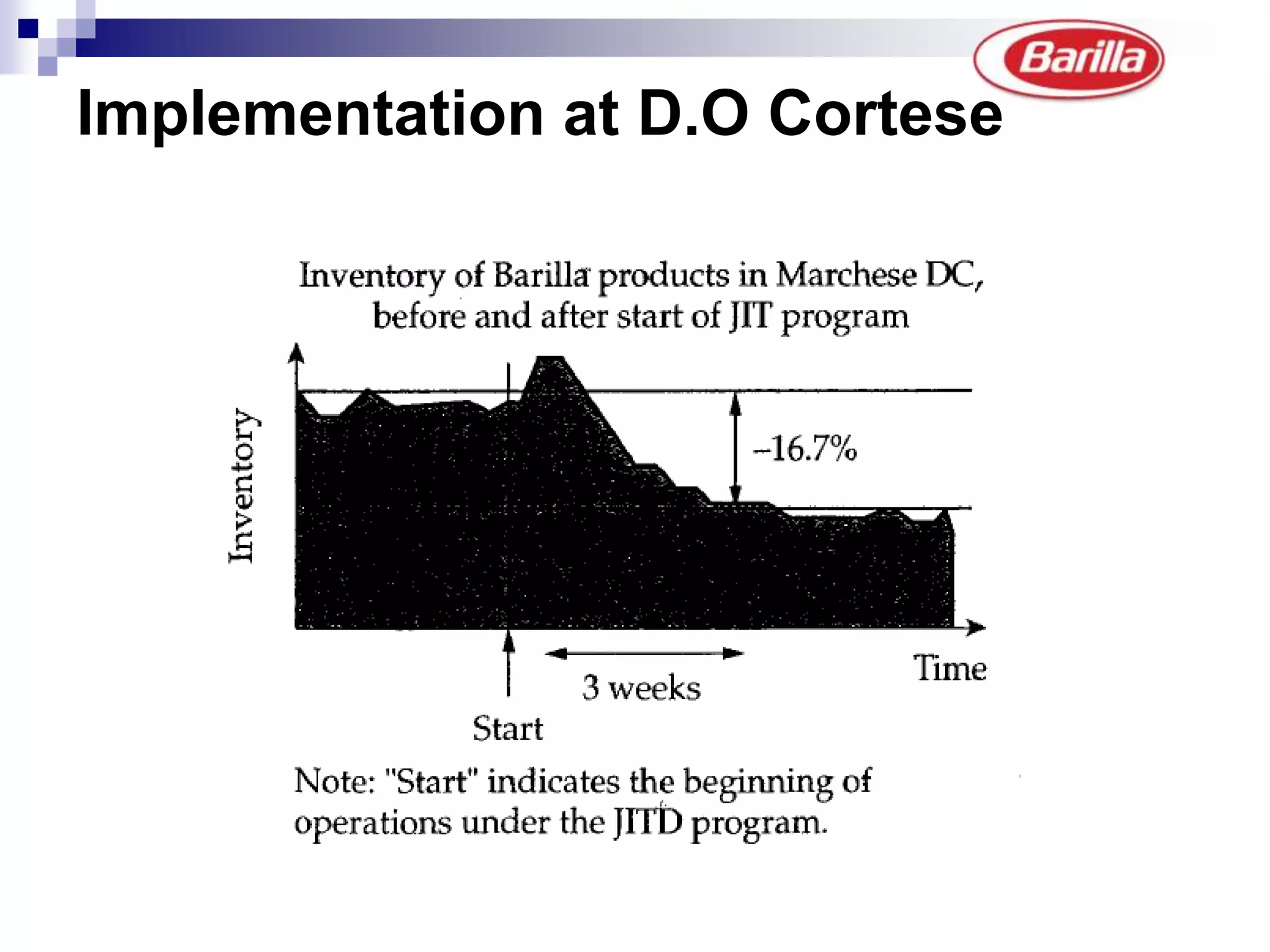
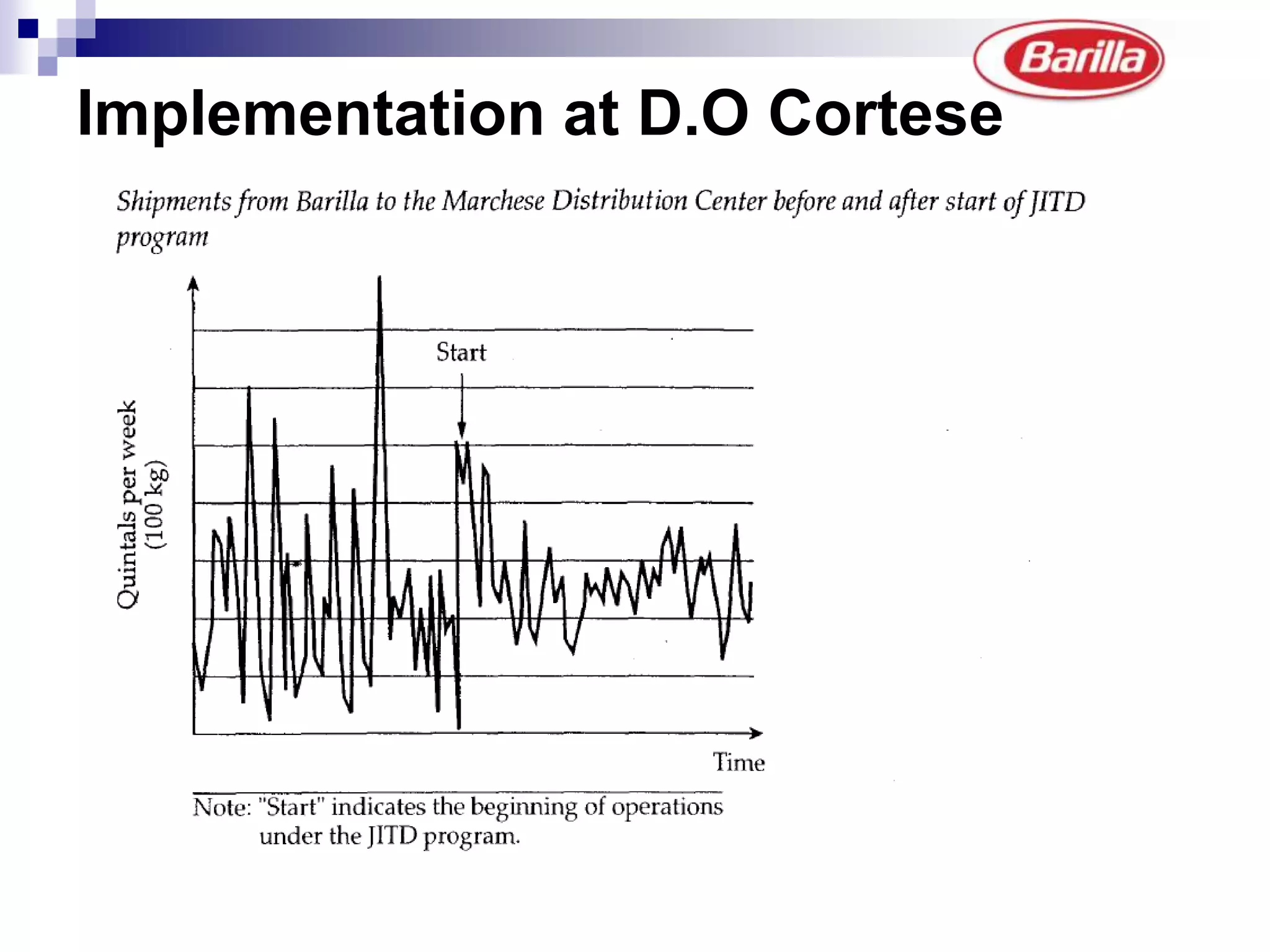
Barilla is the world's largest pasta producer. It faced issues like extreme demand fluctuations, high inventory costs, and low service levels. It implemented a Just-in-Time Distribution system where it took over inventory management from distributors. Pilots showed lower inventory, higher service levels. Implementation with other distributors included daily electronic data sharing. The system reduced costs and improved supply chain visibility for both Barilla and distributors.