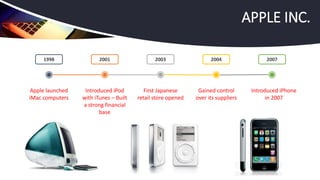
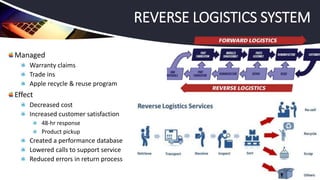
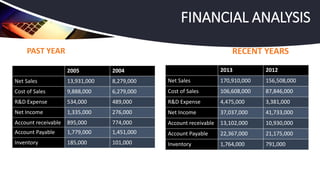
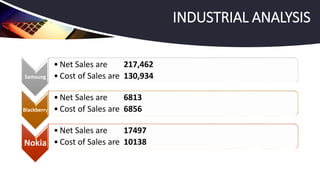
Apple Inc. has successfully managed a global supply chain, combining creative development in the U.S. with outsourced manufacturing in Asia, leading to its position as the world's largest company by market capitalization. Despite challenges such as stock performance and skepticism about future product innovations, CEO Tim Cook reassured investors of a strong product pipeline and effective supply chain coordination. The company employs a just-in-time production strategy, tight supplier relationships, and extensive retail presence to enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.