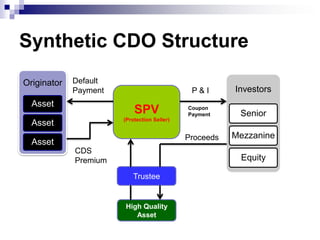
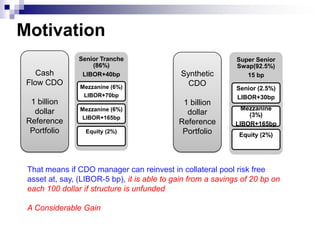
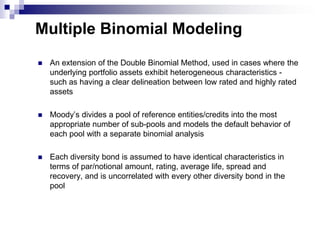
This document discusses the basics of synthetic CDOs including: how they transfer credit risk from an originator to investors through an SPV without actual asset transfer; the difference between cash and synthetic CDO structures; typical synthetic CDO structures using credit default swaps; and types of synthetic CDOs such as unfunded, funded, and partially funded. It also covers motivation for synthetic CDOs, risk factors associated, and how ratings agencies model and analyze synthetic CDOs.