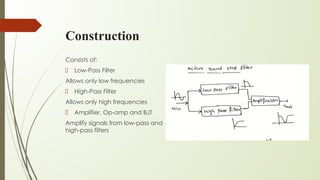
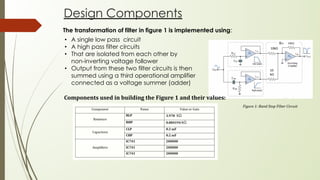
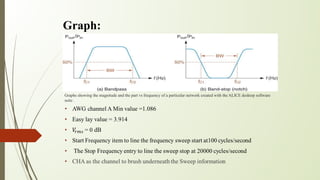
A band stop filter eliminates a band of frequencies by using a low-pass filter to allow only low frequencies and a high-pass filter to allow only high frequencies. The outputs of the low-pass and high-pass filters are amplified and summed to restrict signals in the stopband while allowing signals around it. Band stop filters are used in applications like Raman spectroscopy and live sound processing to affect only a narrow frequency range. They work in the opposite way of band-pass filters by rejecting frequencies in the stopband rather than passing them.